Decay of emf Between SS316 Electrodes in KOH
advertisement

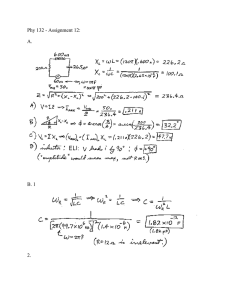
Decay of emf Between SS316 Electrodes in KOH Solution Shweta Ganguly*, Jyoti Agarwal* & Abhra Shau** *3rd Semester (B.Tech ), **Research Scholar Chemical Engineering, Universuty of Calcutta Abstract Shau (personal communication) reported the generation of emf between two SS316 electrode immersed in KOH solution . It is seem to be unexpected to get an emf between same material in a solution. Investigation is being carried out in the laboratory. Introduction Shau while working on electrolysis of water using SS316 electrodes, reported the formation of thin scales/ deposits on the surface of the electrode material as shown in Fig. 1. He also found an emf to develop between the two electrodes, when both are placed in the same solution with initial value of 863.2 mV. The emf decayed over a period of 56 hrs and became steady at 0.11 mV. The experimental setup used by Shau is shown in Fig. 2 and the decay of emf in Fig. 3. 0.9 1.0 0.7 Potential difference, mV Potential difference, V 0.8 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 0 200 400 600 Time, sec 0.0 40000 20000 80000 120000 160000 Time, sec Figure 1: Packing materials of elcctrode before & after electrolysis. Figure 2: Experimental set-up used by Shau. Figure 3.a: Decaying of Potential difference for first 10 hrs. Figure 3.b: Decaying of Potential difference after 10 hrs until steady state reached. Objective Normally, one would not expect an emf to be generated between the electrodes of same material and geometry placed in the same solution. Thus the objective of our work was to verify whether such an emf is produced, and if so, try to find out an explanation for the origin of this emf. Potential difference between electrodes, mV Figure 4: Experimental set-up. 40 30 20 10 0 -10 0 400000 800000 Experimentation Experimental setup is a simple electrolytic cell as shown in Fig. 4 with two flat plate electrodes of same material (SS316). The area of the electrodes (portion immersed in solution) was 10cm2. The area could be adjusted by a suitable threaded bolt and nut arrangement. In the current study, though, the electrode area was not changed. Distance between the electrodes was 1 inch. The electrolyte i.e. KOH solution of concentration of 0.50 wt%, was made by dissolving KOH pellets (with assay ≥ 84%) in double distilled water. The potential difference between the electrodes was measured by a 4 & half digit digital voltmeter of range 0.01 to 1000 V and the experimental data were obtained as illustrated in Fig. 5. 1200000 Time, Sec Result and Discussions i. An emf is produced though it does not seem to be repeatable. ii. Figure 6 depicted that the change in emf measure with room electrical appliances on & off it may be inferred that switching on power to room appliance lights, fans has an effect on the observed potential. So a part of the emf observed may be due to stray over induced by external fields. Potential difference netween electrodes, mV Figure 5: Change in potential difference with time. In absence of electromagnetic field -6.5 -8.5 In presence of electromagnetic field -9.0 -9.5 -10.0 1381000 1381200 1385000 1386000 1387000 1388000 Time, sec iii. The exact mechanism of production of this emf is not clear at present, but it may be related to the corrosion, and may be due to impurities in the electrodes setting of local electrochemical cells. Figure 6: Effect of electromagnetic field in generation of emf. Presented at Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Calcutta on December 22, 2012