Waves and Light Review Packet 1
advertisement

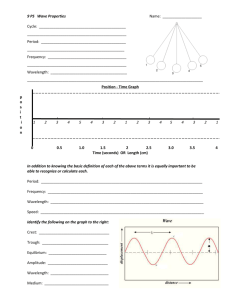
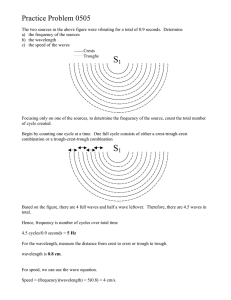
NAME DATE CLASS Chapter 2 Use with Section 2 REINFORCEMENT Wave Properties Complete each sentence by circling the correct answers and crossing out the incorrect answer. 1. The amplitude of a wave can be measured from the (medium, crest) or the (trough, wavelength) to the rest position of the wave’s medium. 2. Waves with greater amplitudes carry (more, less) energy than waves with smaller amplitudes. 3. The wavelength of a transverse wave is often measured from (crest to crest, crest to trough). 4. The number of waves that pass a point in one (second, minute) is the wave’s (amplitude, frequency). 5. Waves with longer wavelengths have a (lower, higher) frequency and waves with shorter wavelengths have a (lower, higher) frequency. Use the words in the box to label the diagram. You will use each term more than once. Then answer the questions. amplitude wavelength 8. wavelength 7. amplitude 6. amplitude 1m 2m 9. wavelength 10. What is the wavelength of the wave shown in the diagram? 11. What is the amplitude of the wave shown in the diagram? Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 5 NAME DATE CLASS Chapter 3 Use with Section 1 REINFORCEMENT Properties of Light Use the light waves below and a metric ruler to answer the questions that follow. B A 1s 1s 1. What is the wavelength of wave B? 2. What is the frequency of wave A? 3. What is the frequency of wave B? 4. Which wave carries more energy? Why? 5. Which wave could represent a radio wave? Why? Complete the charts by filling in the missing colors and answer the questions. 6. Green 7. Red Yellow 8. Magenta Red 11. 12. Magenta 14. Yellow Black Blue 9. 10. White Cyan 15. Cyan Blue 13. Green C D 16. Which chart shows what happens when pigments are mixed? 17. What colors of light are reflected by an object that appears white? Answer the following questions. 18. Why can’t you see a book in a dark room? 19. How is an opaque object different from a translucent object? Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 7 NAME ______________________________________ DATE _______________ CLASS _____________________ CHAPTER REVIEW Chapter Waves 17 I. Vocabulary Review Use the clues to complete the puzzle. 1. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 2. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 3. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 4. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 5. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 6. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 7. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 1. type of wave interference in which the crest of one wave meets the trough of another 2. the lowest part of a wave 3. the distance from crest or trough to the level of the undisturbed medium 4. the way the ear recognizes frequency 5. The medium vibrates in the same direction the wave travels. 6. the distance from crest to crest 7. the highest part of a wave 8. Use the word spelled out in the box to complete the following sentence: The change in pitch as a sound source moves relative to a receiver is called the effect. II. Concept Review If the underscored word or phrase makes the sentence true, write “TRUE” in the space provided. If the underscored word or phrase makes the sentence false, write the correct term or phrase in the space provided. 9. In a longitudinal wave, the medium travels at right angles to the direction of the wave itself. 10. The amplitude of a sound wave is the number of compressions that pass by a point in one second. 11. In the same medium, wavelength increases as frequency decreases. 12. When two wave crests meet, each having an amplitude of X, the new amplitude will be equal to 2X. 13. As an ambulance moves away from you, the pitch of the siren will decrease because the sound waves will be compressed. Answer the following questions in the spaces provided. 14. How are all waves made? Copyright © Glencoe Division of Macmillan/McGraw-Hill 101 NAME ______________________________________ DATE _______________ CLASS _____________________ Chapter Review 17 (continued) 15. The amplitude of waves A and B in Figure 1 is the same. Explain what happens when the crest of wave A meets the trough of FIGURE 1 Crest C B wave B at point C. A Trough 16. Draw a wave and label its parts. Rarefactions Crest Amplitude Wavelength or Trough Compressions III. Skills/Process Review Answer the following questions in phrases or complete sentences. 17. In the Find Out! activity, you made a wave by having several students sit in a large circle and raise and lower their hands in a continuous motion. Using the data in the table below from a similar activity, calculate the speed of the wave. Distance around the circle 36 meters Time for a pulse to travel around the circle 12 seconds 18. In the table, what happens to the speed of the wave as the number of pulses increases? 19. In the table, what is the wavelength when three pulses are going around the circle, evenly spaced? Two pulses? IV. EYV Review 20. Technology Connection: Wave Energy What are some advantages of a wave-powered station? 102 Copyright © Glencoe Division of Macmillan/McGraw-Hill