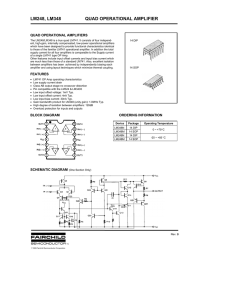
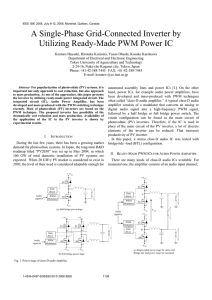
[1] For the Multistage amplifier shown in Fig.1, RL = 250 Ω, RSig = 3
advertisement
![[1] For the Multistage amplifier shown in Fig.1, RL = 250 Ω, RSig = 3](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018111916_1-f6a12ba465c3ae339f41af78ec6e65c7-768x994.png)
Mansoura University Faculty of Engineering Communication Engineering Department Second Year Communication Microelectronic Circuits Sheet (8) [1] For the Multistage amplifier shown in Fig.1, RL = 250 Ω, RSig = 3 KΩ. - The BJT Stage has β =100, R1 = 820 KΩ, R2 = 100 KΩ, RE = 2 KΩ, RC = 18 KΩ, VCC = 15 V. - The FET Stage has VTN = 1 V, Kn = 200 µA/V2, R3 = 910 KΩ, R4 = 1.2 MΩ, RS = 3 KΩ, VDD = 15 V. (a) Specify the configuration of each transistor. (b) What is the main function of C2, and C3 capacitors? (c) Determine the overall voltage gain vo/vsig. (d) Determine the input Resistance Rin. (e) Determine the current gain io/ii. (f) Determine the output resistance Rout. (g) Determine the overall power gain. [2] The BJTs in the Darlington follower of Fig.2 have β = 100. If the follower is fed with a source having a100 kΩ resistance and is loaded with 1 kΩ, find the following input resistance and the output resistance (excluding the load). Also find the overall voltage gain, both open-circuited and with load. [3] The circuit shown in Fig.3 consists of two stages: Stage 1: CE amplifier with Vcc = 12 V, Rc = 1.0 kΩ and re = 5 Ω. Stage 2: Darlington emitter follower [CC] amplifier with voltage divider bias, given R1 = 10 kΩ, R2 = 22 kΩ, RE = 22 Ω, RL = 8 Ω, Vcc = 12 V and β1= β2 = 100. Determine the following: (a) The voltage gain of the Darlington emitter-follower. (b) The voltage gain of the CE stage. (b) The overall voltage gain of the amplifier. (c) Suppose the CE stage is connected directly to the speaker load, Find its voltage gain and compare the result with b showing the effect of Darlington stage. Page 1 Mansoura University Faculty of Engineering Communication Engineering Department Second Year Communication Microelectronic Circuits Sheet (8) Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Page 2

![[1] For the emitter follower (Common collector) in Fig.1, the signal](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018848159_1-aa5fa5ac259be0a4d4f84cd0bee4f687-300x300.png)