Color
advertisement
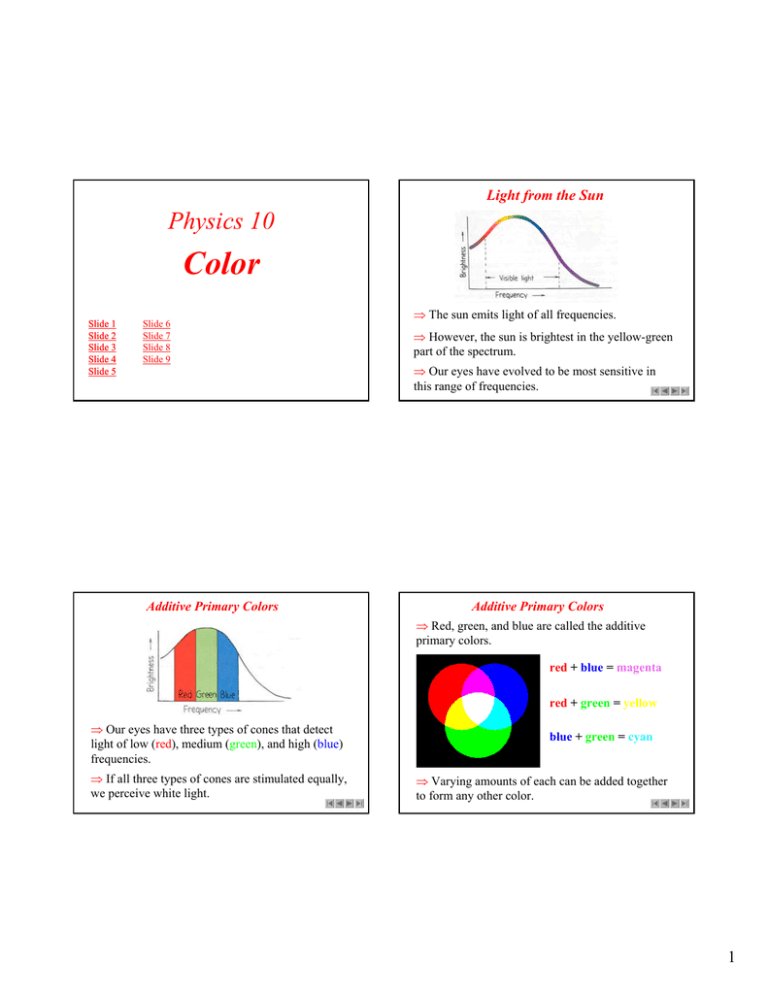
Light from the Sun Physics 10 Color Slide 1 Slide 2 Slide 3 Slide 4 Slide 5 Slide 6 Slide 7 Slide 8 Slide 9 Additive Primary Colors ⇒ The sun emits light of all frequencies. ⇒ However, the sun is brightest in the yellow-green part of the spectrum. ⇒ Our eyes have evolved to be most sensitive in this range of frequencies. Additive Primary Colors ⇒ Red, green, and blue are called the additive primary colors. red + blue = magenta red + green = yellow ⇒ Our eyes have three types of cones that detect light of low (red), medium (green), and high (blue) frequencies. ⇒ If all three types of cones are stimulated equally, we perceive white light. blue + green = cyan ⇒ Varying amounts of each can be added together to form any other color. 1 Exercise 20 Exercise 20 Complete the following equations: Using the figure to the left, complete the following equations: Yellow light + blue light = _______ light. Green light + _______ light = white light. Magenta + yellow + cyan = ________ light. Exercise 13 Supposed two flashlight beams are shown on a white screen, one beam through a pane of blue glass and the other through a pane of yellow glass. What color appears on the screen where the two beams overlap? Suppose, instead, that the two panes of glass are placed in the beam of the single flashlight. What then? ⇒ The overlapping blue and yellow beams will produce white light. When the two panes of glass are overlapped and placed in front of a single flashlight, however, little or no light will be transmitted. Yellow light + blue light = _______ light. Green light + _______ light = white light. Magenta + yellow + cyan = ________ light. ⇒ Yellow light + blue light = white light. Green light + magenta light = white light. Magenta + yellow + cyan = white light. Subtractive Primary Colors ⇒ Mixing colored pigments in paints and dyes is entirely different than mixing colors. ⇒ The colors, magenta, cyan, and yellow are called the subtractive primary colors. ⇒ All color photographs in books are the result of magenta, cyan, and yellow dots. ⇒ The rules of color subtraction are different from the rules of light addition. 2 Exercise 40 You're explaining to a youngster at the seashore why the water is cyan colored. The youngster points to the whitecaps of overturning waves and asked why they are white. What is your answer? ⇒ The water is broken up into a multitude of different size droplets when the wave breaks, and like the droplets in clouds overhead, light of many visible frequencies is scattered to produce the white color. 3