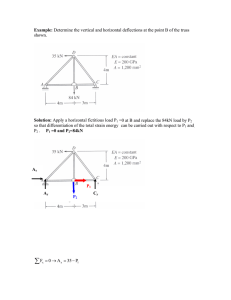
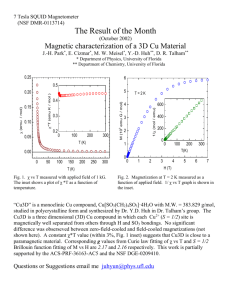
Enhanced average thermoelectric figure of merit of n
advertisement

Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information for Enhanced average thermoelectric figure of merit of n-type PbTe1−xIx–MgTe Priyanka Jood,a Michihiro Ohta,†,a Masaru Kunii,a Xiaokai Hu,a Hirotaka Nishiate,a Atsushi Yamamoto,a and Mercouri G. Kanatzidisb,c aResearch Institute for Energy Conservation, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8568, Japan. *E-mail: ohta.michihiro@aist.go.jp bDepartment cMaterials of Chemistry, Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois 60208, USA Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, Illinois 60439,USA. Fig. S1 Temperature dependences of (a) thermal diffusivity (D), and heat capacity (CP) for PbTe1-xIx-yMgTe (0.0012 ≤ x ≤ 0.006; y = 0 and 1 mol%). Fig. S2 Temperature dependence of the (a) electrical resistivity (ρ), Seebeck coefficient (S), (b) total thermal conductivity (κtotal), and thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT) for PbTe0.9972I0.0028–2 mol% MgTe. Fig. S3 Zoom-in powder X-ray diffraction patterns of PbTe0.9972I0.0028–yMgTe (y = 0, 1 and 2 mol%) showing the onset of peak splitting in PbTe0.9972I0.0028–2% MgTe Fig. S4 Log-log plot of electrical resistivity and temperature for PbTe1−xIx–yMgTe (x = 0.004 and 0.006; y= 0 and 1 mol%) The Lorenz number can be expressed as a function of the reduced chemical potential (η) for a single parabolic band: 𝐿= 𝑘𝑏 3𝐹0(𝜂)𝐹2(𝜂) ‒ 4𝐹1(𝜂)2 () 2 𝐹0(𝜂)2 𝑒 (1), where 𝑘𝑏 and 𝑒 are Boltzmann constant and elementary charge, respectively. η was obtained from the fitting of the experimental S values using the following equation for the single parabolic band model dominated by acoustic phonon scattering. 𝑆= 𝑘𝑏 2𝐹1(𝜂) ( 𝑒 𝐹0(𝜂) ‒𝜂 ) (2), where the Fermi integrals Fm(η) are defined as: ∞ 𝐹𝑚(𝜂) = ∫ 0 𝑥𝑚 𝑑𝑥 1 + 𝑒𝑥𝑝(𝑥 ‒ 𝜂) (3). The temperature dependence of the calculated L from the fitting procedure for PbTe1−xIx–yMgTe (0.0012 ≤ x ≤ 0.006; y = 0 and 1 mol%) is given in Fig. S5 Fig. S5 Temperature dependence of the calculated Lorenz number (L) for PbTe1−xIx–yMgTe (0.0012 ≤ x ≤ 0.006; y = 0 and 1 mol%) Table S1 Room-temperature electron mobility (μ) and carrier concentration (n) for PbTe1−xIx–yMgTe (0.0012 ≤ x ≤ 0.006; y = 0 and 1 mol%) Sample μ (cm2 V−1 s−1) n (1019 cm−3) x= 0.0012 296 1.62 x= 0.0012, 1% MgTe 327 1.31 x= 0.0028 168 2.27 x= 0.0028, 1% MgTe 403 1.63 x= 0.0028, 2% MgTe 164 0.38 x= 0.0040, 610 4.05 x= 0.0040, 1% MgTe 451 2.24 x= 0.0060 538 7.40 x= 0.0060, 1% MgTe 436 5.73 Table S2 Density (d) of the sintered compacts of PbTe1−xIx–yMgTe (0.0012 ≤ x ≤ 0.006; y = 0 and 1 mol%) measured using Gas pycnometer method. Sample d (g cm-3) x= 0.0012 8.20 x= 0.0012, 1% MgTe 8.18 x= 0.0028 8.20 x= 0.0028, 1% MgTe 8.17 x= 0.0040 8.16 x= 0.0040, 1% MgTe 8.09 x= 0.0060 8.14 x= 0.0060, 1% MgTe 8.07