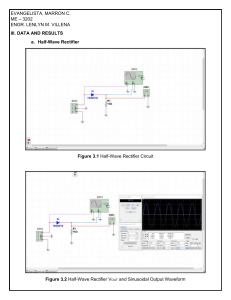
EXPERIMENT - 7 AIM: To assemble variety of clipper and clamper circuits on the breadboard using tinkercad THEORY: Clipper and clamping circuits are applications of diode as a switching device. Input to these circuits must be of alternating nature with different shapes like sinusoidal, square, triangular etc. Clippers circuit clips off a particular portion of the input signal without distorting the remaining part of the input waveform. It increases the average value of the input signal by clipping (removing) a particular portion of the wave. Often DC source is also used to change the average level. A clipping circuit requires at least two fundamental components, a diode and a resistor. A dc battery, however, is also used in biased clippers. The output waveform can be clipped at different levels simply by interchanging the position of the various elements and changing the magnitude of the dc battery. Generally, ideal diodes are considered and the complete analysis can be based on non-ideal diodes with specific V-I characteristic. Clippers can be series or parallel type, based on the position of diode w.r.t. load. Further these are classified as positive and negative clippers depending on the portion of half cycle it clips off. The clamping circuit clamps a signal to different D.C. Levels. The circuit must have a capacitor a diode and a resistive element, and an independent DC supply to introduce an additional shift. The magnitude of R&C must be chosen that the time constant t= RC is large enough to ensure that the voltage across the capacitor does not discharge significantly during the interval the diode is non-conducting. Clampers circuits can be classified as positive and negative clampers. Those who shift positive part of waveform are positive clampers, else negative clampers. APPARATUS/COMPONENTS REQUIRED: Bread Board Diode (Si ) - IN001 Resistance - 1K Capacitor - 1uF Power supply - 0 – 10V DC Connectors - 06 CRO and Function Generator CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: Positive Clipper Negative Clipper Dual Clipper PROCEDURE: (A) CLIPPER CIRCUIT Make connections as shown in the figures for clipper circuits on breadboard. Apply an input signal of 1KHz and 20 V, using function generator & check the input on CRO. Connect CRO probes to output and observe the output waveforms. (B) CLAMPER CIRCUIT Make connections as shown in the figures for Clamper circuits on the bread board. A pply on input signal of 1KHz & 20V using function generator & check the input on CRO. Plot the output waveform for each circuit. Measure the voltage across capacitor & observe the output waveform on CRO. Vary the input and observe the output on CRO. (I) OBSERVATION TABLE: Positive Clipper: S. No. 1 2 3 4 5 Negative Clipper: S. No. 1 2 3 4 5 Input Waveform Vpp (V) Freq. (Hz) 10 1000 15 1000 20 1000 25 1000 30 1000 Output Waveform Vpp (V) 5 7.5 10 12.5 15 Input Waveform Vpp (V) Freq. (Hz) 10 1000 15 1000 20 1000 25 1000 30 1000 Output Waveform Vpp (V) 5 7.5 10 12.5 15 Dual Clipper: S. No. 1 2 3 4 5 Input Waveform Vpp (V) Freq. (Hz) 10 1000 15 1000 20 1000 25 1000 30 1000 Output Waveform Vpp (V) 6 8.5 12 13.5 16 PRECAUTIONARY MEASURE TO BE TAKEN: 1. 2. 3. 4. Before switch ON the power supply, make sure connections are proper: No loose connections Do not rotate the knobs of course and fine in power supply frequently. Handle the electronic devices and equipments delicately