The English Learner and Response to Intervention
advertisement
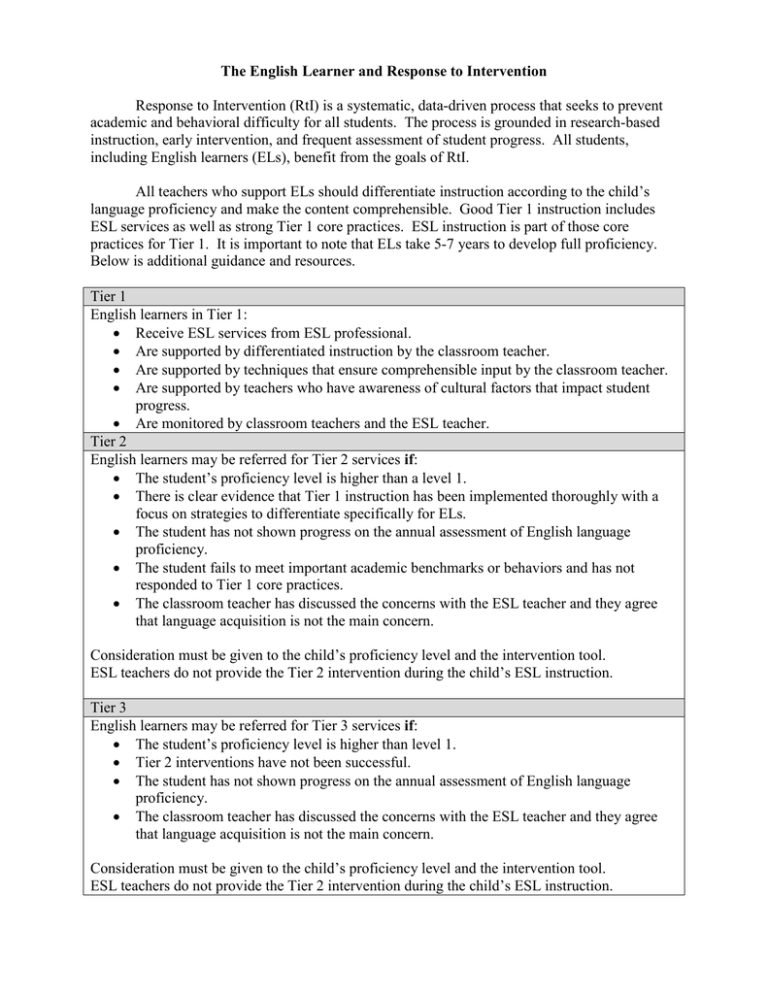
The English Learner and Response to Intervention Response to Intervention (RtI) is a systematic, data-driven process that seeks to prevent academic and behavioral difficulty for all students. The process is grounded in research-based instruction, early intervention, and frequent assessment of student progress. All students, including English learners (ELs), benefit from the goals of RtI. All teachers who support ELs should differentiate instruction according to the child’s language proficiency and make the content comprehensible. Good Tier 1 instruction includes ESL services as well as strong Tier 1 core practices. ESL instruction is part of those core practices for Tier 1. It is important to note that ELs take 5-7 years to develop full proficiency. Below is additional guidance and resources. Tier 1 English learners in Tier 1: Receive ESL services from ESL professional. Are supported by differentiated instruction by the classroom teacher. Are supported by techniques that ensure comprehensible input by the classroom teacher. Are supported by teachers who have awareness of cultural factors that impact student progress. Are monitored by classroom teachers and the ESL teacher. Tier 2 English learners may be referred for Tier 2 services if: The student’s proficiency level is higher than a level 1. There is clear evidence that Tier 1 instruction has been implemented thoroughly with a focus on strategies to differentiate specifically for ELs. The student has not shown progress on the annual assessment of English language proficiency. The student fails to meet important academic benchmarks or behaviors and has not responded to Tier 1 core practices. The classroom teacher has discussed the concerns with the ESL teacher and they agree that language acquisition is not the main concern. Consideration must be given to the child’s proficiency level and the intervention tool. ESL teachers do not provide the Tier 2 intervention during the child’s ESL instruction. Tier 3 English learners may be referred for Tier 3 services if: The student’s proficiency level is higher than level 1. Tier 2 interventions have not been successful. The student has not shown progress on the annual assessment of English language proficiency. The classroom teacher has discussed the concerns with the ESL teacher and they agree that language acquisition is not the main concern. Consideration must be given to the child’s proficiency level and the intervention tool. ESL teachers do not provide the Tier 2 intervention during the child’s ESL instruction. Resources to Support ELs Title Performance Definitions Can-do Descriptors Developing a Culturally and Lingustically Responsive Approach to Response to Instruction & Handbook for Educators of Students Who Are English Language Learners With Suspected Disabilities The Special Education Referral and Decision-Making Process for English Language Learners: Child Study Team Meetings and Placement Conferences September 2013 Location http://www.wida.us/standards/eld. aspx (on the right under 2007 ELP Standards http://www.wida.us/standards/CA N_DOs/ http://www.wida.us/resources/ Content A tool that defines proficiency levels A tool to assist teachers in differentiating for ELs and for understanding the various performance/proficiency levels. A document that serves as a bridge between English language development standards and RtI. http://www.doe.virginia.gov/instru A collaborative project resulting in ction/esl/resources/handbook_educ a research-based tool to assist ators.pdf educators in determining if an EL has a disability. http://www.colorado.edu/educatio n/faculty/janetteklingner/Docs/Kli ngner%20&%20Harry_The%20Sp ecial%20Education%20Referral% 20and%20DecisionMaking%20Process.pdf At research-based article on the identification of English learners for exceptional education.