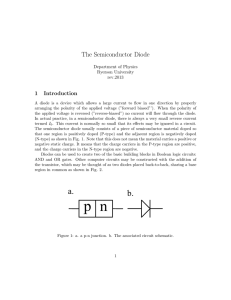
TCOM 308-5 Solid state devices

Solid state devices
• Crystal diodes – a crystal and a bronze wire
• Semiconductors – made from poor conductors with conductive impurities
– Poor conductors = silicon and germanium
– Impurities =
• “P” substances with a shortage of electrons
• “N” substances with excess electrons
Solid state diode
N P
Solid state diode
N P
Solid state diode
N P
Solid state diode
Junction transistor
• Transfer + Resistance = Transistor
• Made up of “sandwich” of PNP or NPN materials
Junction transistor
N
P
N
Junction transistor collector base emitter
Junction transistor
Solid state devices
• Junction transistor – “junction” refers to the junction between materials – where voltage appears.
– Current amplifier (tubes are voltage amps)
• Field effect transistor – “FET” is a low power high impedance device
• Silicone controlled rectifier – “SCR” controls current flow – used in varispeed and dimmer
Solid state devices
• Zener diode – allows output voltage to be fixed for use in power supply
Solid state –v- vacuum tube
Solid state
• Efficient (little heat)
• Infinite lifespan
• Compact
• Physically rugged
• Low power ouput
• Low impedance
Vacuum tube
• Requires and produces heat
• Finite lifespan
• Large
• Delicate
• High power output
• High impedance
Transistors
Printed circuit
Printed circuit
Integrated circuit