Permissible Rotational Speed
advertisement

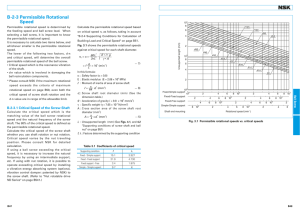
510E Permissible Rotational Speed [Dangerous Speed of the Screw Shaft] When the rotational speed reaches a high magnitude, the Ball Screw may resonate and eventually become unable to operate due to the screw shaft’s natural frequency. Therefore, it is necessary to select a model so that it is used below the resonance point (dangerous speed). Fig.13 on A15-34 shows the relationship between the screw shaft diameter and a dangerous speed. If determining a dangerous speed by calculation, it can be obtained from the equation (7) below. Note that in this equation, a safety factor of 0.8 is multiplied to the result. 60 • λ1 2 2π •ℓb 2 N1 = N1 ℓb E I I= E 10 • I γ•A 3 0.8 = λ2 • : Permissible rotational speed determined by dangerous speed (min-1) : Distance between two mounting surfaces (mm) : Young’s modulus (2.06×105 N/mm2) : Minimum geometrical moment of inertia of the shaft (mm4) π d14 d1: screw-shaft thread minor diameter (mm) 64 A A= d1 7 • 10 2 ℓb : Density (specific gravity) (7.85×10-6kg/mm3) : Screw shaft cross-sectional area (mm2) π d12 4 1, 2 : Factor according to the mounting method Fixed - free 1=1.875 2=3.4 Supported - supported 1=3.142 2=9.7 Fixed - supported 1=3.927 2=15.1 Fixed - fixed 2=21.9 1=4.73 A15-32 ………(7) 510E Point of Selection Permissible Rotational Speed [DN Value] The permissible rotational speed of the Ball Screw must be obtained from the dangerous speed of the screw shaft and the DN value. The permissible rotational speed determined by the DN value is obtained using the equations (8) to (16) below. Model SBK (SBK3636, SBK4040 and SBK5050) N2 = 210000 ………(8-1) D Model SBK (For cases other than the above model numbers and small size model SBK*) N2 = 160000 ………(8-2) D Models SBN, HBN and SBKH 130000 N2 = D Model WHF N2 = 120000 ………(10) D N2 = 70000 D Large Lead Caged Ball Precision Standard lead Super Lead FullComplement Ball Model WGF Large Lead Models BLW, BLK, DIR and BLR Standard lead Models BIF, DIK, BNFN, DKN, BNF, BNT, DK, MDK, MBF, BNK, BNS and NS Standard lead Models EBA, EBB, EBC, EPA, EPB and EPC 100000 N2 = D Model WHF N2 = 100000 ………(13) D N2 = 70000 D Super Lead Rolled Models WTF and CNF FullComplement Ball Large Lead Models BLK and BLR Model BTK-V 100000 N2 = D Models JPF, BNT and MTF N2 = Standard lead 50000 D ………(11) ………(12) ………(14) ………(15) ………(16) : Permissible rotational speed determined by the DN value (min-1(rpm)) : Ball center-to-center diameter (indicated in the specification tables of the respective model number) Of the permissible rotational speed determined by dangerous speed (N1) and the permissible rotational speed determined by DN value (N2), the lower rotational speed is regarded as the permissible rotational speed. For small size SBK (SBK1520 to 3232) and SDA, the permissible rotational speed (N2) is the maximum permissible rotational speed shown in the dimensional tables.(See dimensional tables on pages A15-74 to A15-75, and A15-78 to A15-79) If the service rotational speed exceeds N2, contact THK. N2 D A15-33 Ball Screw Full-Complement Ball (DIN Standard Compliant) ………(9) 510E 10000 8000 Distance between two mounting surfaces (mm) 6000 4000 2000 1000 φ 100 φ 80 φ 70 φ 63 φ 55 φ 50 φ 45 φ 40 φ 36 φ 32 φ 30 φ 28 φ 25 φ 20 φ 18 φ 16 φ 15 φ 14 φ 12 φ 10 φ8 φ6 800 600 400 200 Fixed - free Fixed - supported 4 6 2 Fixed - fixed 4 8 102 2 4 6 6 8 103 4 8 103 6 2 2 8 103 4 4 6 Mounting method Rotational speed (min-1) Fig.13 Permissible Rotational Speed Diagram A15-34 2 6 8 104 8 104 2