Chapter 13 Class 10th
advertisement

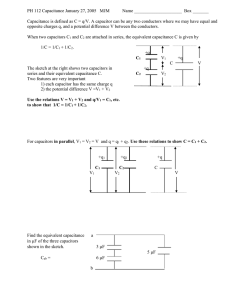
Electrostatics Electrostatics The branch of physics that deals with the study of static charges is called electrostatics. Q.1 What is charge? Discuss the nature, existence and transferring of electric charge. (Ans) Electric charge It is the property of a substance due to which it can attract or repel another substance. Nature, existence and transferring of charge Charge is basically electric in nature. It may be positive or negative. Same charges repel while opposite charges attract each other.Transfer of charges can be explained by the following experiments. Take two small pith balls that are suspended by means of a thread. In the beginning, the two balls remain at their mean position, because they are neutral. If the two balls are touched with positive charge glass rod and becomes free. These balls will repel each other and moves away from each other. + + Now if one ball is touched with positive charge rod and the other with negative charged rod and becomes free. These balls will attract each other and moves closer to each other. - + Conclusion It is concluded from the above experiments that charge can be transferred from one object to another. It is also concluded that similer charges repel while opposite charges attract each other. Q.2 How an object can be charged by rubbing? (Ans) Charging by rubbing A body can be charged by rubbing it with another body. It is because some electrons from the surface of one body transferred to the surface of other body during rubbing. For example When a comb is rubbed with hair, the hair loses an electron and becomes positively charge while the comb gain electron and becomes negatively charge. Q.3 What is meant by electrostatic induction? (Ans) Electrostatic induction The rearrangement of charges inside a neutral body when a charged body is brought closer to it is called electrostatic induction.” This new arrangement of charges is temporary and will regain original after the removal of charged body. Electrostatic induction can take place in both conductors and insulators. Charging of insulators by induction When a comb is rubbed with hair, the comb gains negative charge due to the accumulation of charges from the hair over it. When this comb is brought closer to a neutral body such as a piece of paper, then the electrons push locally away, whereas the positively charged protons remain at their original position. Thus the attractive forces become stronger as compared to the repulsive forces and the piece of paper is attracted towards the comb. This separation of positive and negative charges inside the insulator is known as polarization of insulators Charging a conductor by induction Take a metallic sphere that is fixed on an insulated stand. When a positive charge glass rod is brought closer to the sphere. The rearrangement of charges takes place inside the metallic sphere. The negative charges come closer to the positive charged glass rod. In this way, a conductor is charged by induction. Q.4 Write a note on Electroscope. (Ans) Electroscope A sensitive device used for the detection and testing of charge is called Electroscope. Construction It consists of a metallic rod, whose one end is connected to a disc while at the other end two gold leaves are attached. The rod is fitted in a glass case as shown in figure. Detection of charge In order to detect the presence of charge on a body, bring it near the disc of an uncharged electroscope. If the body is charged, the leaves of the electroscope diverge to a definite extent. If the body is uncharged then the leaves remain at their normal position. Testing the nature of charge In order to test a charge, we need to charge the Electroscope first by placing a negative charge on the disc. In this way, the leaves become negatively charged. Now bring the testing charge body near the disc. If the leaves diverged, the charge will be negative. If the leaves collapse, the charge will be positive. Q.5 State and explain Coulombs law? (Ans) Statement This law states that “the force of attraction or repulsion between the two charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges.” Explanation Consider two spherical charges “q1” and “q2” are placed at a distance“r” from each other as shown in figure. r q1 q2 Mathematical expression F q1q2 (1) F 1 (2) r2 Combining equation (1) and (2) we get F q1q2 r2 F (Constt) F k q1q2 r2 q1q2 r2 Where “k” is constant of proportionality and it is known Coulombs constant, its value is 9 10 9 Nm2/C2. k 1 4 F 1 q1 q 2 4 r 2 Q.6 What is meant by electric field and electric field intensity? (Ans) Electric field The region around a charge body in which it can interact another charge is known as electric field. It is a vector quantity. It is represented by electric lines of force. Electric field intensity The strength of the field at any point is known as electric field intensity. It can also be defined as “the electric force exerted per unit positive test charge is known as electric field intensity. It is denoted by “E”. It is a vector quantity. Mathematically F E q qq F k 2 r qq q Ek k q r 2 r2 This equation shows the electric field intensity of a point charge “q”. The SI unit of electric field intensity is Newton/coulomb (N/C). Q.7 What are electric lines of force? Describe its characteristics. (Ans) Eectric lines of force An electric line of force in general shows the path through which an electric charge would move. The direction of the lines shows the direction of the field. The number of electric lines per unit area represents the intensity of the field. General characteristics of the electric lines of force are as under: A positive charge always emits lines of force. A negative charge always absorbe lines of force. When two opposite charges are placed nearer, then the lines of force start from the positive charge and ends at negative charge. As a result, they attract each other. When two identical charges are placed nearer, the lines of force behave as shown in figure. Consider two infinite oppositely charge plates are placed parallel to each other. The electric lines of force emit from positive charge and absorbe by the negative charge. The lines of force are straight and parallel at the centre of the plates. Whereas at the ends of the plates, the lines of force are a little bulging out. This shows that the field is uniform at the centre and non-uniform at the ends of the plates. Q.8 Define and explain electric potential and its unit? (Ans) Electric potential The work done on a unit positive charge to move it from one place to another against the electric field is called electric potential. It is denoted by “V”. Mathematically V W q Potential difference The work done on a unit positive charge to move it from point “A” to point “B” against the electric field is called potential difference. OR The energy supplied by a unit positive charge as it moves from a point of higher potential to a point of lower potential is called potential difference. It is denoted by “ V ”. Mathematically W A B q V V A V B V W A B q q (V A VB ) V A VB W A B Q.9 Write the practical applications of electrostatics. (Ans) The practical applications of electrostatics are as under: (1) Electropainting Electrostatics is used in applying paint on the surface of different articles. The body of the car is earthed. The particles of the paint emerge out of the nozzle of the spray machine, they aquire a positive charge. As they reached to the body of the car due to electrostatic induction negative induced on the body of the car. As a result, an electrostatic force established and firm coating of the paint is formed on the surface of the car. This method is efficient, effective and cheap. (2) Dust extraction Electrostatics is used for the separation of smoke and dust particles from a coal-burning power station by means of an electroastatic precipitator. Q.10 What is a capacitor? Describe the capacitance of a capacitor. (Ans) Capacitor A device used to store an electric charge is called capacitor. Construction A capacitor consists of two parallel metallic plates having a small distance between them. The medium inside the plates is air or some other insulating material known as dielectric. Charging a capacitor Consider a charge “+Q” is transferred to plate A, then by electrostatic induction a “-Q” charge is induced on plate B. A force of attraction is established between the plates due to which the charges are bound with the plates and remain stored for long period. Capacitance of a capacitor The capacity of a capacitor to store charge is called capacitance of the capacitor. Experiments show that the charge store in a capacitor is directly proportion to the potential difference across the plates of the capacitor. Mathematically Q V Q CONSTANT (V ) Q CV Where “C” is costant and is known as capacitance of the capacitor. The SI unit of capacitance of a capacitor is farad (F). Farad It can be defined as “the capacitance of a capacitor is one farad if one coulomb charge is stored by the capacitor providing a potential difference of one volt to their plates.” Q.11 How capacitors can be connected in a circuit? (Ans) There are two basic ways of connecting capacitors in a circuit. 1. Series combination A type of combination of two or more than two capacitors in which the capacitors are connected plate to plate is called series combination of the capacitors. Explanation Consider three capacitors of capacitance c1, c2 and c3 are connected in series. A battery of voltage “V” is connected to the circuit. The battery provide a positive charge “Q” to the left plate of capacitor C1 due to electrostatic induction a negative charge is induced on the right plate and charges distribute on the other plates similarly. The flow of charges to each capacitor is constant in series combination. Q1 Q2 Q3 Q Voltage across each capacitor decreases. The sum of all the voltage across the capacitors is equal to the total voltage. V V1 V2 V3 We know that Q V Q CV C V V1 V2 V3 Q Q Q Q 1 2 3 Ceq C1 C2 C3 Q Q Q Q Ceq C1 C2 C3 Q 1 1 1 Q( ) Ceq C1 C2 C3 1 1 1 1 Ceq C1 C2 C3 Now for “n” number of capacitor the formula can be written as; 1 1 1 1 1 Ceq C1 C2 C3 Cn Similarly for two capacitor C1 and C2 the formula becomes; 1 1 1 Ceq C1 C2 1 C C1 2 Ceq C1C2 Ceq C1C2 C1 C2 2. Parallel combination of capacitor A type of combination of two or more than two capacitors in which the plates of the capacitors are connected parallel to each other as shown in figure is called parallel combination of capacitors. Explanation Consider three capacitors of capacitance c1, c2 and c3 are connected in series. A battery of voltage “V” is connected to the circuit. The battery provide a positive charge “Q” to the left plate of capacitor C1 due to electrostatic induction a negative charge is induced on the right plate and charges distribute on the other plates similarly. The voltage across each capacitor remains constant in parallel combination of capacitors. V1 V2 V3 V The flow of charge to each capacitor is distributed in parallel combination of capacitors. The total charge is equal to the sum of charge across each capacitor. Q Q1 Q2 Q3 ----------- (A) We know that Q CV Qeq CeqVeq , Q1 C1V1 , Q2 C2V2 , Q3 C 3V3 Put these values in equation (A) CeqVeq C1V1 C2V2 C3V3 As V1 V2 V3 V C eqV C1V C 2V C 3V C eq C1 C 2 C 3 For "n" numbers of capacitors, we have Ceq C1 C2 C3 Cn Q.12 Write different types of capacitors. (Ans) There are two types of capacitors. 1. Fixed capacitors 2. variable capacitors 1. Fixed capacitors Those capacitors whose parts are fixed by design and its plates are immovable is called fixed capacitors. The capacitance of these capacitors does not change (constant). Examples of these capacitors are paper capacitors and mica capacitors. 2. Variable capacitors A type of capacitors whose area of the plates can be changed is called variable capacitors. The capacitance of these capacitors can be changed by increasing or decreasing the area between the plates. For example The capacitors used in tuning of a radio frequency. (Fixed capacitors) (Variable capacitors) SHORT QUESTIONS 1. A. 2. A. 3. A. A balloon is negatively charged by rubbing and then clings to a wall. Does this mean that the wall is positively charged? Why does the balloon eventually fall? The wall is neutral in the beginning, when we brought a negatively charged balloon closer to the wall. Due to electrostatic induction, the positive charges present in the wall moves forward to attract the balloon. As a result, the balloon sticks with the wall for a while. The negative charges of balloon neutralized the positive charges induced on the wall due to the transferred of charges. Now as a result the balloon eventually falls. Why is it not good to seek shelter under a tree during a lightning storm? it is not a good idea to seek shelter under a tree during a lightning storm. Because when the charge clouds pass over a tree, then an opposite charge is induced on the tree due to electrostatic induction. The force of attraction is established between the tree and clouds due to which there is a greater possibility for the lightning discharge to take place. A charge comb often attracts small bits of dry paper that then fly away when they touch the comb. Explain? See Q.3 (charging an insulator by induction). 4. A. Define the term volt? Volt is the SI unit of potential difference. It can be defined as “if 1 joule work is done on a charge body of 1 coulomb to move it from one point to another against the electric field.” Mathematically 1 joule 1Volt 1coulomb 5. A. What is meant by electrostatic induction? See Q.3 6. A. What is meant by charging an object electrically? To make an electrical contact between the object and the earth by a conducting wire is known as earthing an object electrically. By doing so the additional charge will flow towards the earth surface. 7. Two isolated copper sphere, A and B, are initially uncharged. They are placed near each other as shown in figure. What is the charge distribution on A when B is given a negative charge? A. The rearrangement of charges occurs in A due to electrostatic induction. Positive charges present in A move towards the negative charges on B, while negative charges present in A moves away to the other side as shown in the figure. 8. A. Why electric charge is produced on bodies by friction? Electric charge is produced on bodies by friction. Because when two bodies rubbed with each other, transferred of charges occur. As a result, charges are produced on the objects. For example When a glass rod is rubbed with silk. The glass rod loses electrons and the silk gain these electrons. The glass becomes positively charged, while the silk becomes negatively charged. 9. Two capacitors with capacitance 1µF and 0.01µF are charged to the same potential. Which will give more intense shock if touched? The charge stored in the capacitors depends on the capacitance of the capacitor if voltage across the capacitor is constant. Greater the capacitance greater will be the charge store. Therefore, the capacitor having capacitance 1µF give more intense shock as compared to the capacitor of capacitance 0.01µF. A. 10. A. As shown in the figure a chain is hanging from the rear side of petrol supply tanker. What is its purpose? When the petrol supply tanker moves on a road, charge may be induced on its body due to friction. To avoid these charges a chain is made to hang from the rear side of petrol supply tanker. This chain works like earth wire and supply these charges to the earth. 11. A. The tyres of an aircraft are made from special rubber that conducts electricity. Explain why? The tyres of an aircraft are made from special rubber that conducts electricity. It is because charges are induced on the tyres due to friction between the tyres and the ground. To transferred these charges to the ground the tyres of an aircraft are made from a special conducting rubber to work as earth wire. NUMERICAL PROBLEMS 1. Two charges 5µC and 15µC are placed at a distance of 100cm. Find the Coulombs force between them. Given data q1 5C 5 10 6 C q 2 15C 15 10 6 C r 100cm 1m K 9 109 Nm 2 / C 2 F ? We know that qq F K 1 22 r (5 10 6 )(15 10 6 ) F 9 109 (1) 2 F 675 109 6 6 F 675 10 3 F 0 675N 2. Two identical charges are 25cm apart. They repel each other with a force of 2x10-6N. Find each charge? Given data q q q ( say) ? r 25cm 0.25m F 2 106 N K 9 109 Nm 2 / C 2 We know that q1 q 2 r2 qq F K 2 r F K Fr 2 K q2 ( 2 10 6 )(0 25) 2 9 109 ( 2 10 6 )(0 0625) q2 9 109 0 125 10 6 2 q 10 9 9 2 q 0 01389 10 69 q2 q 2 13 89 10 6 9 3 13 89 10 18 q 13 89 10 18 3 72 10 9 C 3. How far apart must the charge of +5.0x10-6 and -4.0x10-6 to be in order that the charges attract each other with a force 0f 2.2N? Given data q1 5 0 10 6 C q 2 4 0 10 6 C K 9 109 Nm 2 / C 2 F 2 2N r ? We know that qq F K 1 22 r qq r2 K 1 2 F (5 10 6 )(4 10 6 ) r 2 9 109 22 Negative sign shows that force is attractive. (5 10 6 )(4 10 6 ) r 2 9 109 22 180 10966 22 r 2 81 81 10 3 r2 r 2 8 181 10 2 r 2 86 10 1 0 286m 4. When a 10µC charge is placed at a point in an electric field, it experience a force of 10-4N. Find the value of electric field intensity at this point. Given data q 10C 10 106 C F 104 N E ? We know that E E E E E E 5. F q 10 4 10 10 6 10 4 10 6 10 10 4 6 10 10 2 10 10 N / C Three capacitors of capacitance 100µF, 200µF and 300µF are connected in parallel. Find the equivalent capacitance of the combination. If a battery of 12V is connected across the combination, find the charge on each capacitor. Given data C1 100F 100 106 F C 2 200F 200 106 F C3 300F 300 106 F V 12V C eq ? q1 ? q2 ? q3 ? We know that C eq C1 C 2 C 3 C eq 100 200 300 C eq 600F We also know that Q CV Q1 C1V 100 106 12 1200C 1 2mC Q2 C 2V 200 106 12 2400C 2 4mC Q3 C3V 300 106 12 3600C 3 6mC 6. The potential difference between two points is 110V. If an unknown charge is moved between these points, the amount of work done is550J. Find the amount of charge? Given data V 110V W 550J Q? We know that W Q W 550 Q 5C V 110 V