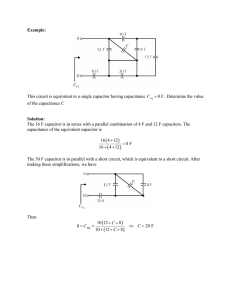
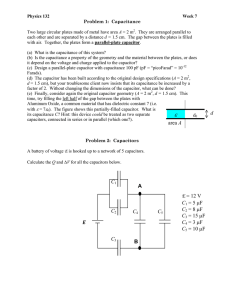
Electricity review Electrostatic forces Electrostatic forces Electric
advertisement

Electricity review 21 Electrostatic Charges and Forces Coulomb’s Law Superposition of Forces 21 Electric Fields and Dipoles Electric field, point charge Uniform electric field Charges in motion Electric fields for certain shapes Electric field lines Dipoles, torque, potential energy 22,23 Electric Flux and Potential Gauss’ Law Flux Potential energy of point charges Electric potential Electron Volt Equipotential Surfaces EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 Electrostatic forces 24 Capacitance Capacitors Capacitors in a vacuum Capacitors in series and parallel Energy stored in a capacitor Dielectrics 25 Current, Resistance, EMF Current Resistivity, conductance Resistance Electromotive force Energy and power Potential changes in a circuit 26 DC Circuits Resistors in series and parallel Kirchhoff’s rules RC circuits Applications 1 Electrostatic forces EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 2 Electric potential Find q EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 3 Capacitance EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 4 Capacitor dielectric Calculate the voltage across each capacitor. If C2=6.0 µF calculate the charge on the other capacitors. EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 5 EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 6 Resistance and power Voltage, Power, Current, Resistance The internal resistance of the power supply is 1700 Ω. What is the current through the body and the power dissipated in her body? EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 What is the resistance of a 150 W bulb? How much current does the 150 W bulb draw? 7 Equivalent Resistance, Power EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 8 Circuit What is the maximum power the circuit can dissipate? What are the unknown currents and voltages? EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 9 RC circuit A 700 Ω resistor is in series with a 7 µF capacitor. What capacitance must be placed in parallel with the original capacitor to change the time constant to three times its original value? EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 11 EF 152 Fall, 2009 Lecture 4-8 10