Appendix C: Oscilloscope.
advertisement

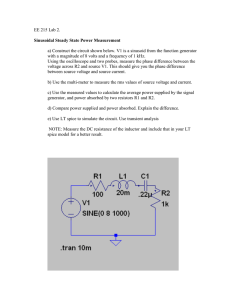
Appendix C: Oscilloscope. This appendix will instruct you on how to use the Oscilloscope (Hewlett Packard 54600B). You will learn how to use the oscilloscope to measure different signal parameters such as rms, peak, peak to peak and average or DC voltages and currents as well as some other parameters such as phase, frequency and period. For the instructions on how to measure phase see Measurements using cursors in section C-4. C-1 Setting things up. First of all we need to know some things that have to be set up before we start measuring any parameter. • Probe Attenuation factor: This factor changes the vertical scaling of the oscilloscope so that the measurement results reflect the actual voltage levels at the probe tip. To check or set up this factor do the following. 1. Press the 1 buttton or the 2 button depending on what channel you will be using, or repeat the steps for both channels if you will use both. 2. Press the Probe key as many times you need to match the probe you are using. • The ground: If you are using the function generator and the oscilloscope in the same circuit and you have a cable that comes from the function generator’s SYNC connector to the Oscilloscope’s external trigger connector, then both instruments share the ground. The above means that you can not connect the oscilloscope ground in a different node from the function generator’s ground node. In other words all of your voltage measurements are going to be related to that node. If you need to measure a voltage in a component which none of its pins are connected to ground then you have to measure the voltage in one pin and then the voltage in the other pin and subtract one measurement from the other. Also you can disconnect the cable mentioned before and do the measurement on the component itself since now you can have the freedom to place the oscilloscope ground wherever you want in the circuit. The last approach can give you problems due to trigger, to solve it read the trigger section in this appendix. • To display a signal automatically: The oscilloscope has an Autoscale feature that automatically sets up the oscilloscope to best display the input signal. Using Autoscale requires signals with a frequency greater than or equal to 50 Hz and a duty cicle greater than 1%. When you press the Autoscale key, the oscilloscope turns on and scales all channels that have signals applied, and it selects a time base range based on the trigger source. The trigger source selected is the highest numbered input that has a signal applied. (If a signal is connected to the external trigger input, then it is selected as the trigger source). • Trigger:As we have told above, the trigger source can be the channel 1, channel 2 or an external source. In most of our experiments, if not all of them, the trigger will be the external source. The trigger signal is used to tell the oscilloscope when to start showing the signals on the screen. So if you select different trigger source you will see in a different way the same signal. To change the trigger source do the following. 1. Press the Source button. 2. Select the trigger source you want to use by pressing the appropriate key. C-1 C-2 Measuring Voltages. Once we have the signal we want to measure displayed on the screen we can now do the measurements. • RMS voltage: Measuring the RMS voltage is very easy all you have to do is the following. 1. Press the voltage button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the V rms key. And the RMS value will be displayed on the screen. • Average or DC voltage: This value is also easy to measure all you have to do is: 1. Press the voltage button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the V avg key. And the avg value will be on screen. • Peak to Peak voltage: This is another easy to do measurement. 1. Press the voltage button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. press the V p-p key. • Other kind of measurements: You can perform different measurements using the cursors. To measure using the cursors do the following. 1. Press the Cursors button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the V1. This will make appear one cursor and a voltage reading. That reading is the voltage from the cursor to ground. You can move the cursor using the knob below the Cursors button. This knob will move the previously selected cursor only. 4. Press the V2. This will make appear another cursor and a voltage reading will be on screen related to the voltage from the new cursor to ground. An additional value will be on screen and that is the difference between cursors readouts. C-3 Measuring Currents. The only way this instrument can measure current is using the indirect way. That is using a resistor of known value measuring the voltage on that resistor and the use the Ohm’s Law to find the current value. So all the voltage measurement procedures apply to current also. C-2 C-4 Measuring time related parameters. The different time related parameters we can measure using the oscilloscope are the frequency, the period, Duty cycle, The Rise time and the Fall time as well as delay between signals therefore phase can also be measured. • Frequency: To measure frequency do the following. 1. Press the Time button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the Freq key. • Period: To measure the period do the following. 1. Press the Time button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the Period key. • Duty Cycle: To measure the Duty cycle proceed as follows. 1. Press the Time button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the Duty Cy key. • Rise time: to measure the Rise time proceed as follows. 1. Press the Time button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the Next Menu key. 4. Press the RiseTime key. • Fall time: to measure the Fall time proceed as follows. 1. Press the Time button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the Next Menu key. 4. Press the FallTime key. • Measurements using cursors: The use of cursors help us to measure the delay between signals or some other time related parameters. To perform measurements using cursors do the following. 1. Press the Cursors button. 2. Use the Source key to select whether the measurement is going to be made on the channel 1 or channel 2. 3. Press the T1 key. This will make appear one cursor and a time reading. That reading is the time between the zero seconds point and the cursor’s point. You can move the cursor using the Knob below the Cursors button. This Knob will move the previously selected cursor only. C-3 4. Press the T2 key. This will make appear another cursor, and a time reading will be on screen related to the time between the zero seconds point and the new cursor’s point. Two additional values will be on screen one of them will be the difference between time measurements and the other will be the inverse of that measurement. Note that if you select the source of measurement for T1 as channel 1 and the source for T2 as channel2 the difference readout can be the delay between the two signals, then that delay can be used in combination with the period value to find the phase value. The period will represent 360 degrees and all you have to do is find the equivalent in degrees for the delay value. C-4