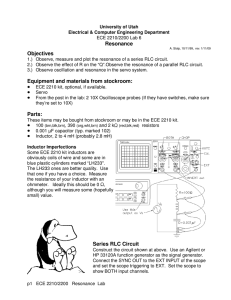
The Phase Constant
advertisement
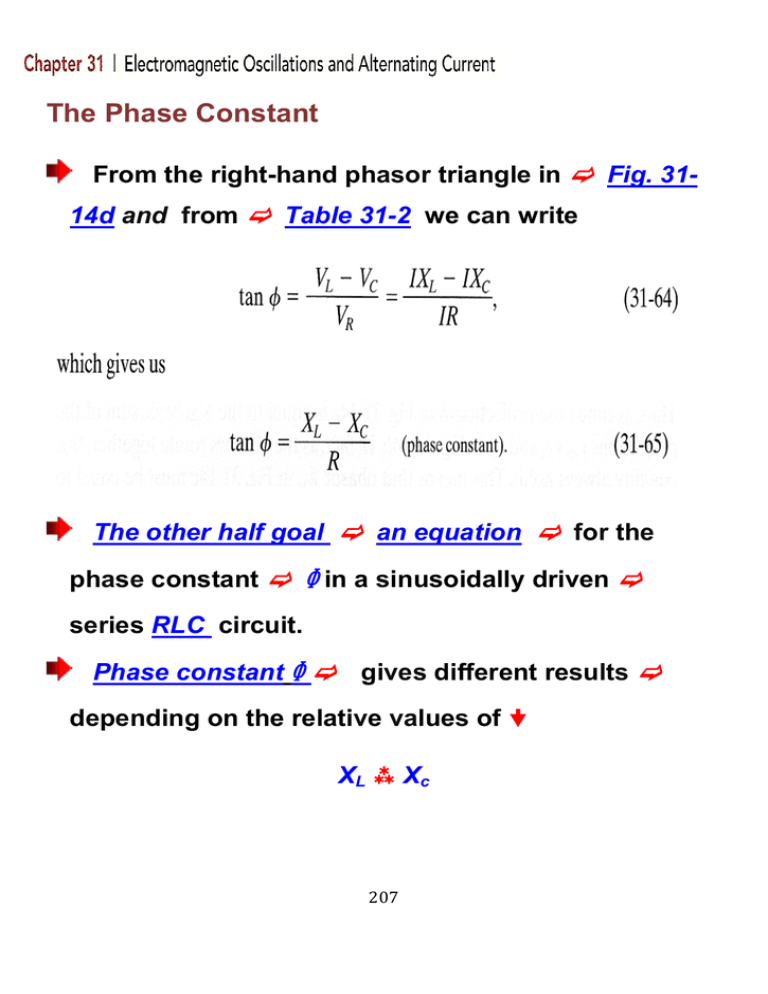
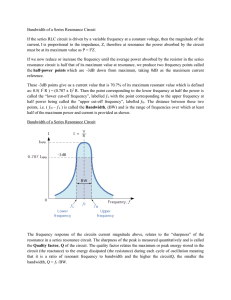
The Phase Constant From the right-hand phasor triangle in Fig. 3114d and from Table 31-2 we can write The other half goal an equation for the phase constant in a sinusoidally driven series RLC circuit. Phase constant gives different results depending on the relative values of XL Xc 207 XL > Xc XC > XL 208 XC = XL 209 Resonance Equation 31-63 I maximum when dL – 1/dC = 0 Natural angular frequency of the RLC circuit equal to 1/LC Resonance and Maximum current amplitude I occur when 210 211 In summary The low-angular-frequency side of a resonance curve dominated by the capacitor's reactance, The high-angular- frequency side is dominated by the inductor's reactance, and resonance occurs in the middle. Ans: a) 1 lags : 2 lead: 3 in phase. b) 3 (d = when XL = XC 212 213 214