Vertical and Horizontal Translations
advertisement

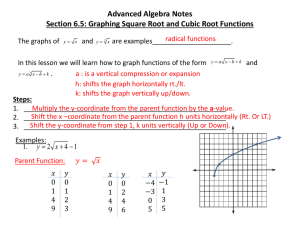
2­6: Vertical and Horizontal Translations Objectives: • To identify vertical and horizontal translations of • absolute value functions. • To accurately graph absolute value functions. Key Terms: Translation: the shifting of a graph vertically, horizontally, or both; horizontal shift = left/right shift vertical shift = up/down shift diagonal shift = a combination of horizontal and vertical shifts Parent function: the most basic form of any type of function (a line, a parabola, an absolute value...); it occurs without any translation Checking your graphs using the Graphing Calculator: [ Y = ] If any Plots are highlighted, you will need to turn them off. Go to [ 2nd ] [ Y = ] 4: Plots Off [ ENTER] [ MATH ] [ ] [ 1: ] Enter your equation. [ GRAPH ] If you cannot see the "V" [ ZOOM ] [ 6: ] [ ZOOM ] [ 5: ] Then ZOOM 5: to "square" the window. Vertical Shifts: shifts the parent function up "k" units shifts the parent function down "k" units Horizontal Shifts: shifts the parent function left "k" units shifts the parent function right "k" units Homework: pg. 95 #1­4, 9­11, 16­18, 21­25, 27­30, 40­42 Use graph paper.