Document
advertisement
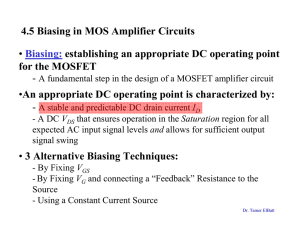
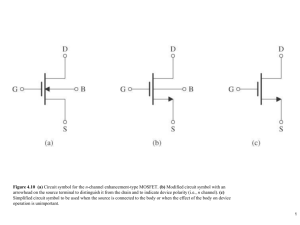
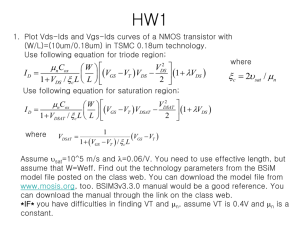
4.2 Current-Voltage Characteristics • In this section, we focus on the MOSFET Characteristics at DC or low frequencies (Static Characteristics) • High-frequency characteristics and high switching speeds are covered in section 4.8 in Sedra (Out of the Scope of this course) Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 1 Circuit Symbol for npn enhancement-type MOSFET (aka n-channel MOSFET) • Spacing between two vertical lines indicates that the Gate is insulated from the Body • MOSFET is a symmetric device, however, its useful to designate one terminal as Source (S) and the other terminal as Drain (D) Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 2 The Current-Voltage Characteristics Family of curves, each measured at constant vGS 2 3 1 • From the curves, there are 3 distinct regions of operation: 1. Cutoff Region 2. Triode (Linear) Region 3. Saturation Region Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 3 The Triode (Linear) Region • Characterized by: - vGS ≥ Vt - vDS < vGS – Vt (induce a channel) (keep the channel continuous) • As we derived last time, the iD-vDS characteristics in the Triode region is given by: W iD = k L ' n 1 2 ( ) v V v v − − GS t DS DS 2 where kn’ = µn Cox • For Small vDS: the iD-vDS relationship near the origin can be approximated by : iD ≈ k’n W/L (vGS - Vt) vDS Linear resistor rDS Dr. Tamer ElBatt The Saturation Region • Characterized by: - vGS ≥ Vt - vDS ≥ vGS – Vt (induce a channel) (pinched-off channel) • The iD-vDS characteristics in the Saturation region is obtained when vDS = vGS – Vt which yields: [ 1 'W 2 iD = k n (vGS − Vt ) 2 L ] In saturation, iD becomes independent of vDS. It depends only on vGS Dr. Tamer ElBatt iD-vGS characteristic for an ,MOS transistor in Saturation iD = 0.5 k’n W/L (vGS - Vt)2, Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith vGS > Vt Dr. Tamer ElBatt 6 Large-signal equivalent circuit model of an ,MOS Transistor in Saturation The saturated MOSFET behaves as an Ideal VoltageControlled Current Source (controlled by vGS) Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 7 Terminal Voltages and Operation Regions for ,MOS Transistors Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 8 Channel Length Modulation (in Saturation Region) • In practice, increasing vDS beyond vDSsat does affect the channel • As vDS is increased, the channel pinch-off point is moved slightly, away from the Drain, toward the Source • The depletion region between the end of the channel and the drain region widens as (vDS - vDSsat) increases and, hence, the channel length reduces from L to L-"L (a phenomenon known as Channel Length Modulation) Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 9 Channel Length Modulation cont. 1 'W 2 iD = k n (vGS − Vt ) (1 + λvDS ) 2 L where λ is a process technology parameter Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 10 Channel Length Modulation cont. • The Output Resistance r0 is given by, ' n k W 2 −1 (vGS − Vt ) ] ro = [λ 2 L Figure 4.17 Large-signal equivalent circuit model of the n-channel MOSFET in saturation, incorporating the output resistance ro. The output resistance models the linear dependence of iD on vDS and is given by Eq. (4.22). Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 11 Characteristics of the p-Channel MOSFET Figure 4.18 (a) Circuit symbol for the p-channel enhancement-type MOSFET. (b) Modified symbol with an arrowhead on the source lead. (c) Simplified circuit symbol for the case where the source is connected to the body. (d) The MOSFET with voltages applied and the directions of current flow indicated. Note that vGS and vDS are negative and iD flows out of the drain terminal. Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 12 Terminal Voltages and Operation Regions for PMOS Transistors Figure 4.19 The relative levels of the terminal voltages of the enhancement-type PMOS transistor for operation in the triode region and in the saturation region. Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Dr. Tamer ElBatt 13