lab4:Zener Diode
advertisement

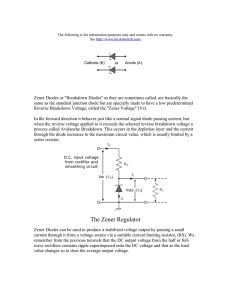
Zener Diode Electronics I Lab Objectives: • • Measure and plot VI Characteristics of zener diodes. To study zener diode as voltage regulator. Part I : VI Characteristics of zener diodes Theoretical Background: A zener diode is a special kind of diode which allows current to flow in the forward direction in the same manner as an ideal diode, but will also permit it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value known as the breakdown voltage, "zener knee voltage" or "zener voltage." The device was named after Clarence Zener, who discovered this electrical property. Zener diodes are heavily doped silicon diodes that, unlike normal diodes, exhibit an abrupt reverse break-down at relatively low voltages . The Zener diode is designed to operate in reverse breakdown region. Zener diode is used for voltage regulation purpose. Zener diodes are designed for specific reverse breakdown voltage called Zener breakdown voltage (Vz). The value of Vz depends on amount of doping. Zener diodes are available in various families (according to their general characteristics , encapsulations and power ratings) with reverse breakdown (Zener) voltages in the range 2.4 V to 200 V. PartII : Zener Diode Voltage Regulator Circuit Orcad Pictured above is a very simple voltage regulator circuit requiring just one zener diode and one resistor. As long as the input voltage is a few volts more than the desired output voltage, the voltage across the zener diode will be stable. As the input voltage increases the current through the Zener diode increases but the voltage drop remains constant - a feature of zener diodes. Therefore since the current in the circuit has increased the voltage drop across the resistor increases by an amount equal to the difference between the inp ut voltage and the zener voltage of the diode . For fixed values of RL the voltage Vi must be sufficiently large to turn the Zener diode on. The minimum turn-on voltage Vi = Vimin is determined by V= V= L z V in min = R L *V i RL + R (R L + R )V Z RL • Determine Vin(max) = V i max I R max R +V Z I= I R min or max − I Lconstant Z min or max ∴ I R max = I Z max + I Lconstant I Z max Pz = Vz Work sheet 1-Testing Diode: Check your diode using Digital Multimeter 2.VI Characteristics of zener diodes 330 Forward Bias Vs .2 .5 .7 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 Vd Id Reverse Bias I z < I z max V in max −V z R V in max < < Pz Vz Pz R +V z Vz 330 Vs .5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7.5 8 9 10 11 12 Vd Id Draw V-I characteristics of diode: 1. Describe the characteristics in your own words. 2. Compute Vin(max) for the circuit ? 3. What is the breakdown voltage of Zener diode used in your practical? 4. Can we operate normal PN junction diode in breakdown region for longer duration? Give reason 5. Why the series resistor in the zener circuit is necessary? PartII : Ze ner Diode Voltage Regulator Circuit 330 1K Vs 3 5 7 8 9 9.5 10 11 12 13 14 15 Vload 1. 2. 3. 4. Iz ILoad Draw Vsource and Vload and comment the graph Draw Vsource and Iload and comment the graph Calculate Vin(min) Calculate Vin(max) Is Vload/ Iload Vs Part III: Implement all the above work using Orcad .