Environmental Biology
advertisement

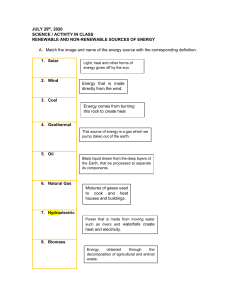
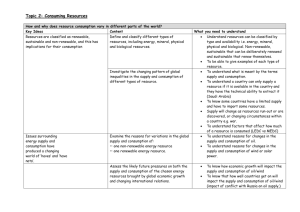
Environmental Biology Welcome What is the intention of this course? To equip you with the necessary background knowledge and tools to fully comprehend environmental factors Course Organization 3 Hours 1st hour 2nd hour Introduction to the issues, with appropriate news stories Debate - classroom discussions 3rd hour Conclusions, possible interventions, and long term outcomes Grading Total of 200 points 100 points for the final 10 x 10 quizzes Text Book Essential Environment: The Science Behind The Stories, J. Withgott & S. Brennan, Second Edition, Pearson. ISBN 0-8053-0640-4 Mission to Mars… What would one need? SPACESHIP EARTH Case study - Easter Island Discovered in the 1700’s by European adventurers Found a small population of about 600 living in caves No trees and little food. No animals Their source of protein was each other… What is EB? It is the study of how the natural world works. How our environment affects us. And how we effect our environment. Environment? Just the ‘natural world’? Includes all the living and non-living things around us. It also includes the man made items It also includes the complex web of human relationships EVERYTHING in the Universe Limits…. Natural Resources - the various substances and energy sources needed for our survival Renewable and non-renewable Renewable are either Non-renewable Unlimited - sunlight, wind, wave Replenished quickly - water, soil, food crops Fixed amounts - oil, gas, land Consumption increases based on life style and population Limits…. Human population size For the most part of the last 5 million years the human population has remained at several million That was until two events took place… Human population 1) Agricultural Revolution @ 10,000 years Change in human lifestyle - security and children 2) Industrial revolution @ 1750’s Rural to urban life, with machines aiding us with the use of fossil fuels The Scientific Method EB is a science and therefore the rules of scientific procedure must be applied The Scientific Method is a process A technique for testing ideas with observations Make observations Ask questions Develop a hypothesis Make predictions Test the predications Analyze and interpret results. Conservation vs Preservation Preservation Leave it alone as exists without human activity Yosemite National Park Conservation Use it is a sustainable manner National Forests Ecological Footprints Relative resource consumption by each person from each country US - 9.5 ha Canada - 6.4 ha China - 1.5 ha Pakistan - 0.7 ha Ethiopia - 0.7 ha