AC Simulation and Noise Contributions
advertisement

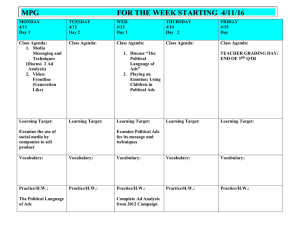
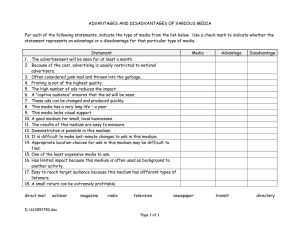
AC Simulation and Noise Contributions ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 1 AC Simulation ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 2 AC Simulation Controller ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 3 AC Noise calculations Nodes for noise are Wire/Pin Labels. Sort by name or by value: in the dataset. Blank gives you all contributors. ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 4 AC sources are for AC simulations • V_AC, P_AC, and I_AC are component names. • SRC3, PORT1, and SRC4 are instance names which you can change. • Vac = polar (1,0)V is the default value. The polar function can be removed (next slide). • Freq = freq is a global variable - you set the start & stop values in the simulation controller. • P sources are also ports (ok for S-parameter) • Num=1 is the port number. • I current sources can be used for other simulations to inject current. • Arrow in symbol shows the direction of current flow. ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 5 Setting AC source values POWER: The dbmtow function converts power in dbm to power in watts for the simulator. PHASE: The polar function specifies phase. By default, all sources are cosine waves. Use -90 for a sinewave. NOISE and Vdc: By default, noise is turned on for the P_AC source. Use Display tab/settings to make visible. Vdc 10 mV is an offset (superposition). Equations can also be used: P=1W, P=1+j*1W, P=complex(1,0), etc. ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 6 Summary of ADS equation types • VAR: pre-simulation Use for initializing sweep variables or other settings. VARs are available in the dataset if you select them in the schematic Output tab of the simulation controller. • MeasEqn: pre-simulation Use on schematic pre-simulation and it is available in the dataset after simulation. It uses node labels and functions. • Eqn: post-simulation - data display Use for calculations in the data display. Use node voltages, functions, and any dataset data. ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 7 Review of Data Display equation editor Insert button gives full path (dataset..) if not the default. Click here for DDS equations: Schematic MeasEqns appear in the dataset. Click Functions Help = on-line manuals: Functions (measurement expressions) are defined with examples… Invalid equations are red: Valid equations are black: ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 8 Printing ADS schematics and data Print… shows printer name, type (most HP Desk Jets & Laser Jets). Use Properties for colors, size, orientation, etc. Export JPG, BMP, GIF to Windows tools. ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 9 Stopping an ADS processes If your computer is locked up or if there is any other problem (Data Display), you can safely stop some processes: hpeesofde.exe - closes the ADS program (same as exit) hpeesofsim.exe - stops the simulation or in schematic: hpeesofdds.exe – ends the data display server UNIX users kill processes - PC users end processes PC task manager NT: ctrl-alt-delete In a UNIX window, use: ps -ef | tail and you can kill (xxx) a processes. ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 10 Useful Data Display features... • Copy/Paste: Ctrl C copies / Ctrl V pastes • ALSO for the Data Display: - Hot Keys & Predefined Equations HOT KEY and DDS command to your keyboard for efficiency and speed - similar to schematic Hot Keys! ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Document your plots! Slide 4 - 11 Lab 4: AC Simulations and Noise Contributions ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 12 Steps in the Design Process You are here: ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 • Design the RF sys behavioral model receiver • Test conversion gain, spectrum, etc. • Start amp_1900 design – subckt parasitics • Simulate amp DC conditions & bias network • Simulate amp AC response - verify gain • Test amp noise contributions • Simulate amp S-parameter response • Create a matching topology • Optimize the amp in & out matching networks • Filter design – lumped 200MHz LPF • Filter design – microstrip 1900 MHz BPF • Transient and Momentum filter analysis • Amp spectrum, delivered power, Zin - HB • Test amp comp, distortion, two-tone, TOI • CE basics for spectrum and baseband • CE for amp_1900 with GSM source • Replace amp and filters in rf_sys receiver • Test conversion gain, NF, swept LO power • Final CDMA system test CE with fancy DDS • Co-simulation of behavioral system Slide 4 - 13 Simulation setup with Noise Noise is turned on and the noise node defined. NOTE: By default, the AC controller sweeps the global variable freq using the settings shown and ignores any setting in the source. ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 14 Set up a Meas Eqn and Outputs... Generic Meas Eqn from any simulation palette: Use the Controller Output tab (works the same in all controllers) to specify which simulation data is output to the dataset. Here, Vcc Is eliminated from the dataset. NOTE: You can attach specific equations to specific simulation controllers, using the Display tab and checking the box for: ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 15 Operate on data: equations & functions Write an equation using the editor. List the Meas Eqn & DDS equation: Operate directly on listed or plotted data by typing in a function (dB): Edit and change to another plot type: ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 16 Plot phase and calculated group delay Plot the phase of Vin and Vout: Calculate group delay with an equation using Phase data. Also, control marker readout formats: ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 17 Variables and the what function…what? • Insert a list of Vout • Click on: Trace Options • Then click: Variable Info… The value of a dataset item, such as a node voltage, depends on its variables: Vout here is dependent on the ADS freq variable. Or, use the what function on any data and get the same information this will be useful later when the data becomes more dependent: Next, sweeping parameters… ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 18 Parameter Sweep: bias voltage AC simulation with a parameter sweep component to sweep a VAR: Vbias. Type in the freq for the marker! Explicit dataset path uses .. Understanding the data… ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 19 Understanding Lab Results: data Concept: data in dataset is a function of one or more variables, and all data is indexed beginning with index value 0. Sweep DC bias and AC frequency: Vout is a function of V_bias and freq: Vout [V_bias,freq] Index for freq: Index for V_bias = 0 if 2V is the first value. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 • Vout returns all data, for all index values 0 through N of each sweep • Vout[0,1] returns V_bias only at index 0, and freq only at index 1 • Vout[::,1] returns all values of V_bias, and freq at index 1 • Vout[0,::] returns V_bias at index 0, and all values of freq • Vout[0::2::6,::] returns V_bias at index values 0, 2, 4, 6 and all values of freq SYNTAX NOTE: Double colon :: is equivalent to “all values” like a wildcard. For example[a::b::c] a=start, b=increment, c=stop. More information in Data Display manual:Working with Multidimensional Data ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 20 Parameter Sweep of voltage For an AC simulation, use a parameter sweep component to sweep a VAR: Vbias. Type in the freq for the marker! Explicit dataset path uses .. Start the lab now! ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 21 ADS 2009 (version 1.0) Copyright Agilent Technologies 2009 Slide 4 - 22