NPN/ PNP Transistor - Rockwell Automation Sensors Catalog
advertisement

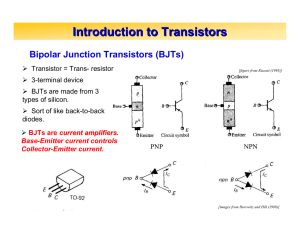
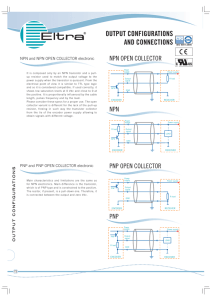
Sensor Technology and Application Basics Outputs & Wiring Solid- state outputs should be considered for applications that require frequent switching or switching of low voltages at low currents. OUTPUT TYPES A solid- state switch is purely electronic — it has no moving parts. NPN/ PNP Transistor Transistors are the typical solid- state output devices for low voltage DC sensors. Consisting of a crystalline chip (usually silicon) and three contacts, a transistor amplifies or switches current electronically. Standard transistors come in two types: NPN and PNP. For an NPN transistor output, the load must be connected between the sensor output and the positive (+) power connection. This is also known as a sinking output. NPN transistor A PNP transistor output is considered a sourcing output. The load must be connected between the sensor output and the negative (—) power connection. PNP transistor Transistors exhibit very low leakage current (measured in mA) and relatively high switching current (typically 100 mA) for easy interface to most DC loads. Response times of sensors with transistor outputs can vary from 2 ms to as fast as 30 ms. However, NPN and PNP transistors are only capable of switching DC loads. FET The FET (Field Effect Transistor) is a solid- state device with virtually no leakage current that provides for fast switching of AC or DC power. It also requires only a small amount of current to change state — as little as 30 mA. As a result, FETs are generally more expensive than standard transistor outputs. Visit our website: www.ab.com/ catalogs. Preferred availability cat. nos. are printed in bold.