Experiment 1: Simulations
advertisement

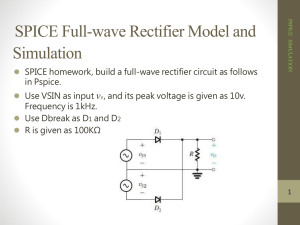
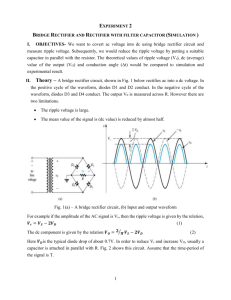
İzmir University of Economics ETE 100 Introduction to Electronics and Communications Engineering EXPERIMENT 1 PSPICE Simulation of Circuits A. Background Download, print and read the tutorial on the usage of ORCAD/PSPICE available at http://homes.ieu.edu.tr/~maskar/CE206/ORCAD-PSPICE-Tutorial.pdf B. Preliminary Work 1. Half-wave Rectifier: Consider the half-wave rectifier given in Fig. 1.1. Assume the diode is ideal and a sinusoidal voltage is applied to the input. Plot the input and output voltage waveforms on Fig. 1.2. D + VS R VO VS (t) = 10 cos 2π x 50 t volts R = 10 kΩ Fig. 1.1. Half-wave Rectifier Fig. 1.2. Input and Output Voltage Waveforms at Half-wave Rectifier 9-1 2. Half-wave Rectifier with Filter: Assume a capacitor is added to the output of the halfwave rectifier as shown in Fig. 1.3. Assume the diode is ideal and a sinusoidal voltage is applied to the input. Plot the input and output voltage waveforms on Fig. 1.4. D + VS R VO C VS (t) = 10 cos 2π x 50 t volts R = 1 kΩ C = 200 µF Fig. 1.3. Half-wave Rectifier with Filter Fig. 1.4. Input and Output Voltage Waveforms 3. Full-wave Rectifier: Consider the full-wave rectifier given in Fig. 1.5. Assume the diode is ideal and a sinusoidal voltage is applied to the input. Plot the input and output voltage waveforms on Fig. 1.6. D + VS R VO VS (t) = 10 cos 2π x 50 t volts R = 1 kΩ Fig. 1.5. Full-wave Rectifier 9-2 Fig. 1.6. Input and Output Voltage Waveforms 4. Full-wave Rectifier with Filter: Assume a capacitor is added to the output of the full-wave rectifier as shown in Fig. 1.7. Assume the diode is ideal and a sinusoidal voltage is applied to the input. Plot the input and output voltage waveforms on Fig. 1.8. D + VS R C VO VS (t) = 10 cos 2π x 50 t volts R = 1 kΩ C = 200 µF Fig. 1.7. Full-wave Rectifier with Filter Fig. 1.8. Input and Output Voltage Waveforms 9-3 C. Experimental Work C.1. Part 1: Half-Wave Rectifier 1. Construct the given circuit below (Fig. 1.9) in ORCAD by following the steps. D1 D1N914 V V V1 VOFF = 0 VAMPL = 10 FREQ = 100 R1 1k 0 Fig. 1.9 2. Select File >> New >> Project. Name your project (Fig. 1.10) as “Half_Wave_Rectifier_NAME_SURNAME”. As the location field, select the directory as ”D:\MYWORKS\CE206_ORCAD”. Be sure that you selected “Analog or Mixed A/D”. Fig. 1.10 9-4 3. Now, select “Create a blank project” at the appeared diagram box (Fig. 1.12). Fig. 1.11 4. 5. Add a sinusoidal voltage source (VSIN) and a resistor(R) to your circuit as described in the ORCAD/PSPICE Tutorial. To work your circuit properly, don’t forget to add Ground to your circuit. Set the parameters as shown in Fig. 1.12. (Your laboratory work parameters will be assigned to you during the Laboratory Work D1 D1N914 V V V1 VOFF = 0 VAMPL = 10 FREQ = 100 R1 1k 0 Fig. 1.12 6. After the construction of circuit, create a new profile using Pspice >> New Simulation Profile from toolbar (Fig. 1.13). Write “Half_Wave_Rectifier_NAME_SURNAME” for New Simulation Name. Fig. 1.13 9-5 7. Set the simulation settings as given in Fig. 1.14 Fig. 1.14 8. Run your program by using toolbar as Pspice >> Run. Insert your circuit schematic and simulation results below (The capture method is given in ORCAD/PSPICE Tutorial. i. Circuit Schematic Insert Your Circuit Schematic Here ii. Simulation Results Insert Your Simulation Results Here 9-6 iii. Discussions C.2. Part 2: Half-Wave Rectifier with Filter 1. Add a capacitor to the output of the half-wave rectifier as shown in Fig. 1.15 D1 D1N914 V V V1 VOFF = 0 VAMPL = 10 FREQ = 100 R1 1k C1 1u 0 Fig. 1.15 2. Can you observe the ripples at the output? How do they change with different capacitance values? Discuss this issue in the Discussions box. Insert your circuit schematic and simulation results below. i. Circuit Schematic Insert Your Circuit Schematic Here ii. Simulation Results Insert Your Simulation Results Here 9-7 iii. Discussions C.3. Part 3: Full-Wave Rectifier 1. In Fig. 1.16, a regulator circuit with full wave rectifier is given. Construct this circuit using the knowledge of preceding sections. Run the circuit for before and after connecting of capacitor (To define a single ground point in the circuit, a very large resistor (100 MΩ) is added to the output, since the voltage drop across it is negligibly small) D3 D1 D1N914 V V+ D1N914 V1 VOFF = 0 VAMPL = 10 FREQ = 1k R1 1k C1 1u D2 D4 V- R2 100M D1N914 D1N914 0 Fig. 1.16 Insert your circuit schematic and simulation results below. i. Circuit Schematic (Full-Wave Rectifier without Capacitor) Insert Your Circuit Schematic Here ii. Simulation Results (Full-Wave Rectifier without Capacitor) Insert Your Simulation Results Here 9-8 iii. Discussions (Full-Wave Rectifier without Capacitor) iv. Circuit Schematic (Full-Wave Rectifier with Capacitor) Insert Your Circuit Schematic Here v. Simulation Results (Full-Wave Rectifier with Capacitor) Insert Your Simulation Results Here vi. Discussions (Full-Wave Rectifier with Capacitor) 9-9