Study Guide: Earth Science What are Earth`s resources?
advertisement

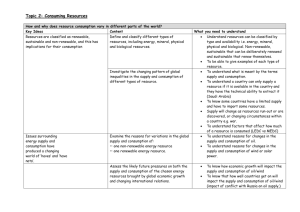
Name: _______________________________ Test Date: ___________________ Study Guide: Earth Science What are Earth’s resources? Vocabulary: • Natural resources – substances that exist naturally on Earth and are not made by humans • Renewable resources – resources that can be replaced at the same rate at which they are used • Non-renewable resources – resources that are used faster than they can be replaced • Fossil fuels – non-renewable resources that formed from the remains of plants and animals that died millions of years ago (ex. Coal, natural gas, petroleum) • Recycling – processing materials again to make new products • Reusing – using materials or products again • Reducing – using less of a material for a certain purpose • Conservation – the practice of using resources wisely • Depletion – use up the supply of something • Indefinite – lasting an unknown length of time, an unknown amount of something • Limited – restricted in amount • Maintained – keep at the same level or rate Key Concepts: • Non-renewable resources are limited and need to be used wisely • Non-renewable resources can be conserved through reducing, reusing and recycling • Earth’s renewable resources can be maintained. Specific Knowledge: • What are non-renewable resources and how can they be conserved? o Natural resources are supplies from nature that are useful or necessary for our lives o Non-renewable resources are resources that cannot be replaced with a human lifetime o Examples: fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, natural gas), soil, minerals o Fossil fuels are formed from the remains of plants and animals o It takes millions of years for these organisms to chemically change into fossil fuels o Non-renewable resources can be conserved by reducing the amount of use, reusing resources, and recycling (the 3 R’s) o Non-renewable resources can be conserved by using alternative resources • What are renewable resources and how can they be maintained? o Renewable resources are resources that can be replaced as fast as they are used. o Examples: water, air, wildlife, most plants, sunlight o Renewable resources can be maintained by protecting the environment (not polluting, reforestation, the 3 R’s) • What are the positives and negatives of using non-renewable resources? o Positives: Humans benefit from many products from fossil fuels (ex. plastics, gasoline, paints) o Negatives: Non-renewable resources can create pollution and damage ecosystems Non-renewable resources cannot be replaced as quickly as they are used. Non-renewable resources cannot re replaced within a human lifetime. • What are the positives and negative of using renewable resources? o Positives: Renewable resources can be replaced in a human lifetime. Renewable resources can be conserved by using alternative resources. o Negatives: Some resources, like fresh water, trees and wildlife only remain renewable if we use them wisely; otherwise we are in danger of limiting their supply. Brain Pop Videos to Review: only works before 5pm (login: scottishcorners, password: dublin) Most Helpful: • Natural resources • Fossil fuels • Recycling • Humans and the environment Also Related to What We’ve Been Learning: • Air pollution • Water pollution • Solar Energy • Wind Energy • • • Biofuel Nuclear Energy Dams