Binary Subtract Binary Subtractor Circuits ircuits
advertisement

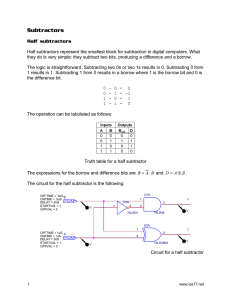
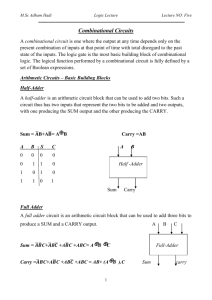
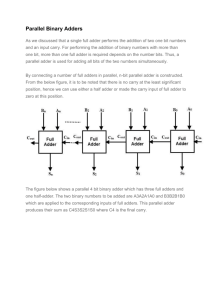
© 2015 IJIRT | Volume 1 Issue 12 | ISSN: 2349-6002 Binary Subtractor Circuits Simran Singh Oberoi ,SangeetKumar,Virenderpratap Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Dronacharya College of Engineering, Gurgaon, India Abstract:In this paper we would be studying about subtractor that are used two subtract two binary numbers. The main focus of this paper is on the two main types of subtractors, i.e. half subtractor and full subtractor. This paper will be mainly focused on the two subtractors but we will also be having a brief on other type of subtractor. Introduction Subtractors are usually implemented within a binary adder for only a small cost when using the standard two's complement notation, by providing an addition/subtraction selector to the carry-in and to invert the second operand. In electronics, a subtractor can be designed using the same approach as that of an adder. The binary subtraction process is summarized below. As with an adder, in the general case of calculations on multi-bit numbers, three bitss are involved in performing the subtraction for each bit of the difference: the minuend ( ), subtrahend ( ), and a borrow in from the previous (less significant) bit order position ( are the difference bit ( ). The outputs ) and borrow bit . The subtractor is best understood by considering that the subtrahend and both borrow bits have negative weights, whereas the X and D bits are positive. Binary Subtractor are of two types. They are classified into:(1) Half Subtractor (2) Full Subtractor HALF SUBTRACTORThe half-subtractor is a combinational circuit which is used to perform subtraction of two bits. It has two inputs, X (minuend) and Y (subtrahend) and two outputs D (difference) and B (borrow).An important point worth mentioning is that the half substractor diagram aside implements (b-a) and not (a-b) as borrow is calculated from equation IJIRT 101878 The half Subtractor subtracts two input bits and generates a difference and borrow, which are the two outputs of a half subtractor. The input variables of a half subtractor are called the Minuend and subtrahend bits. Truth table X Y D B 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 From the above table one can draw the Karnaugh map for "difference" and "borrow". So, Logic equations are: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN TECHNOLOGY 131 © 2015 IJIRT | Volume 1 Issue 12 | ISSN: 2349-6002 FULL SUBTRACTOR As in the case of the addition using logic gates, a full subtractor is made by combining two half-subtractors and an additional OR-gate. A full subtractor has the borrow in capability (denoted as BORIN in the diagram below) and so allows cascading which results in the possibility of multi-bit subtraction. Difference=A'B'C+A'BB'+AB'C'+ABC Reduce it like subtractor Then We got Difference=A B C Borrow=A'B'C+A'BC'+A'BC+ABC =A'B'C+A'BC'+A'BC+A'BC+A'BC+ABC ---------> A'BC=A'BC+A'BC+A'BC =A'C(B'+B)+A'B(C'+C)+BC(A'+A) Borrow=A'C+A'B+BC 1 1 1 1 1 So, Logic equations are: A Truth table The truth table for the full subtractor is given below.[1] X Y Z D B 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 IJIRT 101878 REFERENCE www.google.com www.circuits-today.com www.wikipedia.com Digital Electronics By J B Gupta INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN TECHNOLOGY 132