Wheels and Levers - Glossary
advertisement

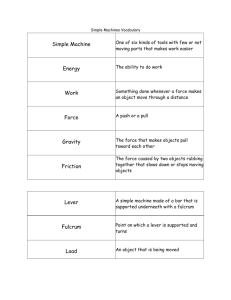
- Wheels and Levers - GlossaryAxle: A shaft or rod on which a wheel turns (fixed or free). Balance: A condition in which opposing forces exactly balance or equal each other; state of equilibrium. Block and Tackle: A unit made up of several pulleys linked together by ropes. Cog: Another term for gear wheel. Conservation of energy: Energy can neither be created or destroyed. The energy output of a machine is equal to the energy input. Driver: Wheel or gear that transfers force to other wheels or gears. Driven gear or wheel: The wheel or gear that is moved by the force of a driver wheel or gear. Effort: The force (push or pull) that produces an action. Energy: Ability to do work. Force: A push or pull that makes an object move. Force equals mass times distance. Friction: A force that resists motion between two objects that touch - there is less friction between smooth surfaces than between rough surfaces. Fulcrum: The supporting point of a lever; also called a pivot. Gear: Toothed wheel that transmits motion from one shaft to another. Gears: (beveled) Alter direction of motion by 90, e.g. a hand mixer. Gears: (rack and pinion) Change circular motion to linear (straight) motion. e.g. a steering column. Gears: (worm) Changes direction of motion by 90 and alters speed, e.g. an electric mixer. Idler: A gear that transmits force and motion from one gear to another. Lever: A bar that can rest on a pivot or support point called a fulcrum. Force or effort is applied to one place to move a load at another place. Mass and weight: Mass is the amount of matter that is contained in a body measured in kilograms. Weight is the attraction of the force of gravity on that body measured in Newtons. On the Earth, a person whose mass is 50 kg has a weight of approximately 500 N. Mesh: To smoothly interlock the teeth of two or more gear wheels. Motion: Change in the position of an object (speed = rate of motion). Newton: Newton (N) is the force required to give a one kg mass an acceleration of one meter per second. Perpetual Motion: Endless motion without friction.. Power: The rate at which work is done. Power is the product of the time the force acts, the force required and the distance a load is moved. Pulley: A wheel with a groove in the rim in which a rope or belt moves. Resistance: The force that must be overcome to produce work in a machine also called load. Shaft: Another term for axle. Work: The result of a force moving an object.