AP Physics Chapter 17 Electric Potential and
advertisement

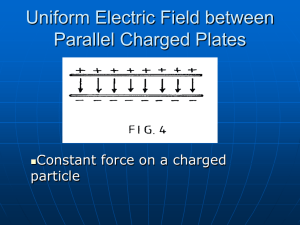
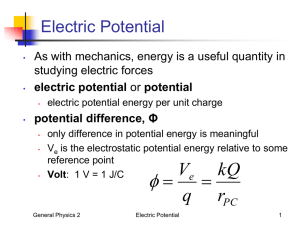
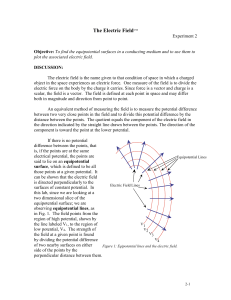
AP Physics Chapter 17 Electric Potential and Electric Energy; Capacitance 17-1 Electric Potential and Potential Difference •Potential or electrical potential is the potential per unit charge. Va=Pea/q •Potential difference is the difference is the work done by the electric force in moving a charge from point a to b. Vab=Va-Vb=-Wba/q •The SI unit for DV is the volt… J/C DV=PEb-Pea=qVba 17-1 (Cont’d) • See chart and diagram p 504 • See Example 17-1 p505 17-2 Relation Between Electric Potential and Electric Field • W=qVba • W=Fd=qEd where d is the distance ll to field lines from point a to b… • qV=qEd …so V=Ed and E=V/d • See Example 17-2 p 506 17-3 Equipotential Lines • Equipotential lines, or in 3-D, equipotential surfaces are areas of equal potential and are perpendicular to the electric field at any point. (See pg. 507 diagram.) • There can be no electric field in a conductor in the static state. 17-4 The Electron-Volt …a unit of Energy • 1eV= 1.6 x10-19J • You must use the J value to calculate with KE=1/2 mv2 17-5 Electric Potential Due to Point Charges • V=k Q/r = 1/(4pe0) (Q/r) for a single pt. charge. • See Example 17-3 p509 • See Diagrams pg 509 See Example 17-4 and 17-5 p510/511 HOMEWORK • P522 1-8&10,13-14 due Tuesday BOP