Electrolysis - The Electrolytic Cell
advertisement

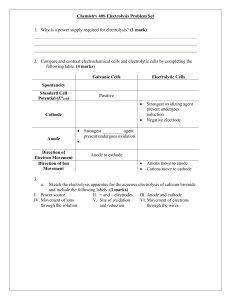
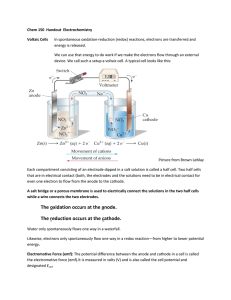
1 Electrolysis - The Electrolytic Cell Electrolysis: The decomposition of some substance by means of an electric current. Electrolytic Cell: · A cell that requires electrical energy to cause nonspontaneous oxidation-reduction reactions to occur. · it utilizes an external source of electrical energy. · it forces electrons to flow in the opposite direction by applying a voltage greater than the cell potential. · it converts electrical energy into chemical energy Voltaic Cell Spontaneous redox reaction releases energy Anode = oxidation = negative (negative charge supplied by reaction) Cathode = reduction = positive Ecell > 0 Note: · · · Electrolytic Cell Nonspontaneous redox reaction absorbs energy to drive it Anode = oxidation = positive Cathode = reduction = negative (negative charge supplied externally) Ecell < 0 A salt bridge can be used in the Electrolytic Cell Look for reversal of charge (anode is positive and cathode is negative) energy is supplied 2 Example: Consider the spontaneous electrochemical cell: Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) E o cell = + 1.100 V · If instead this cell was connected to an external electric source of voltage greater than 1.100 V then the reverse reaction could take place. · That is, electrons would be forced into the zinc electrode and removed from the copper electrode. · The net reaction taking place in the electrolytic cell is the reverse of that taking place in the electrochemical cell, and the resulting E ocell is negative. Cu2+(aq) + 2eZn2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) Cu (s) EoCu2+/Cu = - 0.337 V oxidized anode o E Zn2+/Zn = - 0.763 V reduced cathode _________________________________________________________ Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq) · Cu2+(aq) + Zn(s) E o cell = - 1.100 V Recall that the anode and the cathode are assigned based on the half reactions that are taking place at the electrode surface. LEOA (Loss of Electrons Oxidation Anode) – Oxidation always occurs at the anode. In an electrochemical cell electrons are freed at the anode, hence it is (-). In an electrolytic cell electrons are withdrawn from the anode, hence it is (+). GERC (Gain of Electrons Reduction Cathode) – Reduction always occurs at the cathode. In an electrochemical cell electrons are removed by the reduction half reaction, hence the cathode is (+). In an electrolytic cell electrons are forced into the cathode, hence it is (-). 3 Electrolysis of Water · Pure water cannot carry a current. · In order to decompose H2O via electrolysis, some electrolyte, like KNO3 or H2SO4, must be added in low concentrations. · To predict an electrolysis reaction, step 1 is to write out the redox half-reactions. 2 H2O(l) 4 H2O(l) + 4e- O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) + 4e 2H2(g) + 4 OH-(aq) Eo = -1.23 v oxidized anode Eo = -0.83 v reduced cathode ____________________________________________ 6 H2O(l) · 2 H2(g) + O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) + 4 OH-(aq) Eocell = -2.06 v The negative cell potential shows that the reaction is nonspontaneous. All electrolytic cells have negative cell potentials Overvoltage (Overpotential): the voltage in excess of the theoretical value required to produce a particular electrode reaction in electrolysis. 4 Electrolysis of Molten Salts · Ions of molten salts (like NaCl(l)) have some freedom of movement and hence can carry an electrical current. • To predict the electrolysis reaction, first write out the redox half-reactions. Cl2(g) + 2eNa+(l) + e- Na(l) 2 Cl-(l) oxidized anode reduced cathode • Next, balance for charge by multiplying the cathodic reaction by 2 • We do not use E • Add the two half reactions together to obtain the overall reaction. o values here since this is the electrolysis of molten ions, not aqueous! Cl2(g) + 2e2Na+(l) +2 e 2Na(l) 2 Cl-(l) ______________________ 2 Na+(l) + 2 Cl-(l) Recall that: • 2 Na+(l) + 2 Cl-(l) 2 Na(l) + Cl2(g) 2 NaCl(l) So the net reaction for the electrolysis of NaCl(l) is: 2 NaCl(l) 2 Na(l) + Cl2(g) 5 Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions · Unlike the electrolysis of molten salts, the electrolysis of aqueous solutions involves competing reactions at the cell electrodes. · There are two possible oxidation half-reactions and two possible reduction half-reactions. · To predict the products, examine the reduction potentials of all possible half-reactions and then determine the overall cell reaction that requires the lowest external current (minimum voltage). Rules: 1. 2. 3. 4. Need to be given an electrolyte (the one that is aqueous) Write the heading “anode possibilities” Write the anion and then its half-reaction (see reduction sheet). Then, write its voltage. Write H2O and its half-reaction and voltage value. H2O(l) ½ O2(g) + 2 H+(aq) + 2e- 5. 6. 7. Write the heading “cathode possibilities” Write the cation, its half-reaction and its voltage Write the cathode H2O half-reaction and its voltage. H2O(l) + 2e- 8. Eo = -1.23 v H2(g) +2 OH-(aq) Eo = -0.83 v Choose the more positive voltage value at each electrode. Example 1: Predict the half-reactions and determine the actual products from the electrolysis of: S2O82-(aq) + 2eCu2+(aq) + 2 e- Cu(s) 2 SO42-(aq) Anode possibilities: Eo = 0.34 V S2O82-(aq) + 2e- 2 SO42-(aq) H2O(l) Eo = -2.01 V oxidation ½ O2(g) + 2 H+(aq) + 2e- Cathode possibilities: Reduction anode cathode Eo = -2.01 V Eo = -1.23 V (more positive) Cu(s) Eo = 0.34 V (more positive) H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) Eo = -0.83 V Cu2+(aq) + 2 eH2O(l) + 2eThe products of this reaction: ½ O2(g) + 2 H+(aq) + 2eCu2+(aq) + 2 e- Cu(s) H2O(l) __________________________ Cu2+(aq) + H2O(l) Cu(s) + ½ O2(g) + 2 H+(aq) Eocell = -0.89 V 6 Example 2: Predict the products of the electrolysis of CuCl 2 Anode possibilities: (anion) Cl2 (g) + 2eH2O(l) ½ O2(g) + 2 H+(aq) + 2e2Cl-(aq) Cathode possibilities: (cation) Overall: Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s) H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) Eo = -1.36 V Eo = -1.23 V Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Eo = 0.34 V H2O(l) + 2e- Eo = -0.83 V Cu(s) Eo = 0.34 V H2O(l) ½ O2(g) + 2 H+(aq) + 2e- Eo = -1.23 V _______________________________________ Cu2+(aq) + H2O(l) Cu(s) +½ O2(g) + 2 H+(aq) Eocell = -0.89 V Example 3: Predict the products of the electrolysis of NaBr Anode possibilities: (anion) Br2 (aq) + 2eH2O(l) ½ O2(g) + 2 H+(aq) + 2e2Br-(aq) Cathode possibilities: (cation) Na(s) H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) Na+(aq) + 2eH2O(l) + 2eOverall: 2Br-(aq) Br2 (aq) + 2e- Eo = -1.07 V Eo = -1.23 V Eo = -2.71 V Eo = -0.83 V Eo = -1.07 V H2O(l) + 2e- H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) Eo = -0.83 V _______________________________________ 2Br-(aq) + H2O(l) Br2 (aq) + H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) Eocell = -1.90 V Applications of Electrolysis The development of the electric cell (battery) lead to the discovery of electrolysis since the electrical energy produced could be used to cause non-spontaneous reactions to occur. The development of the electrolytic cell lead to: 1. The discovery of several elements (Sir Humphrey Davy) 7 · Davy, in the early 1800s, passed the current from a voltaic pile through molten salts of several metals (Na, K, Mg, Sr, and Ba). The metals were deposited on metal strips attached by wires to the ends of the voltaic pile. 2. The development of electroplating (Micheal Faraday) · Electroplating is the process in which a metal is deposited (plated) onto the cathode of an electrolytic cell. · It’s used to protect the surface of the base metal or to make the object more attractive. 3. The purification of impure metals · Electrowinning is used to produce very pure sodium and other reactive metals from electrolysis of molten salts · Electrorefining is used to obtain ultra-pure silver, lead and copper from the electrolysis of impure solid metal 8 ELECTROLYSIS WORKSHEET #6 1. The electrolysis of molten calcium chloride produces calcium and chlorine. Write the halfreaction that takes place at the anode and the half-reaction that takes place at the cathode. Also, write the overall cell reaction for this process. 2. An electrolytic cell containing one half-cell consisting of a nickel electrode in a 1 mol/L nickel (III) chloride solution and the other half-cell consisting of a cadmium electrode in a 1 mol/L cadmium chloride solution is assembled. 3. (a) Sketch the cell and label the anode, the cathode, and the direction of electron flow. Be sure to include a salt bridge and a power supply in your sketch. (b) Find the cell potential. (c) Write the oxidation half-reaction, the reduction half-reaction and the overall cell reaction. d) Explain how the electrolytic cell works. What would be the minimum voltage to operate the following cell: Ag(s)|Ag+(aq) || Cu2+(aq)|Cu(s) 4. 5. 6. Predict whether the following reactions would be spontaneous or non-spontaneous. (a) Br2(aq) + 2 I-(aq) I2(aq) + 2Br (b) I2(aq) + 2Br (c) Cl2(aq) + 2 I-(aq) I2(aq) + 2Cl- (aq) (d) I2(aq) + 2Cl- (aq) Cl2(aq) + 2 I-(aq) - (aq) - (aq) Br2(aq) + 2 I-(aq) Which of the following reactions occurs spontaneously and which can only be brought about through electrolysis, assuming that all reactants and products are in their standard states? For those requiring electrolysis what is the minimum voltage required? (a) Zn(s) + Fe2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Fe(s) (b) 2 Fe2+(aq) + I2(s) 2 Fe3+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) (C) Cu(s) + Sn4+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + Sn2+(aq) Predict the products for the electrolysis of 1 mol/L (a) LiBr(aq) (b) NaI (aq) (c) CaI2(aq) (d) NiBr2(aq)