IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering | Volume 1 | Issue 11 | May 2015
ISSN (online): 2349-784X
Design Analysis and Improvement of EOT Crane
Wheel
Yogi Raval
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MEFGI
Abstract
The wheel assembly is an integral part of Electric Overhead Travelling Crane systems that are intended to move in a guided path.
Design is an important industrial activity which influences the quality of the product. There is research gap of optimization of
track wheel. It is always beneficial to optimize any component for the purpose where it is applicable. Optimization techniques
carried out for track wheel to find out the optimum material distribution. Based on these optimization outputs, new practical
designs were generated and FEanalysis was carried out for the optimized design to verify the stress induced on track wheeland
compare with original design. A solver mode in analysis software calculates the stresses, deflections, bending moments. The
finite element method as well as optimization techniques were included as basis of mathematical simulation. With these tools,
optimization of track wheel carried out.
Keywords: Yield Strength, Density, Young’s Modulus,(E)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
I. INTRODUCTION
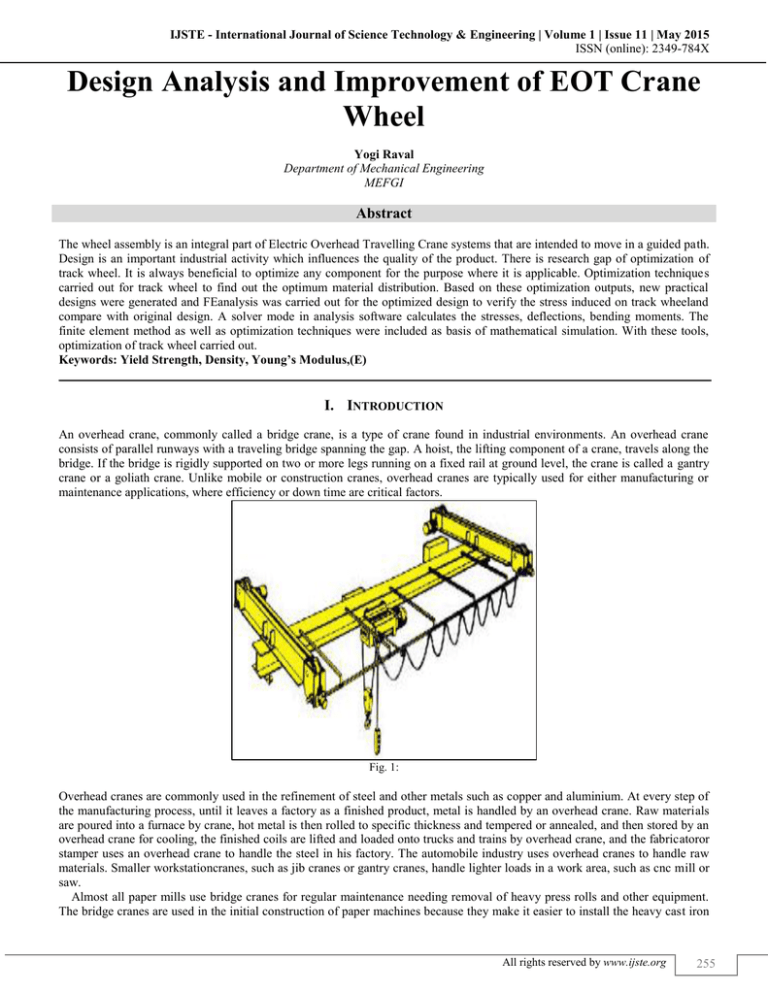
An overhead crane, commonly called a bridge crane, is a type of crane found in industrial environments. An overhead crane
consists of parallel runways with a traveling bridge spanning the gap. A hoist, the lifting component of a crane, travels along the
bridge. If the bridge is rigidly supported on two or more legs running on a fixed rail at ground level, the crane is called a gantry
crane or a goliath crane. Unlike mobile or construction cranes, overhead cranes are typically used for either manufacturing or
maintenance applications, where efficiency or down time are critical factors.
Fig. 1:
Overhead cranes are commonly used in the refinement of steel and other metals such as copper and aluminium. At every step of
the manufacturing process, until it leaves a factory as a finished product, metal is handled by an overhead crane. Raw materials
are poured into a furnace by crane, hot metal is then rolled to specific thickness and tempered or annealed, and then stored by an
overhead crane for cooling, the finished coils are lifted and loaded onto trucks and trains by overhead crane, and the fabricatoror
stamper uses an overhead crane to handle the steel in his factory. The automobile industry uses overhead cranes to handle raw
materials. Smaller workstationcranes, such as jib cranes or gantry cranes, handle lighter loads in a work area, such as cnc mill or
saw.
Almost all paper mills use bridge cranes for regular maintenance needing removal of heavy press rolls and other equipment.
The bridge cranes are used in the initial construction of paper machines because they make it easier to install the heavy cast iron
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org
255
Design Analysis and Improvement of EOT Crane Wheel
(IJSTE/ Volume 1 / Issue 11 / 042)
paper drying drums and other massive equipment, some weighing as much as 70 tons.In many instances the cost of a bridge
crane can be largely offset with savings from not renting mobile cranes in the construction of a facility that uses a lot of heavy
process equipment.
II. ANALYSIS OF EOT CRANE WHEEL
In this wheel we have used material is EN9 steel and its material properties are given in below table.
Table – 1
Material Properties
Material selected
EN9
Young’s Modulus,(E)
206E03 MPa
Poisson’s Ratio
0.30
Tensile Ultimate strength
850MPa
Yield strength
570MPa
Density
7.8E-06 Kg/MM^3
Behaviour
Isotropic
Fig. 2:
Fig. 3:
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org
256
Design Analysis and Improvement of EOT Crane Wheel
(IJSTE/ Volume 1 / Issue 11 / 042)
Fig. 4:
Fig. 5:
Fig. 6:
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org
257
Design Analysis and Improvement of EOT Crane Wheel
(IJSTE/ Volume 1 / Issue 11 / 042)
REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]
[13]
[14]
taneltelliskivi, Ulf Olofsson, Ulf Sellgren and Patrik Kruse, “A TOOL AND A METHOD FOR FE ANALYSIS OF WHEEL AND RAIL
INTERACTION”, Machine Elements, Department of Machine Design Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Stockholm, Sweden
vahidmonfared, “Contact Stress Analysis in Rolling Bodies by Finite Element Method (FEM) Statically” Journal of Mechanical Engineering and
Automation 2012, 2(2): 12-16 DOI: 10.5923/j.jmea.20120202.03
aleksandersladkowski,mareksitarz, “Analysis of wheel–rail interaction using FE software”, Department of Railway Transport, Silesian Technical
University, Krasinski Street 8, Katowice 40-019, Poland Received 13 June 2003; received in revised form 12 December 2003; accepted 1 March 2004
Mehmet Ali Arslan , Og˘uzkayabas, “3-D Rail–Wheel contact analysis using FEA”, Gebze Institute of Technology, Mechanical Engineering Department,
P.K. 141, 41400 Gebze, Kocaeli, Turkey
P. Meghashyam, S. Girivardhan Naidu and N. Sayed Baba, “Design and Analysis of Wheel Rim using CATIA & ANSYS”, International Journal of
Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management (IJAIEM) Web Site: www.ijaiem.org Email: editor@ijaiem.org, editorijaiem@gmail.com
Volume 2, Issue 8, August 2013
Sourav Das, “design and weight optimization of aluminium wheel”, International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 6, June
2014 1 ISSN 2250-3153
Parth Patel,hirenprajapati, Sunil Prajapati, “Parametric optimization of belt conveyor supporting structure using FEA-DOE hybrid modelling” IOSR Journal
of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-ISSN: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. IV (May- Jun. 2014)
Tushar M. Patel, Dr. M. G. Bhatt, Harshad K. Patel, “ Parametric Optimization of Eicher 11.10 Chassis Frame for Weight Reduction Using FEA-DOE
Hybrid Modeling”IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-ISSN: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 6, Issue 2 (Mar. Apr. 2013)
Thomas H. Brown, Jr., Mark’s calculation by Machine Design
IS 807 : 2006 Design, Erection And Testing (Structural Portion ) Of Cranes And Hoists Code Of Practice
Is 3177:1999 Code Of Practice For Electric Overhead Travelling Cranes And Gantry Cranes Other Than Steel Work Cranes
adwaitjoshi, “Stress Analysis of a Rail Wheel Assembly of an EOT Crane”, Http://www.adwaitjoshi.com/misc/eotcrane. , Pdf.
PSG Design Data Book, PSG College of Engineering, Coimbatore, India.
Mechanical Engineering Design, Joseph Shigley& Charles Mischke.
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org
258



