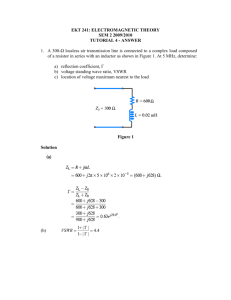
ω π ω π ω ω γ α β λ β β
advertisement
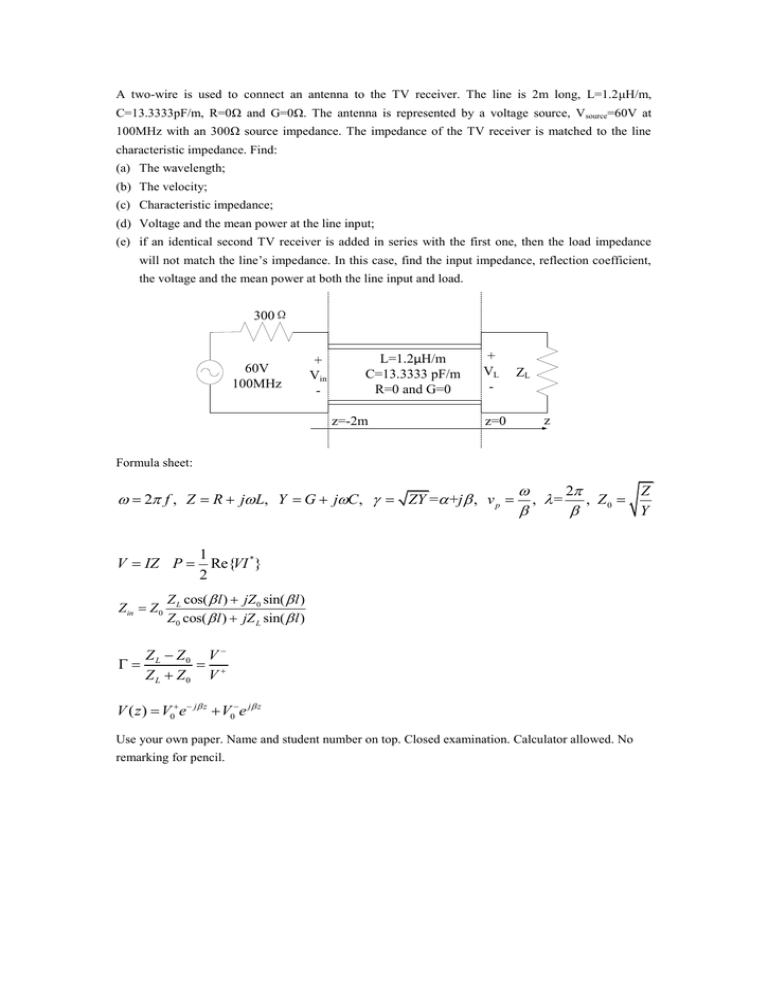
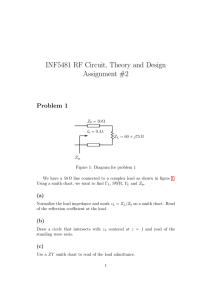
A two-wire is used to connect an antenna to the TV receiver. The line is 2m long, L=1.2μH/m,
C=13.3333pF/m, R=0Ω and G=0Ω. The antenna is represented by a voltage source, Vsource=60V at
100MHz with an 300Ω source impedance. The impedance of the TV receiver is matched to the line
characteristic impedance. Find:
(a) The wavelength;
(b) The velocity;
(c) Characteristic impedance;
(d) Voltage and the mean power at the line input;
(e) if an identical second TV receiver is added in series with the first one, then the load impedance
will not match the line’s impedance. In this case, find the input impedance, reflection coefficient,
the voltage and the mean power at both the line input and load.
300Ω
60V
100MHz
+
Vin
-
L=1.2μH/m
C=13.3333 pF/m
R=0 and G=0
z=-2m
+
VL
z=0
ZL
z
Formula sheet:
2 f , Z R jL, Y G jC , ZY = +j , v p
V IZ P
Zin Z 0
2
Z
, =
, Z0
Y
1
Re{VI *}
2
Z L cos( l ) jZ 0 sin( l )
Z 0 cos( l ) jZ L sin( l )
Z L Z0 V
Z L Z0 V
V ( z ) V0e j z V0e j z
Use your own paper. Name and student number on top. Closed examination. Calculator allowed. No
remarking for pencil.
Solutions (7.5’ in total):
(a)
2 f 6.2832 109 rad/s
Z R j L j 7.5398 103 /m
Y G jC j 0.008378S/m
ZY 0 j15.0796 1/m= +j
2.5133 rad/m
=
2
(b)
vp
(c)
Z0
2.5m
0.5'
0.5'
2.5 108 m/s
Z
300
Y
0.5'
0.5'
(d) As load impedance is matched to the line’s characteristic impedance,
Zin Z L 300 , Vin
I in
Vin
0.1A
Zin
Pin
Zin
Vs 30V
Zin Z g
1
Re{VI *} 1.5W
2
Z L Z0 300
0.5'
0.5'
(e) Now
Z L 600
Zin Z 0
Z L cos( l ) jZ 0 sin( l )
161.57 j 71.218 176.5690.4152 176.56923.7875o
Z 0 cos( l ) jZ L sin( l )
0.5’
Z L Z0 1
Z L Z0 3
0.5'
Vin
Zin
Vs 21.9094 j5.8772 22.68400.2621 22.684015.0162V 0.5'
Zin Z g
I in
Vin
0.1270 j 0.0196 0.1285 0.1531 0.1285 8.7714A
Zin
Pin
1
Re{VI *} 1.333W
2
0.5'
Vin V ( z 2m) V0e j z V0e j z V0e j l V0e j l V0 (e j l e j l )
V0
(e
j l
Vin
9.2695 j 28.5321 301.2567 3072V
e j l )
4
VL V ( z 0) V0 V0 V0 (1 ) V0
3
4
VL V0 12.3593 j 38.0428 401.2567 4072V 1'
3
IL
VL
0.0206 j0.0634 0.06671.2567 0.066772A
ZL
PL
1
Re{VI *} 1.333W
2
0.5'
(Or the transmission line is lossless, so
All calculations are correct
All units are correct
0.5’
0.5’
PL Pin )