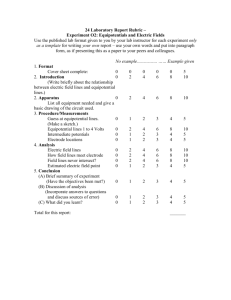
Electric Potential Energy
advertisement
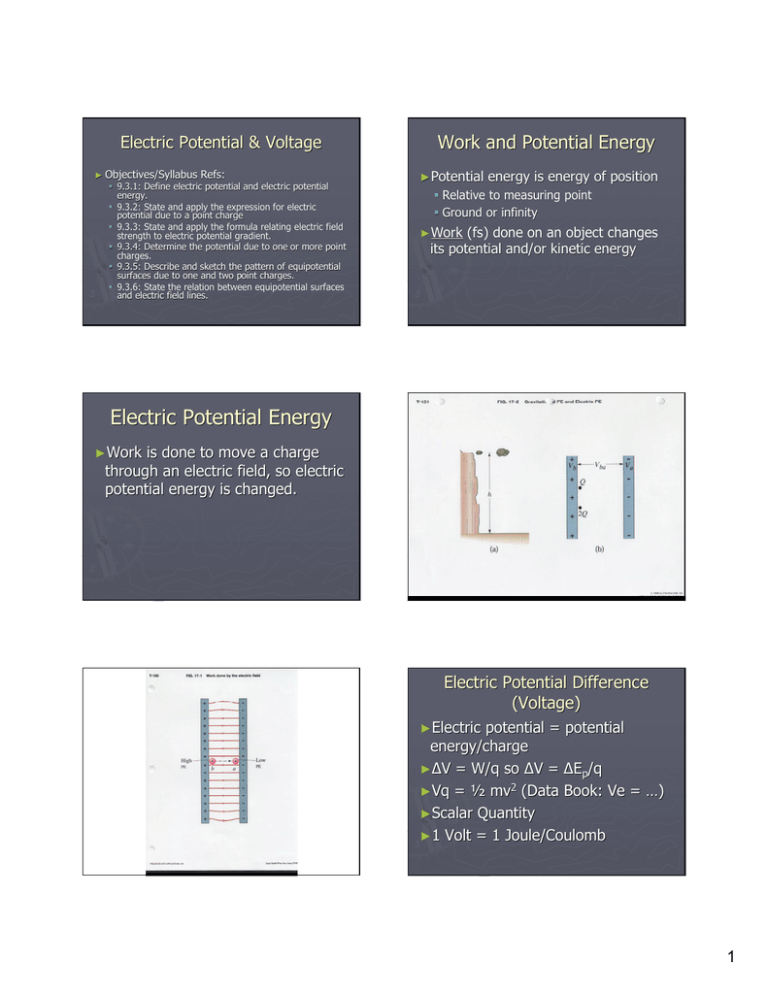
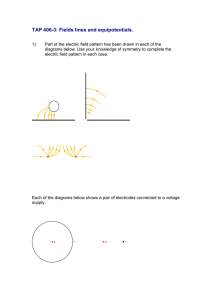
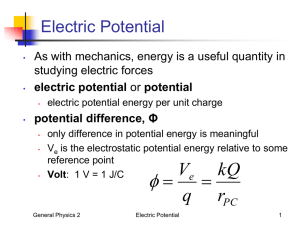
Electric Potential & Voltage ► Objectives/Syllabus Refs: 9.3.1: Define electric potential and electric potential energy. 9.3.2: State and apply the expression for electric potential due to a point charge 9.3.3: State and apply the formula relating electric field strength to electric potential gradient. 9.3.4: Determine the potential due to one or more point charges. 9.3.5: Describe and sketch the pattern of equipotential surfaces due to one and two point charges. 9.3.6: State the relation between equipotential surfaces and electric field lines. Work and Potential Energy ►Potential energy is energy of position Relative to measuring point Ground or infinity ►Work (fs) fs) done on an object changes its potential and/or kinetic energy Electric Potential Energy ►Work is done to move a charge through an electric field, so electric potential energy is changed. Electric Potential Difference (Voltage) ►Electric potential = potential energy/charge ►ΔV = W/q so ΔV = ΔEp/q ►Vq = ½ mv2 (Data Book: Ve = …) ►Scalar Quantity ►1 Volt = 1 Joule/Coulomb 1 More with Potential Equipotential lines •Electric Field Applet ►Using calculus you can show that the work to move a charge from infinity to point p = -kQq/r so… ►V = kq/r = q/(4πε q/(4πε0r) Some typical Voltages Lightning 108 V High-voltage power line 106 V TV tube 104 V Household Outlet 110 V Resting potential across nerve membrane 10-1 V Voltage and Electric Fields ►W = qV and W = Fd = qEd So qV = qEd ► So E = V/d (in a uniform field) ► More generally: E = - ΔV / Δx (in Data book) This would be the slope of a V vs. x graph (derivative with calculus) Gravity vs. Electricity The electronvolt (eV) eV) ►A unit of energy ► Joules are too large for many subatomic applications ► 1 eV = the amount of energy gained by one electron moving through 1 Volt of potential difference ► 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J Gravitation Electricity Acts on Mass (+ only) Charge (+ or -) Force F = Gm1m2/r2 attract only Relative Strength 1 F = kq1q2/r2 attract or repel 1042 Field G = G M/r2 E = kQ/r2 Potential V = -GM/r V = kQ/r Work Done Independent of path U = -GMm/r Independent of path U = kQq/r Potential energy Note K = 1/(4π 1/(4πε0) 2