EE 352-Electromechanical systems-Aamir Rashid
advertisement

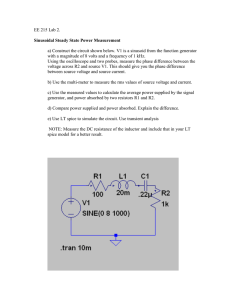
Lahore University of Management Sciences EE 352 – Electromechanical Systems Instructor Room No. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Spring 2014 Dr. Aamir Rashid 9-345A TR 9:30am to 10:30 am aamir.rashid@lums.edu.pk 8358 Course Basics Credit Hours Lecture(s) Lab (per week) Tutorial (per week) Course Distribution Core Elective Open for Student Category Close for Student Category 4 Nbr of Lec(s) Per Week Nbr of Lec(s) Per Week Nbr of Lec(s) Per Week 2 2 1 Duration Duration Duration 75 mins 100 mins 50 mins EE Junior / Senior Freshman / Sophomore COURSE DESCRIPTION This course introduces the fundamentals of DC and AC electromechanical systems to be used for variety of applications. The course starts with the study of fundamental physical laws of electrical devices and appropriate mathematical models are developed to understand their operation and design. The physical construction, operation and mathematical design of transformers, DC machines, and AC machines will be discussed in detail. The speed control of rotating machines will also be introduced. COURSE PREREQUISITE(S) • • • EE 242 Circuit II (Required) PHY 102 Electricity and Magnetism (Required) EE 330 EM Fields and Waves (Recommended) COURSE OBJECTIVES • The main goal of this course is to teach the basic principles of electromechanical System such as electromagnetic actuators, rotating electrical machines and transformers Learning Outcomes • • • At the end of the course the students will be able to understand the operation, construction and design of nearly all types of electromechanical systems. Students will be expected to demonstrate their level of understanding through the laboratory work and solving exam problems. They will also be able to identify the areas of research interests in this field. Lahore University of Management Sciences Grading Breakup and Policy Assignment(s): Home Work: 5% Quizzes: 20% Class Participation: Attendance: Midterm Examination: 35% Final Examination: 40% Lab grades will be assigned separately. Passing grades in both the lab and the course will be required for successful completion of the course. Quiz: TBA Practical Demonstration: TBA Attendance: TBA Lab Manual: TBA Examination Detail Midterm Exam Yes/No: Yes Combine Separate: Combine Duration: 150 mins Preferred Date: Exam Specifications: Calculators allowed, 1-page hand-written formula sheet allowed Final Exam Yes/No: Yes Combine Separate: Combine Duration: 150 mins Exam Specifications: Calculators allowed, 2-page hand-written formula sheet allowed COURSE OVERVIEW Week/ Lecture/ Module • • Recommended Readings Topics Introduction to Machinery Principles, Laws governing linear and rotational motion, The Magnetic Field, Magnetic circuits Electric losses in ferromagnetic materials, Interaction of changing magnetic fields, transformer , motor and generator principle basics 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 • The Ideal Transformer, Theory of Operation of single phase transformer 2.3, 2.4 • Equivalent Circuit of a Transformer, Transformer Voltage Regulation and Efficiency 2.5, 2.7 Per-unit system, Auto Transformers • • 2.6, 2.9 A simple rotating loop between curved pole faces, Commutation in a simple four-loop DC 8.1, 8.2 Objectives/ Application Lahore University of Management Sciences machine • Problems with commutation in real machines, The internal generated voltage and induced torque equations of DC machines 8.4, 8.5 The construction of DC Machines, Power flow and losses in DC Machines 8.6, 8.7 Equivalent circuit, Magnetization curve 9.2, 9.3 • Separately excited and Shunt DC Motors, Permanent Magnet DC Motor 9.4, 9.5 • Series DC Motor, The compound DC Motor, DC motor efficiency calculations 9.6, 9.7, 9.10 • Separately excited DC Generator, Shunt DC Generator 9.12, 9.13 • Series DC Generator, compounded DC Generators 9.14, 9.15, 9.16 • A simple loop in a uniform magnetic field, The rotating magnetic field 4.1, 4.2 • Induced voltage in an AC machine, Induced torque in an AC machine 4.3, 4.4, 4.5 • AC Machines power flows and losses, Voltage and Speed regulation 4.7, 4.8 • • • • • • • • • • • The speed of rotation of a synchronous generator, The internal generated voltage of a synchronous generator The equivalent circuit of a synchronous generator, The phasor diagram of a synchronous generator The synchronous generator operating alone, Parallel operation of AC Generators Basic principles of motor operation, Steadystate synchronous motor operation Effect of load changes on a synchronous motor Power-factor correction, Starting synchronous motors 5.2, 5.3 5.4, 5.5, 5.6 5.8, 5.9 6.1, 6.2 6.2, 6.3, 6.4 Basic induction motor concepts, Equivalent circuit of induction motor Power and Torque in Induction motors 7.2, 7.3 Torque-speed characteristics 7.5 Speed control of induction motors 7.9, 7.12 7.4 Lahore University of Management Sciences The induction generator Textbook(s)/Supplementary Readings Text book: Electric Machinery Fundamentals (4th Edition) by Stephen J. Chapman th Electric Machinery (6 Edition) by A.E. Fitzgerald; Charles Kingsley, Jr; Stephen D. Umans Reference books: Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics (2nd Edition ) by P.C. Sen LAB EXPERIMENT LIST 1 Design of an Inductor using Ferrite Core using different core shapes like (i) Toroid shape (ii) E-I shape (iii) E-E shape 2 Observe Voltage Regulation in a Single Phase Transformer for (i) Resistive Load (ii) Capacitive Load and observe the same for an Auto-Transformer in Step up or Step down configuration 3 Draw the equivalent circuit of a Single Phase Transformer by doing (i) Open Circuit Test (ii) Short Circuit Test 4 Plot the magnetic characteristics (Open Circuit Characteristics) of the Separately Excited DC Generator and Shunt Generator. 5 Load Characteristics of a DC Shunt Generator or Self Excited Generator 6 Load Characteristics of a DC Series Machine (Motor & Generator) 7 Load Test of DC Shunt & Separately Excited Motors 8 Find out the different components of Voltage drop inside a DC Shunt Generator at different loads and plot the curves 9 Load Characteristics of a Single Phase Capacitor Start Induction Motor 10 Load Characteristics of a 3-Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor 11 To run an Induction Motor as an Induction Generator 12 To perform Synchronization of an Synchronous Generator (Alternator) with WAPDA Bus Bar