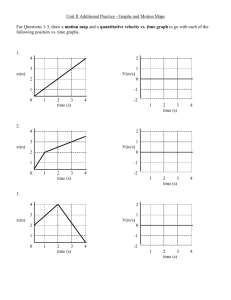
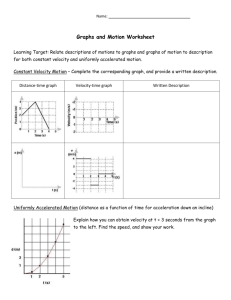
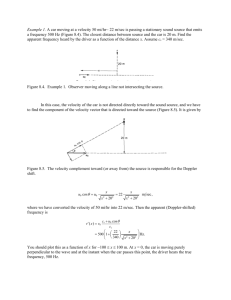
Motion Graphs Homework: Distance & Velocity vs. Time
advertisement

Name____________________________ Lab Partner(s)_____________________ HOMEWORK: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION Distance(Position)-Time Graphs Answer the following questions in the spaces provided. 1. What do you do to create a horizon tal line on a distance-time graph? ________________________________ Stand still. ________________________________ 2. How do you walk to create a straig ht line that slopes up? Walk at a steady (constant) speed away from the ________________________________ D i s t D i s t Time origin (detector). ________________________________ 3. How do you walk to create a straig ht line that slopes down? Walk at a steady speed toward the origin. ________________________________ D i s t ________________________________ 4. How do you move so the graph goes up steeply at first, and then continu es up gradually? ________________________________ First walk quickly away from the origin, ________________________________ at a steady speed then walk away more Time Time D i s t Time slowly also at a steady speed. ________________________________ 5. How do you walk to create a U-shap ed graph? ________________________________ First walk toward the origin, speeding up then ________________________________ slowing down. Reverse direction, speed up ________________________________ then slow down and come to rest. Tools for Scientific Thinking Homework-Introduction to Motion H-1 D i s t Time Motion and Force 9/92 ©1987-92 CSMT Tufts U. Answer the following about two obj ects, A and B, whose motion produc ed the following distance (position) -time graphs. D i s t a) Which object is B moving faster--A or B?_____ 6. B A A b) Which starts ahead? _____ Define what you mean by "ahead." A _________________________ starts out further from the than B and they are both _ origin ________________________ moving away from the origin _________________________ c) What does the intersection mea n? Time ______________________ Objects A and B are at the ______________________ same position at the same time. ______________________ Object B passes object A. D i s t A 7. B Time a) Which object is moving faster? ____ Both about same speed. b) Which object has a negative velocity according to the convention we have established? ____ B 8. a) Which object is moving faster? D i s t B A _____ A b) Which starts ahead? _____ B Explain what you mean by"ahead." Time _______________________ They are both moving toward the _______________________ origin, and B starts closer to the _______________________ origin. Tools for Scientific Thinking Homework-Introduction to Motion H-2 Motion and Force 9/92 ©1987-92 CSMT Tufts U. Sketch the distance (position)-time graph corresponding to each of the following descriptions of the motion of an object. 9. The object moves with a steady (co nstant) velocity away from the origin. 10. The object is standing still. 11. The object moves with a steady (co nstant) velocity toward the origin for 5 s econds and then stands still for 5 seconds. 12. The object moves with a steady vel ocity away from the origin for 5 seconds , then reverses direction and moves at th e same speed toward the origin for 5 seco nds. 13. The object moves away from the origin, starting slowly and speeding up. D i s t a n c 0 e 0 5 10 T i m e(sec) D i s t a n c 0 e 0 5 10 T i m e(sec) D i s t a n c 0 e 0 5 10 T i m e(sec) D i s t a n c 0 e 0 5 10 T i m e(sec) D i s t a n c 0 e 0 5 10 T i m e(sec) Note: These graphs are examples of correct graphs. Tools for Scientific Thinking Homework-Introduction to Motion H-3 Motion and Force 9/92 ©1987-92 CSMT Tufts U. Velocity-Time Graphs After studying the velocity-time graphs you have made, answer the following questions: + V e 0 l Time - 1. How do you move to create a horizontal line in the positive part of a velocity-time graph? Move at a steady (constant)_velocity away from the origin.____________________ _________________________________________________________________ + V e 0 l Time - 2. How do you move to create a straight-line velocity-time graph that slopes up from zero? Move away from the origin speeding up at a steady rate.______________ ________________________________________________________________ + V e 0 l Time - 3. How do you move to create a straight-line velocity-time graph that slopes down? Move away from the origin slowing down at a steady rate.________________ ________________________________________________________________ + V e 0 l Time - 4. How do you move to make a horizontal line in the negative part of a velocity-time graph? Move witht a steady (constant) velocity toward the origin.____________________ ________________________________________________________________ Tools for Scientific Thinking Homework-Introduction to Motion H-4 Motion and Force 9/92 ©1987-92 CSMT Tufts U. 5. The velocity-time graph of an object is shown below. Figure out the total distance traveled by the object. Show your work. Distance = ______8______ meters. . . . . . . . . . 2 4 . - . - . - . - V e l +2 o c 0 i 0 t y -2 m/s . - +4 (2 m/s)(4 sec) = 8 m 6 8 10 . . . . . T i m e (s e c) . -4 6. Both of the velocity graphs below, 1 and 2, show the motion of two objects, A and B. Answer the following questions separately for 1 and for 2. Explain your answers when necessary. a) Is one faster than the other? If so, which one is faster? (A or B) b) What does the intersection mean? c) Can one tell which object is "ahead"? (define "ahead") d) Does either object A or B turn around? Explain. 1 2 A V E L B V E L B 0 A 0 TIME a) A always moves faster.____________ b) They are moving at the same speed at c) d) TIME a) First A ,then B after the intersection. b) They are moving at the same speed that moment in time. at that moment in time.__________ ______________________________ ___________________________ Can't tell. Velocity graph does not show c) Can't tell. Velocity graph does not_ the starting positions. ______________ show the starting positions. _____ ______________________________ started. No Velocities do not change sign._____ Tools for Scientific Thinking Homework-Introduction to Motion d) H-5 __________________ No Velocities do not change sign. Motion and Force 9/92 ©1987-92 CSMT Tufts U. Sketch velocity-time the velocity -time graph corresponding to each of the following descriptions of the motion of an object. 7. The object is moving away from the origin at a steady (cons tant) velocity. + V e 0 l 10 20 Time(sec) 10 20 Time(sec) 10 20 Time(sec) 10 20 Time(sec) - 8. The object is standing still. + V e 0 l - 9. The object moves toward the origin at a steady (constant ) velocity for 10 seconds, a nd then stands still for 10 seconds. + V e 0 l - 10. The object moves away from the origin at a steady (constan t) velocity for 10 seconds, re verses direction and moves back to ward the origin at the same spee d for 10 seconds. Tools for Scientific Thinking Homework-Introduction to Motion + V e 0 l - H-6 Motion and Force 9/92 ©1987-92 CSMT Tufts U. 11. Draw the velocity graphs for an object whose motion produced the distance-time graphs shown below on the left. Distance is in meters and velocity in meters per second. (That is, the velocity is the number of meters the object would move in one second.) Note: Unlike most real objects, you can assume these objects can change velocity so quickly that it looks instantaneous with this time scale. +2 V e +1 l o 0 c i t -1 y (m/s) -2 4 D i 3 s t 2 a n c 1 e (m) 0 4 D i 3 s t 2 a n c 1 e (m) 0 4 D i 3 s t 2 a n c 1 e (m)0 0 0 0 Tools for Scientific Thinking Homework-Introduction to Motion 1 1 1 2 3 Time (sec) 2 3 Time (sec) 2 3 Time (sec) 4 4 4 5 +2 V e +1 l o 0 c i t -1 y (m/s) -2 5 V +2 e +1 l o 0 c i t -1 y (m/s) -2 5 H-7 1 2 3 4 5 Time(sec) 1 2 3 4 5 Time(sec) 1 2 3 4 5 Time(sec) Motion and Force 9/92 ©1987-92 CSMT Tufts U. 12. Draw careful graphs below of distance and velocity for a cart that starts at the origin and— a. moves away from the origin at a slow and steady (constant) velocity for the first 5 seconds. b. moves away at a medium-fast, steady (constant) velocity for the next 5 seconds. c. stands still for the next 5 seconds. d. moves toward the origin at a slow and steady (constant) velocity for the next 5 seconds. e. stands still for the last 5 seconds. . . . . . . . . . . . . - . . . . . - . . . . . - . . . . . - . . . . . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - V +1 e l o c0 i t y m/s -1 m 8 4 - D i s t a n c e 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 T i m e (sec) Tools for Scientific Thinking Homework-Introduction to Motion H-8 Motion and Force 9/92 ©1987-92 CSMT Tufts U.