Malaria: Bringing Down The Burden In Odisha
advertisement

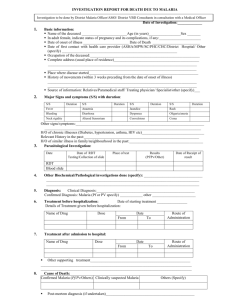
Malaria: Bringing Down The Burden In Odisha Dr. MM Pradhan Dy. Director, NVBDCP, Odisha MMV Stakeholders’ Meeting, Delhi (India), 8th Nov, 2012 Odisha at a glance Area: 156,000 sq kms (4% of India’s land area) Popln: 42 million (3% of India) Rural : 82% , Urban : 18% Tribal - 22% + sch. caste -16% ( St & SC = 36%) Out of 75 Primitive Tribal Groups in India ,13 are in Odisha. There are 30 district with 314 blocks and >51,000 villages Favourable geo-ecotypes: Perennial streams in forest areas -Forest area are also rich in minerals with mining activities and high migratory population Average temperature : 15 0 to 35 0С (extreme: 50С to 48 0С) Rain fall : 1452 mm with high humidity (>60%)} Transmission seasonality 2009 - Death 2011 - Death 40000 22 19 23 16 14 21 15 15 10 4 20 16 19 15 28 19 15 8 11 2 11 14 9 15 12 4 7 12 15 2 15 13 10000 14 20000 25 25 23 30000 35 30 31 50000 40 2010 - Death 2009 - Cases 38 60000 8 10 5 0 0 Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Transmission is perennial with one peak in forested districts (mostly tribal dominated) Forest covers 34.2% Kandhamal ( Pf > 90%) 5000 4500 4000 No of cases 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Malaria cases 1765 1864 2193 2691 2542 3760 4154 4826 4363 3190 2865 2338 Pf cases Death 1678 1771 2077 2549 2410 3583 3935 4543 4143 2975 2644 2203 1 2 7 3 5 7 3 2 3 3 3 0 Malaria Epidemiological Situation, 2002-12 Year Total Tested +ve PF Death ABER SPR Pf% API 83.16 12.64 2002 4570466 473223 393523 465 2007 4945551 371879 323150 221 12.22 7.52 86.90 9.19 2008 5029677 375430 329631 239 12.23 7.46 87.80 9.13 2009 5015489 380904 336047 198 12.00 7.59 88.22 9.12 2010 5240458 395651 350428 247 12.30 7.55 88.57 9.29 2011 4657978 298423 272971 100 11.13 6.41 91.47 7.13 2010 – upto Sept. 3743258 277915 244744 162 7.42 88.06 2011 – upto Sept. 3452288 232911 213029 66 6.75 91.46 2012 – upto Sept. 3457988 187176 173137 46 5.41 92.50 12.21 10.35 Malaria cases decreased by 20% & deaths by 30% (2011 vs 2012 by September) 2007 Status of Malaria API of Odisha from 2007-2011 2009 2010 Year wise distribution of Districts with API Year 0-2 2-5 5-10 >10 2007 7 3 6 14 2008 7 5 5 13 2009 10 3 4 14 2010 10 4 4 12 2011 12 5 3 10 2011 There is a decrease in API 2008 Malaria control strategy: As per the National program with state specific appropriation A. Primary: 1. Early diagnosis (Microscopy & RDT) and completer treatment with effective & appropriate Antimalaria drugs 2. Integrated vector control : LLIN , IRS, source reduction B. Supportive: Monitoring & evaluation, capacity building IEC & BCC – PPP & Social mobilisation advocacy, Operational research Structure of health services in Odisha 30 Districts with 32 Dist Hospital 314 Blocks (125K pop per block) Malaria surveillance, Diagnosis & treatment available free of cost at each Health facility Primary Health Center (20-30K pop) 4-5 PHCs per block Sub-center (5K pop) (4-5 SCs per PHC) 51,000 villages (0.5-1K pop per village) (8-10 villages per SC) Inputs & interventions for malaria control from 2009 onwards. 3000000 2774000 300 2500000 9.29 LLIN ITN 250 247 MO-Mashari 9.12 2000000 200 RDT 150 RDT(Bi-valent) procure by State 1750725 1500000 50 6220 API 0 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 ACT ASHA Capacity building 683400 500000 650000 622875 100 0 121700 674324 100 15000 0 0 700000 254356 101350 83911 0 0 0 0 15000 500000 0 RDT(Monovalent) procure by Sate 7.13 1199000 1000000 1902668 198 Death Surveillance and Early Diagnosis & Complete Treatment (RDT + ACT) at village level Out of 41264 ASHAs, >38000 have been trained (92% ) 646 AYUSH doctors & around 2000 tribal school teachers have been trained on EDCT Around 500 Forest (VSS) Animators have been trained as FTD to provide EDCT service in Forest villages in four tribal districts (Rayagada, Gajapati, Kandhamal and Koraput) Sentinel Site Malaria laboratories-2011 Characteristics of IPD patients at SSL, 2011 2501000 450000 400000 Characteristics of OPD cases at SSL, 2011 380987 2001000 350000 1957077 No of in patients 300000 1501000 250000 200000 1001000 150000 100000 50000 25139 (6.59%) 7203 (1.89%) 501000 158871 (8.1%) 0 Total In Patient In patient suspected Confirmed Malaria as malaria cases 11175 (.57%) 1000 Total New OPD Cases Suspected malaria Confirmed Malaria Cases cases Seasonality of IPD cases in 2011 Total IPD 1569 94156 4220 5773 10575 40000 20000 1500 1000 4571 60000 74368 80000 2000 85844 1405 100000 2500 2280 Total Positive 126619 120000 Total In patients suspected as malaria 1949 140000 Oct - Dec Jul - Sep Apr - Jun 0 Jan - March 0 500 Integrated Vector Control: IRS IRS – 2 rounds protect high risk population ( API > 5) - around 8.7 million in 22 districts Hand Compression Sprayer Pumps (HCSP) have been introduced Integrated Vector Control : LLIN Total 18.99 Lakhs LLIN distributed in 2009-10 and another 19 Lakh in 2011-12 (total around 38 lakh LLIN) - protect around 90 lakh population, State specific LLIN guidelines adopted for LLIN distribution LLIN distribution was done through GKS (village health sanitation committee),followed by intensified IEC & BCC Sundargarh Sonepur Sambalpur Rayagada Nuapada 30000 40000 30000 80000 95000 API-10 150000 150000 140000 Nawarangapur 40000 102600 100000 100000 90000 94000 LLIN Distribution 2009-10 Mayurbhanj Malkangiri 50000 40000 Koraput Keonjhar Kandhamal Kalahandi 40000 30000 20000 Jharsuguda Ganjam Gajapati 68500 80000 Dhenkanal Bolangir 65000 60000 Bargarh 111000 100000 Angul API trend after 1st phase LLIN distribution ( around 19 lakh) 160000 120.00 API-11 0 100.00 120000 80.00 60.00 40.00 20.00 0.00 Encouraging results after the new interventions: positive 2037 pf pv •LLIN in 2009 along with ACT 1707 •Special awareness campaign- NIDHI RATH 925 690 336 •Nil reported death 235 No. of Positive casese pf 650 5000 550 4000 450 3000 350 2000 250 1000 150 50 0 2008 2009 2010 2011 K. Nagar Sub. Divisonal Hospital catering the population of a High Endemic Tribal block of Dhenkanal district State initiative Mo Mashari (my mosquito net) In 2 phases 2.24 Lakh LLINs have been provided to Pregnant mothers in 7 high burden tribal districts to protect pregnant mothers Besides, pregnant mothers, Tribal school boarders and inmates are protected by ITN/LLIN - 2.04 Lakh Single size ITN/ LIIN provided to these vulnerable group. Study findings: •91% of pregnant women slept under LLIN last night (n=809). •88% of pregnant women slept under LLIN last night with their child under 2 years (n=809). •But in general / cluster distributed areas (n=2925), 70% of family members slept under LLIN last night Innovative IEC &BCC • Use of traditional folk theatre, Jatra etc. • Partnership with GKS & CBOs • Advocacy & Inter-sectoral coordination • Involvement of School teacher & student, Traditional / Faith healers Nidhi Mausa Adalat NGO/PPP and Inter Sectoral Co-ordination NGOs engaged under NRHM are involved in screening of malaria cases, impregnation of bed nets, laboratory diagnosis and community mobilization and monitoring. Other departments: Women & Child Development., Forest and Environment, Schedule Caste & Schedule Tribe, School and Mass Education, Panchayati Raj Institutions, ICMR institutes Lot Quality Assurance Sampling: LQAS LQAS : ME tool in malaria program. Conducted twice a year –at present conducted in 21 districts. The LQAS findings from 2009 to 2011 on % of people protected either by ITN/LLIN. Sundargarh Mayurbhanj Nabarangpur Kandhamal Mon Target 70% 60% 50% 40% Sundargarh 30% Mayurbhanj 20% Nabarangpur Kandhamal 10% Mon Target 0% Nov (2009) Aug (2010) Nov(2010) Aug(2011) Nov (2011) Research & Documentation Operational research (Dfid support): • Vector study by VCRC in 10 southern districtspublication awaited • Mo-Mashari (my mosquito nets) by T & MST (of Dfid) – report released • LLIN impact study by ICMR institutes – reports awaited Guidelines and reports: – LLIN state Guidelines – Operational manuals – Annual Activity report – used for advocacy – Training manuals for doctors, Health workers, ASHA – FAQs for school students and others Comprehensive case management(Pilot): MMV-NIMR - Odisha 3Ts: test, treat & tract Rationale: • Case management of malaria, beyond ‘treating the sick’, could reduce the infectious reservoir. • The size of the infectious reservoir is an important determinant of malaria transmission in low & medium endemic areas Universal vector control is difficult and expensive where large populations are at variable risk Objectives of the Study Primary • To assess the impact of CCM for uncomplicated malaria on its incidence/ transmission in different transmission settings in the state of Odisha, India Secondary • Determine the mix of interventions and related costs needed for scale-up of comprehensive case management • Develop a community based surveillance model for reporting and timely action • Better define the burden and epidemiological profile of malaria in the area • Identify challenges in the radical cure of malaria, particularly P. vivax • Strengthen the pharmaco-vigilance system to generate community level data on adverse events Project design High case load (ca. 2000 patients p.a) Medium transmission (API: 8) Mixed vivax (30%) Medium case load (ca. 1000 patients p.a.) Intervention / Control High transmission (API: 18) Low vivax (10%) Intervention / control Intervention / Control • Operational research project with NVBDCP • Total study population 800,000 • 3 year study period (October 2012 – 2015) Low transmission (API: 3) High vivax (50%) Low case load (ca. 300 patients p.a) I want to play at school - help me for no malaria Challenges: •Tribal areas - cultural and language barrier •Forest villages •Inaccessibility and poor health services •Inadequate health staff •Increased mining and developmental activities •Urban set ups with migratory population & poor health structure for public health activities Thanks Challenges: More research for newer interventions Health system research -functioning of ASHA & other health volunteers -Community based organizations (GKS) -Community mechanism - Role of Traditional healers in tribal areas -Role of general practitioners, chemists, private and other sectors