EC332 Electronic Devices II DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS
advertisement

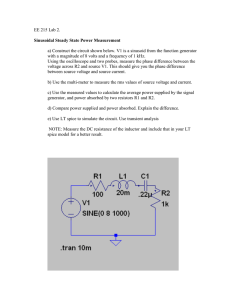
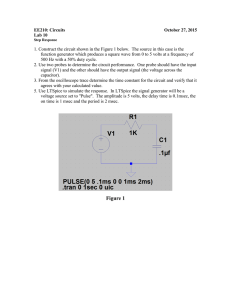
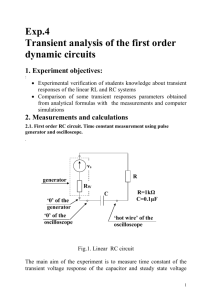
Arab Academy for Science & Technology & Maritime Transport College of Engineering and Technology Cairo Campus Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering EC332 Electronic Devices II Lab. Report Exp. No.: 1 Title : DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS Name: …………………………………………………………………………………………... ID No.: …………………………………………………………………………………………... Class: …………………………………………………………………………………………... Grade: LAB-1 : DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS EC332 Electronic Devices II 1.Objective: • Understanding the operating principle of diode clipping circuit • Understanding the waveform change of diode clipping circuits when the bias is applied. 2.Theory: Theory of Operation: As you know, diodes can be used as switches depending on the biasing type, reverse or forward. The clipping circuit also referred to as clipper, clips off some of the portions of the input signal and uses the clipped signal as the output signal. 3.1Circuit Diagram 1: Figure 1. 3.1.1Equipment: …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 1 LAB-1 : DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS EC332 Electronic Devices II 3.1.2 Procedure: 1- Configure the function generator to output a sinusoidal signal with a frequency of 1K Hz and peak amplitude of 5V with a 0 V DC offset. 2- Connect the output of the function generator to the input of the oscilloscope and set the controls on the oscilloscope: select channel 1. 3- Build the circuit shown in circuit figure 1 on your breadboard. 4- The voltage source will be your function generator, set the function generator with the input signal that you obtained from 1. 5- Use the oscilloscope to view the voltage across VD on channel 2 and the input voltage on channel 1. 6- Set the horizontal scale to show three periods. Then plot them in Graph 1. 3.1.3 Measurements and Results: Graph 1 2 LAB-1 : DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS EC332 Electronic Devices II 4.1Circuit Diagram 2: Figure 2. 4.1.1Equipment: …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4.1.2 Procedure: 1- Configure the function generator to output a sinusoidal signal with a frequency of 1K Hz and peak amplitude of 5V with a 0 V DC offset. 2- Connect the output of the function generator to the input of the oscilloscope and set the controls on the oscilloscope: select channel 1. 3- Build the circuit shown in circuit figure 2 on your breadboard. 4- The voltage source will be your function generator, set the function generator with the input signal that you obtained from 1. 5- Use the oscilloscope to view the voltage across VD on channel 2 and the input voltage on channel 1. 6- Set the horizontal scale to show three periods. Then plot them in Graph 2. 4.1.3 Measurements and Results: Graph 2 3 LAB-1 : DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS EC332 Electronic Devices II 5.1Circuit Diagram 3: Figure 3. 5.1.1Equipment: …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 5.1.2 Procedure: 1- Configure the function generator to output a sinusoidal signal with a frequency of 3K Hz and peak amplitude of 6V with a 0 V DC offset. 2- Connect the output of the function generator to the input of the oscilloscope and set the controls on the oscilloscope: select channel 1. 3- Build the circuit shown in circuit figure 3 on your breadboard. 4- The voltage source will be your function generator, set the function generator with the input signal that you obtained from 1. 5- Use the oscilloscope to view the voltage across VD on channel 2 and the input voltage on channel 1. 6- Set the horizontal scale to show three periods. Then plot them in Graph 3. 5.1.3 Measurements and Results: Graph 3 4 LAB-1 : DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS EC332 Electronic Devices II 6. OrCAD Results: 5 LAB-1 : DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS EC332 Electronic Devices II 7. Conclusion and comments: (Justify and compare between theoretical, empirical and Spice simulation results) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6