Lab 2 Instruction Manual
advertisement

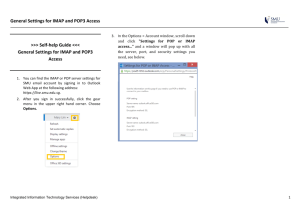
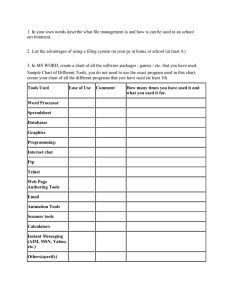
Institute of Telecommunications Faculty of Electronics and Information Technology Warsaw University of Technology, March 2015 EINTE LAB EXERCISES LAB EXERCISE #2 – EMAIL SERVICE PREPARATIONS REMOTE SESSION Before starting the exercise, please familiarize yourself with the documents related to remote access to lab facilities (Remote Access User Guide) and lab resource reservation system (Resource Reservation User Guide). Before connecting to the remote virtual machine please make sure that Remote Desktop is configured such that it is possible to transfer files from the virtual machine to a local drive (appropriate local resources are attached in the connection options of the remote desktop session). It is necessary to transfer files (eg. Wireshark application logs) required to be attached to the final report. Do not manually change anything in the network configuration of the host that has been assigned to you to execute the exercise as it may lead to disturbances in lab infrastructure setup. Do not attempt this lab exercise with a “trial-and-error” approach – it will not work! Prepare by reading and understanding the course materials and RFCs listed in the next section. EMAIL BASICS You should familiarize yourself with the protocols used to implement the Internet email service: POP3 ( http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1939 ) IMAP ( http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3501 ) SMTP ( http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2821 ). During the exercise you will need a basic knowledge of the above protocols. The RFCs above contain also useful information to answer questions required in the report. However, there is no need to read all these documents in full. The following example of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol session can be helpful in executing the exercise. Institute of Telecommunications Faculty of Electronics and Information Technology Warsaw University of Technology, March 2015 NETSH Netsh command allows viewing and modifying a network configuration of the host. This command is invoked from the command line in Windows. Please review (briefly) the documentation for the command available at: http://www.microsoft.com/resources/documentation/windows/xp/all/proddocs/enus/netsh.mspx?mfr=true In particular, pay attention to the commands used to configure the TCP/IP protocols. TELNET Telnet client application is available from the Windows command line. It will be used for sending and receiving the email access protocol messages to the mail server. You should become familiar with the capabilities of the telnet application. To do this, run the application from the Windows command line with the /? parameter. STEP 1: SET THE DNS SERVER ADDRESS Using netsh add a new DNS server and set it as the primary server. The DNS server IP address is 194.29.169.68. To do this, first open the Windows command line terminal (on Windows 7 you need to run it with elevated permissions – “run as administrator”). Start by checking the network name with: netsh interface show interface It will show the name under the "Interface Name" column. If the output is empty, you can always check the interface name in Control Panel, under “Network Connections” (“Network and Sharing Center” in Windows 7). Then you can change the primary dns (index=1). Assuming that your network name is “Local Area Connection”, the netsh command should look like: in Win7: netsh interface ipv4 add dnsserver "Local Area Connection" address=194.29.169.68 index=1 in WinXP: netsh interface ip add dns “"Local Area Connection" 194.29.169.68 index=1 Institute of Telecommunications Faculty of Electronics and Information Technology Warsaw University of Technology, March 2015 Note: do not use the Windows GUI to change anything in the network configuration of the host! Note: When performing the next tasks, please pay attention to the context of communication with the above address using the DNS protocol. The report should describe the course and purpose of this communication; please also attach the relevant WireShark files to the report. STEP 2: SEND THE FIRST MESSA GE Based on the SMTP session example, use telnet to send the first message. To compose a message, use the following parameters: From: <hostname>@ ztit.lab.org (replace <hostname> with the corresponding value obtained by executing ipconfig / all command) To: lab3@ztit.lab.org Subject: LAB3 Body: login: <username> (where <username> is the username used to log to ztit-gateway). Please note the space after “:” sign and be aware of uppercase and lowercase letters. Next, use telnet to connect to ztit.lab.org server. Communication should use the standard SMTP port number. The report should contain the information obtained from the console when sending messages and the relevant WireShark logs. STEP 3: RETRIEVE AN E-MAIL Using information from the RFCs mentioned at the beginning of the document and information available on the Internet, retrieve email messages from the mailbox. Two messages with the following subjects will be available for retrieval: "LAB3-IMAP" and "LAB3-POP". The first message should be retrieved using IMAP, the second using POP3, for both operations you should use telnet application. The mailbox is located at ztit.lab.org; to connect via POP3 and IMAP, use standard port numbers; the user name is the same as the previously used host name; password is the same as the password for the host used during the exercise. Note: message retrieval is only possible when the message from step 2 has been sent correctly. STEP 4: VERIFICATION Using telnet send a message similar as in step 2, but with different Subject and Body. The new Subject is ANSWER (in capital letters), the new text of the message should look as follows: login: <username> answer: <POP3><IMAP> Please note the space after “:” and be aware of uppercase and lowercase letters. Username is the same as in step 2, <POP> and <IMAP> should be replaced by the content of the respective messages retrieved in step 3, concatenated without any space. If a message is properly constructed and sent in the correct way, the new message with the Subject: RESULT will be sent to the previously used mailbox as a confirmation. You should retrieve this message using the protocol of choice. The report should contain the content of a confirmation message, together with the relevant WireShark logs. Institute of Telecommunications Faculty of Electronics and Information Technology Warsaw University of Technology, March 2015 THE REPORT You need to prepare a document (in PDF format) containing the description of the course of the exercise, observations and conclusions on the types of messages in the network (i.e. explain what types of messages, when and in what order were sent). You should attach the relevant WireShark logs (in .pcap format) to the report as well as any files mentioned earlier as required. The report should also contain the short answers to the following questions. 1. How data is transmitted over telnet protocol and what is the danger associated with it? 2. What is the most popular usage of the telnet protocol? What protocol is used as a secure alternative to telnet? 3. What is the difference between POP3 and IMAP? 4. What is the difference between POP3 and POP3S, IMAP and IMAPS?