Dividers Slides
advertisement

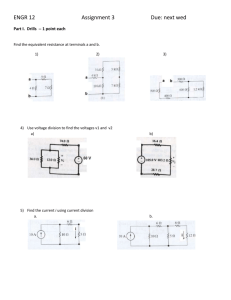
Circuit Analysis Techniques Equivalent Resistance, Voltage & Current Dividers EGR 220, Chapter 2 February 4, 2016 • Review o Bring questions to office hours • Equivalent resistance, Req o Series and parallel resistors • Current divider and voltage divider • Mesh and nodal analysis o Building on KVL and KCL 2 Voltage Divider Rule Voltage Divider: Series R • Resistors and elements in Series… • Current or voltage is the same for R1 & R2? • Current or voltage is partitioned across the elements? • Find v1, v2 in terms of vsrc → derive the expression 3 4 1 Voltage Divider: Series R V-­‐‑Divider Discussion • Solve for v1 and v2 o Which resistor will have the larger V drop? 6 5 Current Divider Rule Current Divider: Parallel R • Resistors, elements and branches in Parallel… • Current Divider: o I is partitioned, flowing through these resistors o What is the relationship of V for each element? • Find i1, i2 in terms of isrc • Derive the expression… i 7 R1 R2 8 2 Current Divider: Parallel R I-­‐‑Divider Discussion • Solve for i1 and i2 o Which R will carry the larger current? 9 Ammeter – Introduced Error 10 Ammeter – Introduced Error • Find the current i in circuit (a). • An ammeter with an internal resistance of 1Ω is inserted in the network to measure i' as shown circuit (b). What is i’? 11 12 3 Voltmeter – Introduced Error Voltmeter – Introduced Error • Obtain the voltage Vo in circuit (a). • Determine the voltage V’o measured when a voltmeter with 6-kΩ internal resistance is connected as in figure (b) o Calculate the percent error as Vo −V 'o ×100% Vo • Find the percent error if the internal resistance were 36kΩ. 13 14 Fundamental Analysis Tools for the Semester • Basic analysis laws o Ohm’s law o KVL: Kirchhoff’s voltage law o KCL: Kirchhoff’s current law • Analysis tools using the basic laws o Equivalent resistance o Current divider o Voltage divider o Mesh analysis o Nodal analysis o Equivalent Circuits 15 16 4