downloaded here - Association of Clinical Research Professionals
advertisement
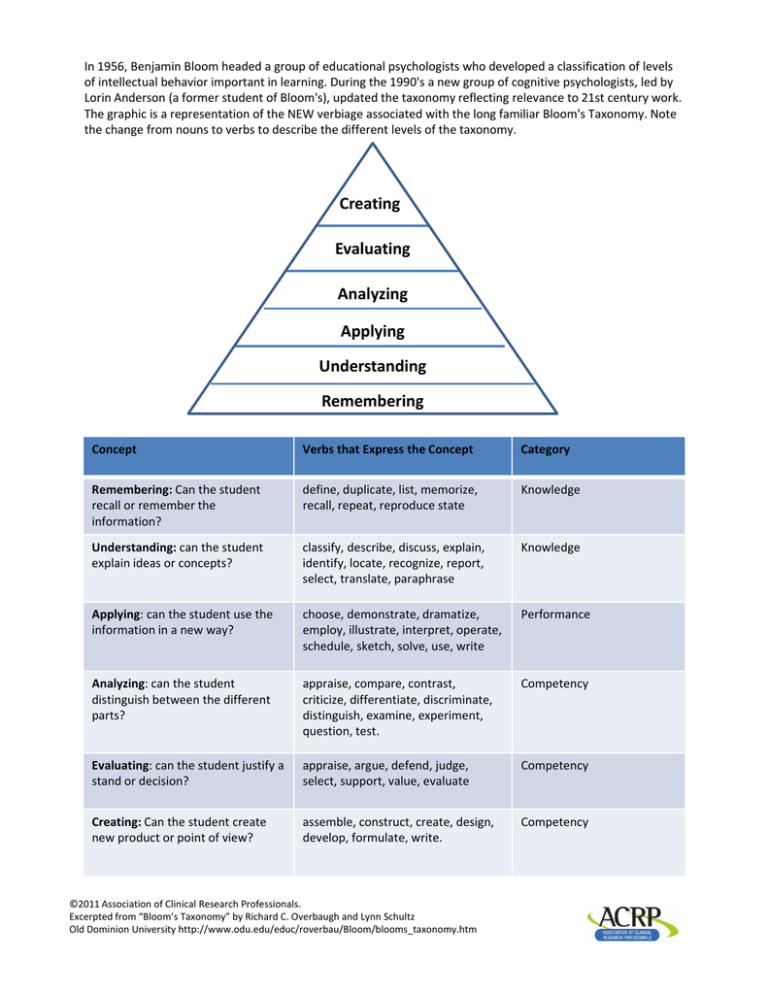
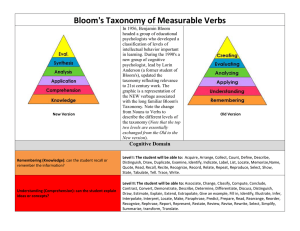
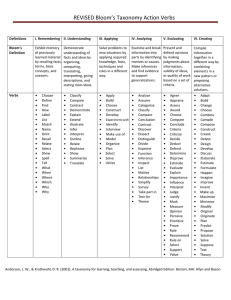
In 1956, Benjamin Bloom headed a group of educational psychologists who developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior important in learning. During the 1990's a new group of cognitive psychologists, led by Lorin Anderson (a former student of Bloom's), updated the taxonomy reflecting relevance to 21st century work. The graphic is a representation of the NEW verbiage associated with the long familiar Bloom's Taxonomy. Note the change from nouns to verbs to describe the different levels of the taxonomy. Creating Evaluating Analyzing Applying Understanding Remembering Concept Verbs that Express the Concept Category Remembering: Can the student recall or remember the information? define, duplicate, list, memorize, recall, repeat, reproduce state Knowledge Understanding: can the student explain ideas or concepts? classify, describe, discuss, explain, identify, locate, recognize, report, select, translate, paraphrase Knowledge Applying: can the student use the information in a new way? choose, demonstrate, dramatize, employ, illustrate, interpret, operate, schedule, sketch, solve, use, write Performance Analyzing: can the student distinguish between the different parts? appraise, compare, contrast, criticize, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, examine, experiment, question, test. Competency Evaluating: can the student justify a stand or decision? appraise, argue, defend, judge, select, support, value, evaluate Competency Creating: Can the student create new product or point of view? d t i t f i ? assemble, construct, create, design, d l develop, formulate, write. f l t it Competency ©2011 Association of Clinical Research Professionals. Excerpted from “Bloom’s Taxonomy” by Richard C. Overbaugh and Lynn Schultz Old Dominion University http://www.odu.edu/educ/roverbau/Bloom/blooms_taxonomy.htm Potential List of Verbs for Formulating Learning Objectives: The following verbs have been found to be effective in formulating learning objectives: Those that communicate knowledge: Information cite count define describe draw identify indicate list name point quote read recite recognize record relate repeat select state summarize tabulate tell trace update write Comprehension assess associate classify compare compute contrast demonstrate describe differentiate discuss distinguish estimate explain express extrapolate interpolate interpret locate predicts report restate review translate Application apply calculate choose complete demonstrate develop employ examine illustrate interpolate interpret locate match operate order practice predict prescribe relate report restate review schedule select sketch solve translate treat use utilize Analysis analyze appraise contract contrast criticize debate deduce detect diagram differentiate distinguish experiment infer inspect inventory measure question separate summarize Synthesis arrange assemble collect combine compose construct create design detect document formulate generalize integrate manage organize plan prepare prescribe produce propose specify validate Evaluation appraise assess choose compare critique decide determine estimate evaluate grade judge measure rank rate recommend revise score select test Those that impart skills: demonstrate diagnose diagram empathize hold integrate internalize listen massage measure operate palpate pass percuss project record visualize write plan realize reflect revise transfer Those that convey attitudes: acquire consider exemplify modify These verbs are better avoided: Those that are often used but open to many interpretations: appreciate believe have faith in know learn understand