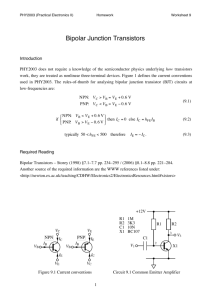
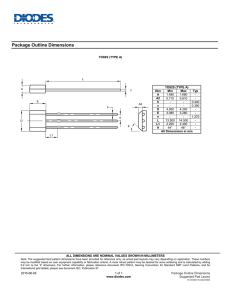
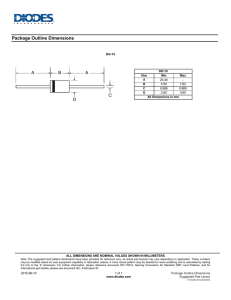
Chapter 5.1 - Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes
advertisement

Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes In Brief . . . New in this revision is Motorola’s GreenLine portfolio of devices. They feature energy–conserving traits superior to those of our existing line of standard parts for the same usage. GreenLine devices can actually help reduce the power demands of your products. Also new are the Small Signal Multi–integrated devices. These are intended to save board space by reduced part count and functionality. Four to six devices have been integrated into one small package. Also, this section highlights semiconductors that are the most popular and have a history of high usage for the most applications. It covers a wide range of Small Signal plastic and metal–can semiconductors. A large selection of encapsulated plastic transistors, FETs and diodes are available for surface mount and insertion assembly technology. Plastic packages include TO–92 (TO–226AA), 1 Watt TO–92 (TO–226AE), SOT–23, SC–59, SC–70/SOT–323 and SOT–223. Plastic multiples are available in 14–pin and 16–pin dual in–line packages for insertion applications: SO–8, SO–14, and SO–16 for surface mount applications. Motorola Master Selection Guide Page Bipolar Transistors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–2 Plastic–Encapsulated Transistors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–2 Plastic–Encapsulated Multiple Transistors . . . . . . . 5.1–8 Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–10 Metal–Can Transistors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–18 Field–Effect Transistors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–20 JFETs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–20 MOSFETs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–22 Surface Mount FETs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–23 Tuning and Switching Diodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–25 Tuning Diodes — Abrupt Junction . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–25 Tuning Diodes — Hyper–Abrupt Junction . . . . . . 5.1–29 Schottky Diodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–33 Switching Diodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–35 Multiple Switching Diodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–39 GreenLine Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–41 Small Signal Multi–integrated Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1–43 5.1–1 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Bipolar Transistors Plastic–Encapsulated Transistors 1 23 CASE 29–05 TO–226AE 1–WATT (TO–92) Motorola’s Small Signal TO–226 plastic transistors encompass hundreds of devices with a wide variety of characteristics for general–purpose, amplifier and switching applications. The popular high–volume package combines proven reliability, performance, economy and convenience to provide the perfect solution for industrial and consumer design problems. All devices are laser marked for ease of identification and shipped in antistatic containers, as part of Motorola’s ongoing practice of maintaining the highest standards of quality and reliability. 1 23 CASE 29–04 TO–226AA (TO–92) Table 1. Plastic–Encapsulated General–Purpose Transistors These general–purpose transistors are designed for small–signal amplification from dc to low ratio frequencies. They are also useful as oscillators and general–purpose switches. Complementary devices shown where available (Tables 1–4). NPN PNP V(BR)CEO Volts Min fT @ IC MHz Min hFE @ IC mA IC mA Max Min Max 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 50 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 5.0 20 20 20 50 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 500 500 250 100 100 100 500 600 100 100 800 100 100 100 100 100 600 600 600 1000 200 200 100 100 100 100 200 200 800 100 100 60 120 120 180 100 100 120 200 100 120 120 180 380 40 100 100 50 50 50 100 110 120 200 420 50 120 100 300 — 400 450 220 450 — 300 500 460 630 800 220 450 800 400 300 300 150 — 150 300 800 220 450 800 150 360 630 mA NF dB Max Style 1.0 100 10 2.0 2.0 2.0 100 150 2.0 2.0 100 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 5.0 150 150 150 500 10 10 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 100 — — — 10 10 10 — — 10 10 — 10 10 10 10 — — — — — 6.0 5.0 10 10 10 10 6.0 4.0 — 1 1 1 17 17 17 1 1 14 17 17 17 17 17 17 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 17 17 17 17 1 1 17 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) MPS8099 MPSA06 2N4410 BC546 BC546A BC546B MPSA05 — BC182 BC237B BC337 BC547 BC547A BC547B BC547C MPSA20 MPS2222A 2N4401 2N4400 MPS6602 2N3903 2N3904 BC548 BC548A BC548B BC548C 2N4123 2N4124 BC338 MPS8599 MPSA56 — BC556 — BC556B MPSA55 MPS2907A BC212 BC307B BC327 BC557 BC557A BC557B BC557C MPSA70 — 2N4403 2N4402 MPS6652 2N3905 2N3906 — — BC558B — 2N4125 2N4126 BC328 80 80 80 65 65 65 60 60 50 45 45 45 45 45 45 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 30 30 30 30 30 25 25 150 100 60 150 150 150 100 200 200(1) 150 210(1) 150 150 150 150 125 300 200 150 100 200 250 300(1) 300(1) 300(1) 300 200 250 210(1) (1) Typical Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–2 Motorola Master Selection Guide Plastic–Encapsulated Transistors (continued) Table 1. Plastic–Encapsulated General–Purpose Transistors (continued) NPN PNP V(BR)CEO Volts Min fT @ IC MHz Min hFE @ IC VCE(sat) @ IC @ IB mA IC A Max Min Max mA Volts Max mA mA Style 200 200 200 200 200 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 40 40 40 80 80 400 400 400 — — 100 100 100 50 50 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.5 0.4 1000 1000 1000 250 250 100 100 100 10 10 1 14 1 1 1 Case 29–05 — TO–226AE (1–WATT TO–92) BDC01D BDB01C MPS6717 MPSW06 BDB02D BDC02D BDB02C MPSW56 100 100 80 80 80 50 50 50 50 50 Table 2. Plastic–Encapsulated Low–Noise and Good hFE Linearity These devices are designed to use on applications where good hFE linearity and low–noise characteristics are required: Instrumentation, hi–fi preamplifier. hFE @ IC NPN PNP V(BR)CEO Volts Min Max mA 250 150 250 120 180 380 500 100 250 200 380 350 450 300 800 500 650 800 450 800 — 300 — 450 800 — — 600 0.1 0.1 0.1 2.0 2.0 2.0 1.0 10 10 2.0 2.0 1.0 1.0 2.0 VT(4) mV Typ NF(5) dB Max fT MHz Typ — — 7.0(7) 2.0 3.0 3.5(8) 2.0(1) 40(2) 40(2) 100(2) Style Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — — MPS6428 BC239 BC550B BC550C MPSA18 MPS3904 — BC549B BC549C 2N5088 2N5089(6) MPS6521 (1) (2) (4) (5) (7) (8) 2N5087 2N5086 — — BC560B BC560C — MPS3906 MPS4250 BC559B BC559C — — MPS6523 50 50 50 45 45 45 45 40 40 30 30 30 25 25 9.5 — — 6.5(1) — — — — — — — 2.5 2.5 — 5.0 2.0 2.5 2.5 3.0 2.0 3.0 280 250 250 160 200(2) — 250 250 50 50 — 1 1 1 17 17 17 1 1 1 17 17 1 1 1 Typical Min VT : Total Input Noise Voltage (see BC413/BC414 and BC415/BC416 Data Sheets) at RS = 2.0 kΩ , IC = 200 µA, VCE = 5.0 Volts. NF: Noise Figure at RS = 2.0 kΩ, IC = 200 µA, VCE = 5.0 Volts. f = 30 Hz to 15 kHz. RS = 10 kΩ , BW = 1.0 Hz, f = 100 MHz RS = 500 Ω , BW = 1.0 Hz, f = 10 MHz Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–3 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Plastic–Encapsulated Transistors (continued) Table 3. Plastic–Encapsulated Darlington Transistors Darlington amplifiers are cascade transistors used in applications requiring very high–gain and input impedance. These devices have monolithic construction. hFE @ IC NPN PNP VCE(sat) @ IC & IB fT @ IC Min Max mA Volts Max mA mA Min mA S l Style 1000 1000 25K 20K 150K — 200 100 1.5 1.5 1000 100 2.0 0.1 100 125 200 10 1 1 500 1000 500 1000 500 500 500 500 500 1000 10K 10K 10K 10K 10K 20K 30K 20K 10K 30K — 160K — 50K — 200K 300K — — — 100 100 100 200 100 100 100 100 100 20 1.5 1.1 1.5 1.1 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.0 100 250 100 200 100 500 500 100 100 100 0.1 0.25 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.5 0.5 0.1 0.1 0.1 125 100 — 150 — — 125 125 125 200(1) 10 100 — 500 — — 10 10 10 10 1 1 1 17 1 1 1 1 1 17 V(BR)CEO Volts IC Max Case 29–05 — TO–226AE (1–WATT TO–92) MPSW45A — — MPSW64 50 30 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) MPSA29 BC373 MPSA27 BC618 — 2N6427 2N6426 MPSA14 MPSA13 BC517 — — MPSA77 — MPSA75 — — MPSA64 MPSA63 — 100 80 60 55 40 40 40 30 30 30 Table 4. Plastic–Encapsulated High–Current Transistors The following table is a listing of devices that are capable of handling a higher current range for small–signal transistors. NPN PNP V(BR)CEO Volts Min fT @ IC hFE @ IC mA IC mA Max Min Max — 50 — 50 1000 1000 50 50 200/150(1) 60 75 75 65 50 10 50 50 10 1000 500 2000 2000 1000 60 40 75 75 60 MHz Min VCE(sat) @ IC & IB mA Volts Max mA mA Style — — 1000 1000 0.5 0.5/0.7 1000 1000 100 100 1 1 400 160 — — — 100 150 1000 1000 1000 0.3/0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 1000 500 2000 2000 1000 100 50 200 200 100 17 14 1 1 1 Case 29–05 — TO–226AE (1–WATT TO–92) MPS6715 MPSW01A MPS6727 MPSW51A 40 40 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) BC489 BC639 MPS651 MPS650 BC368 BC490 BC640 MPS751 MPS750 BC369 80 80 60 40 20 (1) Typical Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–4 Motorola Master Selection Guide Plastic–Encapsulated Transistors (continued) Table 5. Plastic–Encapsulated High–Voltage Amplifier Transistors These high–voltage transistors are designed for driving neon bulbs and indicator tubes, for direct line operation, and for other applications requiring high–voltage capability at relatively low collector current. These devices are listed in order of decreasing breakdown voltage (V(BR)CEO). Device Type V(BR)CEO Volts Min hFE @ IC IC Amp Max Min VCE(sat) @ IC & IB fT @ IC Volts Max mA mA MHz Min mA Style 2.0 0.5 20 20 2.0 2.0 60 50 10 10 14 1 30 0.5 20 2.0 50 10 1 10 100 30 10 10 10 0.5 0.75 0.3 0.2 0.5 0.15 10 50 10 20 20 10 1.0 5.0 1.0 2.0 2.0 1.0 — — 40 50 50 100 — — 10 10 10 10 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 30 10 30 10 20 0.3 0.5 0.3 0.2 20 10 20 10 10 2.0 1.0 2.0 1.0 1.0 50 40 50 40 100 10 10 10 10 10 1 1 1 1 1 mA Case 29–05 — TO–226AE (1–WATT TO–92) — NPN BDC05 MPSW42 300 300 0.5 0.5 40 40 25 30 Case 29–05 — TO–226AE (1–WATT TO–92) — PNP MPSW92 300 0.5 25 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — NPN BF844 MPSA44 2N6517 BF393 MPSA42 2N5551 400 400 350 300 300 160 0.3 0.3 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.6 50 40 30 40 40 80 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — PNP BF493S 2N6520 MPSA92 2N6519 2N5401 350 350 300 300 150 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.6 40 30 40 45 60 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) NPN BF420 BF422 PNP hFE @ IC VCE(sat) @ IC & IB fT @ IC V(BR)CEO Volts Min IC Amp Cont Min mA Volts Max mA mA MHz Min mA Style 300 250 0.5 0.5 50 50 25 25 2.0 2.0 20 20 2.0 2.0 60 60 10 10 14 14 BF421 BF423 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–5 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Plastic–Encapsulated Transistors (continued) Table 6. Plastic–Encapsulated RF Transistors The RF transistors are designed for small–signal amplification from RF to VHF/UHF frequencies. They are also used as mixers and oscillators in the same frequency ranges. Device Type V(BR)CEO Volts Min hFE @ IC IC mA Max Min mA VCE V 7.0 8.0 4.0 3.0 50 4.0 4.0 7.0 20 5.0 8.0 3.0 8.0 10 10 10 10 10 5.0 10 10 10 10 10 10 1.0 10 5.0 5.0 10 10 10 fT MHz Typ CRE/CRB pF Max NF dB Typ 600 400(2) 400(2) 400(2) 500(2) 650(2) 650(2) 2.5 — — 3.2(3) 800 1200(2) 0.28 0.36 0.65 0.3 — 0.9 0.65 0.35 0.65 0.9 1.7 — 1.7 1.3 600(2) 2000(2) 0.85 0.3 f MHz Style — 100 — — 100 — — — 35 200 200 60 200 60 — 21 2 2 1 1 2 2 21 21 2 1 1 1 1 — — — — 2 1 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — NPN BF224 MPSH24 MPSH20 MPSH07A(9) MPS3866 MPSH11 MPSH10 BF199 BF959 MPSH17 MPS918 MPS5179 MPS3563 MPS6595 30 30 30 30 30 25 25 25 20 15 15 12 12 12 50 50 100 25 400 — — 100 100 — 50 50 50 50 30 30 25 20 10 60 60 40 40 25 20 25 20 25 750 600(2) 800(2) 600(2) 2000(3) — — — 2.5 3.0 6.0(3) 6.0(3) 5.0(3) 6.0(3) Case 29–04 — TO–266AA (TO–92) — PNP MPSH81 MPSH69 20 15 50 50 60 30 Table 7. Plastic–Encapsulated High–Speed Saturated Switching Transistors ton & toff @ IC Device Type ns Max ns Max mA V(BR)CEO Volts Min hFE @ IC VCE(sat) @ IC & IB fT @ IC Min mA Volts Max mA mA MHz Min mA Style 15 12 15 15 40 100 30 40 10 10 30 10 0.22 0.22 0.2 0.2 10 10 30 10 1.0 1.0 3.0 1.0 300 300 350 — 10 10 30 — 1 1 1 1 12 30 50 0.15 10 1.0 700 10 1 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — NPN 2N4264 2N4265 MPS3646 MPS2369A 25 25 18 12 35 35 28 18 10 10 300 10 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — PNP MPS4258 15 20 10 (2) Min (3) Max (9) AGC Capable Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–6 Motorola Master Selection Guide Plastic–Encapsulated Transistors (continued) Table 8. Plastic–Encapsulated Choppers Devices are listed in decreasing V(BR)EBO. Device Type V(BR)EBO Volts Min IC Amp(1) Max hFE @ IC Min VCE(sat) @ IC & IB fT @ IC mA Volts Max mA mA MHz Min mA Style Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — NPN MPSA17 15 100 200 5.0 0.25 10 1.0 80 5.0 1 MPSA16 12 100 200 5.0 0.25 10 1.0 100 5.0 1 –12 –0.2 –24 1.0 — — 1 Case 29–04 — TO–266AA (TO–92) — PNP MPS404A –25 –150 30 Table 9. Plastic–Encapsulated Telecom Transistors These devices are special product ranges intended for use in telecom applications. Device Type V(BR)CEO Volts PD mW 25°C Amb hFE @ IC @ VCE fT IC mA Cont Min Max mA Volts MHz Min Style 600 500 75 25 — — 10 1.0 10 10 300 40 17 1 600 500 100 40 — — 10 1.0 10 10 200 40 17 1 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — NPN P2N2222A PBF259,S(10) 40 300 625 625 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — PNP P2N2907A PBF493,S(11) 60 300 625 625 (1) Typical (10) “S” version, h FE Min 60 @ IC = 20 mA, VCE = 10 V. (11) “S” version, h FE Min 40 @ IC = 0.1 mA, VCE = 1.0 V. Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–7 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Plastic–Encapsulated Multiple Transistors The manufacturing trend has been toward printed circuit board design with requirements for smaller packages with more functions. In the case of discrete components the use of the multiple device package helps to reduce board space requirements and assembly costs. Many of the most popular devices are offered in the standard plastic DIP and surface mount IC packages. This includes small–signal NPN and PNP bipolar transistors, N–channel and P–channel FETs, as well as diode arrays. 14 1 CASE 646–06 (TO–116) STYLE 1 16 1 CASE 751B–05 SO–16 STYLE 4 Specification Tables The following short form specifications include Quad and Dual transistors listed in alphanumeric order. Some columns denote two different types of data indicated by either bold or italic typeface. See key and headings for proper identification. This applies to Table 10 and 11 of this section only. KEY TYPE NO. ID hFE2 ton ns Max toff ns Max Unit Subscript PD Watts One Die Only ∆VBE mV Max hFE1 Ref. Point VCE Volts Alphanumeric listing type numbers Identification Code First Letter: Polarity C — both types in multiple device N — NPN P — PNP Second Letter: Use A — General Purpose Amplifier E — Low Noise Audio Amplifier F — Low Noise RF Amplifier G — General Purpose Amplifier and Switch H — Tuned RF/IF Amplifier M — Differential Amplifier S — High Speed Switch D — Darlington Power Dissipation specified at 25°C. Single die rating. Ref. Point: A — Ambient Temperature C — Case Temperature Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes IC Amp Max hFE @ IC Min fT MHz Min Common–emitter DC Current Gain. Units for test Current: A — ampere m — mA u — µA Current–Gain–Bandwidth Product Continuous (DC) Collector Current Rated Minimum Collector–Emitter Voltage Subscript letter identifies base termination listed below in order of preference. SUBSCRIPT: 0 — VCEO, open 5.1–8 Cob pF Max Gp dB Min VCE @ (sat) Volts Max NF @ dB Max IC f & IC Unit IB Gp — Power Gain NF — Noise Figure f — Test Frequency AUD — 10–15 kHz Frequency Units: HĂ— HertząMĂ— MHz K — kHz G — GHz VCE(sat) — Collector–Emitter Saturation Voltage IC — Test Current Current Units: u — µA m — mA A — Amp hFE1/hFE2 — Current Gain Ratio VBE — Differential Base Voltage |VBE1 — VBE2|. Differential Amplifiers ton — turn–on time toff — turn–off time Output Capacitance, common–base. Shown without distinction: Ccb — Collector–Base Capacitance Cre — Common–Emitter Reverse Transfer Capacitance Motorola Master Selection Guide Plastic–Encapsulated Multiple Transistors (continued) Table 10. Plastic–Encapsulated Multiple Transistors — Quad The following table is a listing of the most popular multiple devices available in the plastic DIP package. These devices are available in NPN, PNP, and NPN/PNP configurations. (See note.) hFE2 ∆VBE mV Max ton ns Max toff ns Max 8.0 4.0 35(1) 9.0(1) 285(1) 15(1) 0.3 0.25 10 10 3.0(1) 2.0(1) 8.0 25 10 15 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.5 8.0 8.0 4.0 8.0 8.0 8.0 4.0 4.5 4.5 5.0 5.0 6.0 5.0 45(1) 40 35 50 180(1) 90 60 120 0.4 0.5 0.45 0.55 10 10 10 10 3.0(1) 2.0(1) 37(1) 43(1) 30(1) 30(1) 136(1) 155(1) 225(1) 225(1) 0.2 0.25 0.4 0.4 10 10 10 10 4.0(1) — 30(1) 30(1) 0.8 — 225(1) 225(1) 20 45 150 1.5 0.4 0.4 0.25 0.25 0.15 0.5 0.5 0.7 0.5 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 hFE1 Device ID PD Watts One Die Only VCEO Volts 0.65 0.5 0.625 0.625 0.65 0.75 1.0 0.75 0.625 0.625 0.5 0.5 0.65 0.65 0.5 0.5 0.65 0.65 0.5 0.5 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 40 15 40 40 60 40 40 40 40 60 40 40 30 30 45 30 30 30 45 40 40 250 200 150 250 IC Amp Max hFE @ IC Min fT MHz Min Cob pF Max NF @ dB Max Typ(1) Gp dB Min VCE (sat) Volts Max @ f IC IC IB Case 646–06 — TO–116 MPQ2222A MPQ2369 MPQ2483 MPQ2484 MPQ2907A MPQ3467 MPQ3725 MPQ3762 MPQ3798 MPQ3799 MPQ3904 MPQ3906 MPQ6001 MPQ6002 MPQ6100A MPQ6426 MPQ6501 MPQ6502 MPQ6600A1 MPQ6700 MPQ6842 MPQ7043 MPQ7042 MPQ7051 MPQ7093 NA NS NA NA PA PS NS PS PA PA NG PG CG CG CA ND CG CG CA CA CA NA NA CG PA 0.5 0.5 0.05 0.05 0.6 1.0 1.0 1.5 0.05 0.05 0.2 0.2 0.5 0.5 0.05 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.05 0.2 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 100 40 150 300 100 20 25 35 150 300 75 75 40 100 150 10K 40 100 150 70 70 25 25 25 25 150 m 10 m 1.0 m 1.0 m 150 m 500 m 500 m 150 m 0.1 m 0.1 m 10 m 10 m 150 m 150 m 1.0 m 100 m 150 m 150 m 1.0 m 10 m 10 m 1.0 m 1.0 m 1.0 m 1.0 m 200 450 50 50 200 125 250 150 60 60 250 200 200 200 50 125 200 200 50 200 300 50 50 50 50 150 m 10 m AUD AUD 150 m 500 m 500 m 500 m AUD AUD 10 m 10 m 150 m 150 m AUD 100 m 150 m 150 m 1.0 m 1.0 m 0.5 m 20 m 20 m 20 m 20 m Table 11. Plastic–Encapsulated Multiple Transistors — Quad Surface Mount The following table is a listing of the most popular multiple devices available in the plastic SOIC surface mount package. These devices are available in NPN, PNP, and NPN/PNP configurations. hFE @ IC D i Device fT @ IC V(BR)CEO V(BR)CBO Min mA MHz Min mA 40 15 50 40 40 60 40 40 40 75 40 60 40 60 60 60 40 40 40 20 50 20 25 300 75 75 70 500 100 500 500 500 0.5 10 10 10 200 450 200 125 250 60 250 200 200 20 10 50 50 50 1.0 10 10 10 Case 751B–05 — SO–16 MMPQ2222A MMPQ2369 MMPQ2907A MMPQ3467 MMPQ3725 MMPQ3799 MMPQ3904 MMPQ3906 MMPQ6700 (12) (1) Typical (12) NPN/PNP NOTE: Some columns show 2 different types of data indicated by either bold or italic typefaces. See key and headings. Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–9 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors 1 1 1 This section of the selector guide lists the small–signal plastic devices that are available for surface mount applications. These devices are encapsulated with the latest state–of–the–art mold compounds that enhance reliability and exhibit excellent performance in high temperature and high humidity environments. This package offers higher power dissipation capability for small–signal applications. 4 3 3 2 CASE 318–08 TO–236AB SOT–23 CASE 318D–04 SC–59 6 3 1 1 2 CASE 419–02 SC–70/SOT–323 2 2 5 2 3 CASE 318E–04 SOT–223 3 4 3 CASE 419B–01 SOT–363 1 2 CASE 463–01 SOT–416/SC–90 Table 12. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount General–Purpose Transistors The following tables are a listing of small–signal general–purpose transistors in the SOT–23, SC–59, SOT–223, SC–70, SC–90, and SOT–363 surface mount packages. These devices are intended for small–signal amplification for DC, audio, and lower RF frequencies. They also have applications as oscillators and general–purpose, low voltage switches. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector Devices are listed in order of descending breakdown voltage. hFE @ IC D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CEO Min Max mA fT MHz Min 110 200 100 160 250 110 200 420 100 100 100 110 200 420 220 450 250 400 600 220 450 800 300 300 300 220 450 800 2.0 2.0 100 100 100 2.0 2.0 2.0 150 10 150 2.0 2.0 2.0 100 100 200 200 200 100 100 100 200 200 250 100 100 100 100 125 220 100 100 160 250 125 220 100 100 125 220 420 300 250 475 300 250 400 600 250 475 300 300 250 475 800 1.0 2.0 2.0 150 100 100 100 2.0 2.0 10 150 2.0 2.0 2.0 150 100 100 200 200 200 200 100 100 250 200 100 100 100 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — NPN BC846ALT1 BC846BLT1 BC817–16LT1 BC817–25LT1 BC817–40LT1 BC847ALT1 BC847BLT1 BC847CLT1 MMBT2222ALT1 MMBT3904LT1 MMBT4401LT1 BC848ALT1 BC848BLT1 BC848CLT1 1A 1B 6A 6B 6C 1E 1F 1G 1P 1AM 2X 1J 1K 1L 65 65 45 45 45 45 45 45 40 40 40 30 30 30 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP MMBT8599LT1 BC856ALT1 BC856BLT1 MMBT2907ALT1 BC807–16LT1 BC807–25LT1 BC807–40LT1 BC857ALT1 BC857BLT1 MMBT3906LT1 MMBT4403LT1 BC858ALT1 BC858BLT1 BC858CLT1 2W 3A 3B 2F 5A 5B 5C 3E 3F 2A 2T 3J 3K 3L 80 65 65 60 45 45 45 45 45 40 40 30 30 30 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–10 Motorola Master Selection Guide Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors (continued) Table 12. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount General–Purpose Transistors (continued) Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector Devices are listed in order of descending breakdown voltage. hFE @ IC D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CEO Min Max mA fT MHz Min 25 25 25 20 210 290 120 200 340 460 240 350 2.0 2.0 150 500 150(1) 150(1) 200(1) 200(1) 25 25 25 25 210 290 85 120 340 460 170 240 2.0 2.0 150 150 100(1) 100(1) 200(1) 200(1) 45 45 45 65 65 45 45 45 30 30 30 40 40 20 50 100 160 250 110 200 110 200 420 110 200 420 100 100 70 210 600 400 600 220 450 220 450 800 220 450 800 300 300 140 340 100 100 100 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 150 10 1.0 2.0 — — — 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 300 300 150 — 45 45 65 65 45 45 30 30 30 60 40 45 160 250 125 220 125 220 110 200 420 100 100 210 400 600 250 475 250 475 220 450 800 300 300 340 100 100 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 150 10 2.0 — — 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 250 — 40 40 100 100 300 300 10 10 300 300 – 40 – 40 100 100 300 300 10 10 250 250 Case 318D–04 — SC–59 — NPN MSD601–RT1 MSD601–ST1 MSD602–RT1 MSD1328–RT1 YR YS WR 1DR Case 318D–04 — SC–59 — PNP MSB709–RT1 MSB709–ST1 MSB710–QT1 MSB710–RT1 AR AS CQ CR Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 —NPN BC818WT1 BC818–25WT1 BC818–40WT1 BC846AWT1 BC846BWT1 BC847AWT1 BC847BWT1 BC847CWT1 BC848AWT1 BC848BWT1 BC848CWT1 MMBT2222AWT1 MMBT3904WT1 MSC3930–BT1 MSD1819A–RT1 6I 6F 6G 1A 1B 1E 1F 1G 1J 1K 1L 1P AM VB ZR Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 —PNP BC808–25WT1 BC808–40WT1 BC856AWT1 BC856BWT1 BC857AWT1 BC857BWT1 BC858AWT1 BC858BWT1 BC858CWT1 MMBT2907AWT1 MMBT3906WT1 MSB1218A–RT1 5F 6F 3A 3B 3E 3F 3J 3K 3L 20 2A BR Case 419B–01 — SOT–363 — Dual NPN MBT3904DW1T1 MBT3904DW9T1 MA MB Case 419B–01 — SOT–363 — Dual PNP MBT3906DW1T1 MBT3906DW9T1 A2 A3 (1) Typical Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–11 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors (continued) Table 12. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount General–Purpose Transistors (continued) Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector Devices are listed in order of descending breakdown voltage. hFE @ IC D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CEO Min Max mA fT MHz Min Case 419B–01 — SOT–363 — Dual Combination NPN and PNP MBT3946DW1T1 46 40 100 300 10 250 50 120 560 1.0 180 50 120 560 1.0 140 Case 463–01 — SOT–416/SC–90 — NPN 2SC4617 B9 Case 463–01 — SOT–416/SC–90 — PNP 2SA1774 F9 C (OUT) B (IN) Table 13. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Bias Resistor Transistors Table 13. for General Purpose Applications R1 R2 E (GND) Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector These devices include bias resistors on the semiconductor chip with the transistor. See the BRT diagram for orientation of resistors. NPN NPN PNP 8A 8B 8C 8D 8E 8F 8G 8H 8J 8K 8L 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E 6F 6G 6H 6J 6K 6L 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 35 60 80 80 160 160 3.0 8.0 15 80 80 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 10K 22K 47K 10K 10K 4.7K 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 4.7K 22K 10K 22K 47K 47K ∞ ∞ 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 47K 47K A6A A6B A6C A6D A6E A6F A6G A6H A6J A6K A6L 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 35 60 80 80 160 160 3.0 8.0 15 80 80 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 10K 22K 47K 10K 10K 4.7K 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 4.7K 22K 10K 22K 47K 47K ∞ ∞ 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 47K 47K Marking PNP hFE@ IC V(BR)CEO Volts (Min) Device Min mA IC mA Max R1 Ohm R2 Ohm Case 318D–04 — SC–59 MUN2211T1 MUN2212T1 MUN2213T1 MUN2214T1 MUN2215T1 MUN2216T1 MUN2230T1 MUN2231T1 MUN2232T1 MUN2233T1 MUN2234T1 MUN2111T1 MUN2112T1 MUN2113T1 MUN2114T1 MUN2115T1 MUN2116T1 MUN2130T1 MUN2131T1 MUN2132T1 MUN2133T1 MUN2134T1 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) MMUN2211LT1 MMUN2212LT1 MMUN2213LT1 MMUN2214LT1 MMUN2215LT1 MMUN2216LT1 MMUN2230LT1 MMUN2231LT1 MMUN2232LT1 MMUN2233LT1 MMUN2234LT1 MMUN2111LT1 MMUN2112LT1 MMUN2113LT1 MMUN2114LT1 MMUN2115LT1 MMUN2116LT1 MMUN2130LT1 MMUN2131LT1 MMUN2132LT1 MMUN2133LT1 MMUN2134LT1 A8A A8B A8C A8D A8E A8F A8G A8H A8J A8K A8L Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–12 Motorola Master Selection Guide Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors (continued) Table 13. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Bias Resistor Transistors for General Purpose Applications (continued) Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector NPN NPN PNP 8A 8B 8C 8D 8E 8F 8G 8H 8J 8K 8L 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E 6F 6G 6H 6J 6K 6L 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 35 60 80 80 160 160 3.0 8.0 15 80 80 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 10K 22K 47K 10K 10K 4.7K 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 4.7K 22K 10K 22K 47K 47K ∞ ∞ 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 47K 47K 7A 7B 7C 7D 7E 7F 7G 7H 7J 7K 7L 7M 8A 8B 8C 8D 8E 8F 8G 8H 8J 8K 8L 8M 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 35 60 80 80 160 160 3.0 8.0 15 80 80 80 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 10K 22K 47K 10K 10K 4.7K 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 4.7K 22K 2.2K 10K 22K 47K 47K ∞ ∞ 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 47K 47K 47K Marking PNP hFE@ IC V(BR)CEO Volts (Min) Device Min mA IC mA Max R1 Ohm R2 Ohm Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 MUN5211T1 MUN5212T1 MUN5213T1 MUN5214T1 MUN5215T1 MUN5216T1 MUN5230T1 MUN5231T1 MUN5232T1 MUN5233T1 MUN5234T1 MUN5111T1 MUN5112T1 MUN5113T1 MUN5114T1 MUN5115T1 MUN5116T1 MUN5130T1 MUN5131T1 MUN5132T1 MUN5133T1 MUN5134T1 Case 419B–01 — SOT–363 Duals MUN5211DW1T1 MUN5212DW1T1 MUN5213DW1T1 MUN5214DW1T1 MUN5215DW1T1 MUN5216DW1T1 MUN5230DW1T1 MUN5231DW1T1 MUN5232DW1T1 MUN5233DW1T1 MUN5234DW1T1 MUN5235DW1T1 MUN5111DW1T1 MUN5112DW1T1 MUN5113DW1T1 MUN5114DW1T1 MUN5115DW1T1 MUN5116DW1T1 MUN5130DW1T1 MUN5131DW1T1 MUN5132DW1T1 MUN5133DW1T1 MUN5134DW1T1 MUN5135DW1T1 hFE @ IC D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CEO Min mA IC mA Max R1 Ohm R2 Ohm 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 10K 22K 47K 10K 10K 4.7K 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 4.7K 22K 2.2K 10K 22K 47K 47K ∞ ∞ 1.0K 2.2K 4.7K 47K 47K 47K Case 419B–01 — SOT–363 — Dual Combination NPN and PNP MUN5311DW1T1 MUN5312DW1T1 MUN5313DW1T1 MUN5314DW1T1 MUN5315DW1T1 MUN5316DW1T1 MUN5330DW1T1 MUN5331DW1T1 MUN5332DW1T1 MUN5333DW1T1 MUN5334DW1T1 MUN5335DW1T1 11 12 13 14 15 16 3X 31 32 33 34 35 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 NPN PNP V(BR)CEO Volts (Min) 94 69 — — 59 43 50 50 50 Device NPN 35 60 80 80 160 160 3.0 8.0 15 80 80 80 Marking PNP hFE@ IC Min 100 80 15 mA IC mA Max R1 Ohm R2 Ohm 1.0 5.0 5.0 100 100 100 10K 10K 4.7K ∞ 47K 4.7K Case 463–01 — SOT–416/SC–90 DTC114TE DTC114YE — — DTA114YE DTA143EE Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–13 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors (continued) Table 14. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Switching Transistors The following tables are a listing of devices intended for high–speed, low saturation voltage, switching applications. These devices have very fast switching times and low output capacitance for optimized switching performance. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector hFE@ IC Switching Time (ns) D i Device M ki Marking toff V(BR)CEO Min Max mA fT MHz Min 18 18 18 15 15 12 20 20 40 — — 120 100 100 10 — — 400 25 35 12 20 — 50 500 20 40 20 40 180 1.0 200 ton Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — NPN MMBT2369LT1 MMBT2369ALT1 BSV52LT1 M1J 1JA B2 12 12 12 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP MMBT3640LT1 2J Pinout: 1–Emitter, 2–Base, 3–Collector Case 318D–04 — SC–59 — NPN MSC1621T1 RB Table 15. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount VHF/UHF Amplifiers, Mixers, Oscillators The following table is a listing of devices intended for small–signal RF amplifier applications to VHF/UHF frequencies. These devices may also be used as VHF/UHF oscillators and mixers. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector D i Device M ki Marking fT @ IC V(BR)CEO Ccb(13) pF Max GHz Min mA 25 15 30 0.7 1.7(14) 0.45 0.65 0.6 0.4 4.0 4.0 8.0 20 15 0.85 0.35(13) 0.6 2.0 5.0 10 20 20 20 10 1.5(13) 1.5(13) 1.0(13) — 0.15 0.15 0.45 1.4 1.0 1.0 1.0 5.0 20 20 2.0(13) 2.0(13) 0.15 0.15 1.0 1.0 20 0.85(13) 0.6 5.0 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — NPN MMBTH10LT1 MMBT918LT1 MMBTH24LT1 3EM M3B M3A Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP MMBTH81LT1 MMBTH69LT1 3D M3J Pinout: 1–Emitter, 2–Base, 3–Collector Case 318D–04 — SC–59 — NPN MSC2295–BT1 MSC2295–CT1 MSC2404–CT1 MSC3130T1 VB VC UC 1S Case 318D–04 — SC–59 — PNP MSA1022–BT1 MSA1022–CT1 EB EC Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 — PNP MSB81T1 J3D (13) C re (14) C ob Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–14 Motorola Master Selection Guide Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors (continued) Table 16. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Choppers The following table is a listing of small–signal devices intended for chopper applications where a higher than normal V(BR)CEO is required in the circuit application. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector hFE @ IC D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CEO V(BR)EBO Min Max mA 25 30 400 12 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP MMBT404ALT1 2N 35 Table 17. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Darlingtons The following table is a listing of small–signal devices that have very high hFE and input impedance characteristics. These devices utilize monolithic, cascade transistor construction. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector Devices are listed in order of descending hFE. D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CES hFE @ IC VCE(sat) Volts Max Min Max mA 1.5 1.5 20K 10K — — 100 100 1.5 20K — 100 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — NPN MMBTA14LT1 MMBTA13LT1 1N 1M 30 30 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP MMBTA64LT1 2V 30 Table 18. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Low–Noise Transistors The following table is a listing of small–signal devices intended for low noise applications in the audio range. These devices exhibit good linearity and are candidates for hi–fi and instrumentation equipment. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector Devices are listed in order of ascending NF. D i Device M ki Marking NF dB Typ hFE@ IC V(BR)CEO Min Max mA fT MHz Min 25 60 50 45 400 — 250 500 — 800 — — 10 10 10 10 50 — 100 100 50 250 — 10 40 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — NPN MMBT5089LT1 MMBT2484LT1 MMBT6428LT1 MMBT6429LT1 1R 1U 1KM 1L 2.0(15) 3.0(15) 3.0 3.0 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP MMBT5087LT1 2Q 2.0(15) (15) Max Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–15 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors (continued) Table 19. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount High–Voltage Transistors The following table is a listing of small–signal high–voltage devices designed for direct line operation requiring high voltage breakdown and relatively low current capability. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector Devices are listed in order of descending breakdown voltage. hFE@ IC D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CEO Min Max mA fT MHz Min 15 40 30 — — — 100 30 50 40 50 100 15 25 50 — — — 100 30 50 40 50 100 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — NPN MMBT6517LT1 MMBTA42LT1 MMBT5551LT1 1Z 1D G1 350 300 160 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP MMBT6520LT1 MMBTA92LT1 MMBT5401LT1 2Z 2D 2L 350 300 150 Table 20. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Drivers The following is a listing of small–signal devices intended for medium voltage driver applications at fairly high current levels. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector hFE@ IC D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CEO VCE(sat) VBE(sat) Min Max mA 0.25 0.15 — — 100 20 — — 100 10 – 0.25 – 0.25 – 0.90 — 30 100 — — 25 100 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — NPN MMBTA06LT1 BSS64LT1 1GM AM 80 80 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP BSS63LT1 MMBTA56LT1 T1 2GM 100 80 The following devices are designed to conserve energy. They offer ultra–low collector saturation voltage. Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — PNP MMBT1010LT1 GLP 15 0.1 1.1 300 600 100 15 0.1 1.1 300 600 100 Case 318–03 — SC–59 — PNP MSD1010T1 GLP Table 21. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount General Purpose Amplifiers Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Collector, 3–Emitter, 4–Collector hFE@ IC D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)CEO Min Max mA BH 80 40 250 150 80 40 25 150 Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — NPN BCP56T1 Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — PNP Pinout: 1–Gate, 2–Drain, 3–Source, 4–Drain BCP53T1 AH Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–16 Motorola Master Selection Guide Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Transistors (continued) Table 22. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Switching Transistors Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Collector, 3–Emitter, 4–Collector hFE Device M ki Marking ton toff 35 285 45 100 V(BR)CEO fT Min Max @ IC (mA) Min (MHz) 40 100 300 20 300 60 100 300 50 200 Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — NPN PZT2222AT1 P1F Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — PNP PZT2907AT1 P2F Table 23. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Darlingtons Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Collector, 3–Emitter, 4–Collector Device hFE M ki Marking V(BR)CER VCE(sat) Max (V) Min Max @ IC (mA) ( A) AS3 P1N 80 30 1.3 1.5 2000 20k — — 500 100 BS3 P2V 90 30 1.3 1.5 2000 20k — — 500 100 Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — NPN BSP52T1 PZTA14T1 Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — PNP BSP62T1 PZTA64T1 Table 24. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount High–Voltage Transistors Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Collector, 3–Emitter, 4–Collector hFE Device fT M ki Marking V(BR)CEO Min Max @ IC (mA) Min (MHz) SP19A P1D BF720 SP20A 350 300 250 250 40 40 50 40 — — — — 20 10 10 20 70 50 60 70 ZTA96 P2D BSP16 BF721 450 300 300 250 50 40 30 50 150 — 150 — 10 10 10 10 50 50 15 60 Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — NPN BSP19AT1 PZTA42T1 BF720T1 BSP20AT1 Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — PNP PZTA96T1 PZTA92T1 BSP16T1 BF721T1 Table 25. Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount High Current Transistors Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Collector, 3–Emitter, 4–Collector D i Device hFE@ IC M ki Marking V(BR)CEO VCE(sat) Volts 651 CA 60 20 0.5 0.5 75 60 — — 1000 1000 ZT751 CE 60 20 0.5 0.5 75 60 — — 1000 1000 Min Max mA Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — NPN PZT651T1 BCP68T1 Case 318E–04 — SOT–223 — PNP PZT751T1 BCP69T1 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–17 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Metal–Can Transistors Metal–can packages are intended for use in industrial applications where harsh environmental conditions are encountered. These packages enhance reliability of the end products due to their resistance to varying humidity and extreme temperature ranges. 3 2 1 CASE 22–03 TO–206AA (TO–18) STYLE 1 3 2 1 CASE 79–04 TO–205AD (TO–39) STYLE 1 Table 26. Metal–Can General–Purpose Transistors These transistors are designed for DC to VHF amplifier applications, general–purpose switching applications, and complementary circuitry. Devices are listed in decreasing order of V(BR)CEO within each package group. Device D i Type V(BR)CEO Volts Min fT @ IC MHz Min hFE @ IC mA IC mA Max Min Max mA 50 10 10 20 10 1000 200 200 800 200 50 110 200 100 420 — 450 450 300 800 500 2.0 2.0 150 2.0 50 50 10 10 600 600 200 200 40 100 100 180 120 300 300 460 150 150 10 2.0 50 50 50 20 1000 1000 500 800 100 40 40 100 300 120 120 300 150 150 150 150 — 50 50 50 — 1000 1000 600 600 1000 25 40 40 100 40 — 140 120 300 — 1000 150 150 150 1000 Case 22–03 — TO–206AA (TO–18) — NPN 2N3700 BC107 BC107B 2N2222A BC109C 80 45 45 40 25 80 150 150 300 150 Case 22–03 — TO–206AA (TO–18) — PNP 2N2906A 2N2907A 2N3251A BC177B 60 60 60 45 200 200 300 200 Case 79–04 — TO–205AD (TO–39) — NPN 2N3019 2N3020 2N1893 2N2219A 80 80 80 40 100 80 50 300 Case 79–04 — TO–205AD (TO–39) — PNP 2N4033 2N4036 2N2904A 2N2905A 2N4032 80 65 60 60 60 — 60 200 200 — Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–18 Motorola Master Selection Guide Metal–Can Transistors (continued) Table 27. Metal–Can High–Gain/Low–Noise Transistors These transistors are characterized for high–gain and low–noise applications. Devices are listed in decreasing order of NF. Device D i Type NF Wideband dB Typ Max V(BR)CEO Volts Min fT @ IC hFE @ IC IC mA Max Min Max µA mA MHz Min mA 50 30 30 100 — — 500 600 600 10 10 10 15 45 30 0.05 0.5 0.5 200 50 250 300 600 900 1.0(24) 500 50 30 0.5 0.5 Case 22–03 — TO–206AA (TO–18) — NPN 2N2484 2N930A 2N930 8.0(1) 3.0 3.0 60 45 45 Case 22–03 — TO–206AA (TO–18) — PNP 2N3964 2N3799 4.0 2.5 45 60 Table 28. Metal–Can High–Voltage/High–Current Transistors The following table lists Motorola standard devices that have high collector–emitter breakdown voltage. Devices are listed in decreasing order of V(BR)CEO within each package type. Device D i Type V(BR)CEO Volts Min hFE @ IC IC mA Max Min fT @ IC VCE(sat) @ IC & IB mA Volts Max mA mA MHz Min mA 30 30 0.5 1.0 20 50 2.0 5.0 50 50 10 20 30 0.5 50 5.0 50 20 50 0.5 50 5.0 200 30 Case 22–03 — TO–206AA (TO–18) — NPN 2N6431 BSS73 300 300 50 500 50 40 Case 22–03 — TO–206AA (TO–18) — PNP BSS76 300 500 35 Case 79–04 — TO–205AD (TO–39) — PNP 2N3637 175 1000 100 (1) Typical (24) T = 25°C A Table 29. Metal–Can Switching Transistors The following devices are intended for use in general–purpose switching and amplifier applications. Within each package group shown, the devices are listed in order of decreasing turn–on time (ton). ton & toff @ IC Device D i Type ns Max ns Max mA V(BR)CEO Volts Min hFE @ IC IC mA Max Min 15 15 200 500 40 1000 VCE(sat) @ IC @ IB mA fT MHz Min IC mA 10 10 1.0 1.0 500 500 10 10 500 50 175 50 mA Volts Max mA 40 20 10 10 0.2 0.25 40 500 0.5 Case 22–03 — TO–206AA (TO–18) — NPN 2N2369A BSX20 12 7.0 18 21 10 100 Case 79–04 — TO–205AD (TO–39) — PNP 2N3467 40 90 500 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–19 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Field–Effect Transistors JFETs JFETs operate in the depletion mode. They are available in both P– and N–channel and are offered in both Through–hole and Surface Mount packages. Applications include general– purpose amplifiers, switches and choppers, and RF amplifiers and mixers. These devices are economical and very rugged. The drain and source are interchangeable on many typical FETs. 1 CASE 29–04 TO–226AA (TO–92) 23 Table 30. JFET Low–Frequency/Low–Noise The following table is a listing of small–signal JFETs intended for low–noise applications in the audio range. These devices exhibit good linearity and are candidates for hi–fi and instrumentation equipment. Re Yfs D i Device mmho Min @f Re Yos @ f µmho Max kHz kHz IDSS mA VGS(off) Volts Crss pF Max V(BR)GSS V(BR)GDO Volts Min Min Max Min Max S l Style — 7.0 6.0 7.0 7.0 — 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 40 25 50 25 25 0.8 1.0 — 0.5 2.0 4.0 7.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 0.9 2.0 0.5 1.0 4.0 4.5 9.0 2.5 5.0 16 5 5 5 5 5 7.0 7.0 7.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 40 40 40 0.75 1.0 1.8 6.0 7.5 9.0 1.0 2.0 4.0 5.0 9.0 16 7 7 7 Ciss pF Max Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — N–Channel J202 2N5458 MPF3821 2N5457 2N5459 — 1.5 1.5 1.0 2.0 — 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 — 50 10 50 50 — 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — P–Channel 2N5460 2N5461 2N5462 1.0 1.5 2.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 75 75 75 1.0 1.0 1.0 Table 31. JFET High–Frequency Amplifiers The following is a listing of small–signal JFETs that are intended for hi–frequency applications. These are candidates for VHF/UHF oscillators, mixers and front–end amplifiers. Re Yfs @ f D i Device mmho Min MHz Re Yos @ f µmho Max MHz Ciss pF Max Crss pF Max dB Max f MHz V(BR)GSS V(BR)GDO Volts Min — 2.5 3.0 4.0 4.0 1.5(1) 1.5(1) 1.5(1) — 100 100 400 400 100 100 100 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 NF @ RG = 1K VGS(off) Volts IDSS mA Min Max Min Max S l Style — 0.2 0.3 0.5 2.0 1.0 1.0 2.0 8.0 4.0 3.0 4.0 6.0 6.5 4.0 6.5 2.0 1.0 1.0 4.0 8.0 12 12 24 20 5.0 5.0 10 20 60 30 60 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — N–Channel MPF102 2N5668 2N5484 2N5485 2N5486 J308 J309 J310 1.6 1.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 12(1) 12(1) 12(1) 100 100 100 400 400 100 100 100 200 50 75 100 100 250(1) 250(1) 250(1) 100 100 100 400 400 100 100 100 7.0 7.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 7.5 7.5 7.5 3.0 3.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 2.5 2.5 2.5 (1) Typical Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–20 Motorola Master Selection Guide JFETs (continued) Table 32. JFET Switches and Choppers The following is a listing of JFETs intended for switching and chopper applications. RDS(on) @ ID D i Device Ω Max mA VGS(off) Volts Min Max IDSS mA Min Max V(BR)GSS V(BR)GDO Volts Min 50 50 20 20 20 5.0 25 25 8.0 5.0 5.0 2.0 15 30 60 10 — — — 100 100 — 75 — 80 30 — — — 80 140 — 40 30 35 40 30 35 30 30 30 30 30 35 25 25 25 25 18 18 28 18 18 28 10 10 18 10 10 28 5.0 — — — 8.0 8.0 5.0 8.0 8.0 5.0 3.5 4.0 8.0 3.5 4.0 5.0 1.2 — — — 9.0 9.0 — 10 10 — 15 — 20 15 18 — 10 — — — 25 25 — 50 50 — 35 — 100 55 45 — 25 — — — 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 22 22 5 15 2.0 100 50 30 30 12 12 5.0 5.0 8.0 10 25 120 5 5 Ciss pF Max Crss pF Max ton ns Max toff ns Max S l Style Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — N–Channel MPF4856 MPF4859 J111 MPF4857 MPF4860 J112 MPF4392 2N5639 MPF4861 MPF4393 2N5640 J113 2N5555 BF246A BF246B J110 25 25 30 40 40 50 60 60 60 100 100 100 150 35(1) 50(1) 18 — — — — — — — 1.0 — — 1.0 — — 1.0 1.0 — 4.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 2.0 1.0 — — 0.8 — — 0.5 — 0.6 0.6 0.5 10 10 10 6.0 6.0 5.0 — (8.0)(1) 4.0 (12)(1) (6.0)(1) 3.0 1.0(16) 14 14 4.0 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — P–Channel MPF970 MPF971 100 250 1.0 1.0 5.0 1.0 12 7.0 (1) Typical (16) V GS(f) Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–21 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes CASE 29–05 TO–226AE 1–WATT (TO–92) TMOS FETs 1 2 3 D CASE 29–04 TO–226AA (TO–92) 1 2 3 G S Table 33. TMOS Switches and Choppers The following is a listing of small–signal TMOS devices that are intended for switching and chopper applications. These devices offer low RDS(on) characteristics. VGS(th) Volts RDS(on) @ ID D i Device Ω Max A Min Max V(BR)DSS Volts Min Ciss pF Max Crss pF Max ton ns Max toff ns Max S l Style 15 15 5.0 15 5.0 5.0 — 10 15 15 5.0 15 5.0 5.0 — 10 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 30 10 10 10 8.0 8.0 6.0(1) 30 10 10 10 18 23 12(1) 15 20 10 8.0 15 15 20 10 23 15 22 22 30 22 22 22 7 30 22 22 22 30 Case 29–05 — TO–226AE (1–WATT TO–92) — N–Channel MPF930 MPF960 MPF6659 MPF990 MPF6660 MPF6661 MPF910 VN10LM 1.4 1.7 1.8 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 5.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.5 1.0 1.0 0.8 1.0 0.8 0.8 0.3 0.8 3.5 3.5 2.0 3.5 2.0 2.0 2.5 2.5 35 60 35 90 60 90 60 60 70(1) 70(1) 30(1) 70(1) 30(1) 30(1) 20(1) 20(1) 4(1) 20(1) 4(1) 4(1) — 60 — 5.0 2.5 3.0 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.0 2.7 3.0 2.5 2.5 2.0 3.0 60 60 60 60 170 240 200 200 60 60 240 200 100 60 25(1) 60 125 125 72(1) 60(1) 25 5.0 3.0(1) 5.0 20 20 3.0(1) 6.0(1) 50 60 125 60(1) 5.0 5.0 20 6.0(1) Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) — N–Channel VN0300L 2N7000 BS170 VN0610LL VN1706L VN2406L BSS89 BS107A 2N7008 VN2222LL VN2410L BS107 1.2 5.0 5.0 5.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.4 7.5 7.5 10 14 1.0 0.5 0.2 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.30 0.25 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.2 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.6 0.8 1.0 (1) Typical Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–22 Motorola Master Selection Guide Surface Mount FETs CASE 318–08 TO–236AB SOT–23 3 This section contains the FET plastic packages available for surface mount applications. Most of these devices are the most popular metal–can and insertion type parts carried over to the new surface mount packages. 1 2 6 5 CASE 419–02 SC–70/SOT–323 4 4 1 2 3 CASE 419B–01 SOT–363 1 CASE 318E–04 SOT–223 2 3 Table 34. Surface Mount RF JFETs The following is a list of surface mount FETs which are intended for VHF/UHF RF amplifier applications. Pinout: 1–Drain, 2–Source, 3–Gate NF D i Device M ki Marking dB Typ Yfs @ VDS f MHz mmhos Min mmhos Max Volts V(BR)GSS S l Style 450 450 450 100 100 100 10 8.0 10 4.5 3.0 4.0 20 18 18 7.5 6.0 8.0 10 10 10 15 15 15 25 25 25 30 25 25 10 10 10 10 10 10 100 4.5 7.5 15 30 7 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — N–Channel MMBFJ309LT1 MMBFJ310LT1 MMBFU310LT1 MMBF4416LT1 MMBF5484LT1 MMBF5486LT1 6U 6T M6C M6A M6B 6H 1.5 1.5 1.5 2(3) 2.0 2.0 Case 419B–01 — SOT–363— Dual N–Channel MBF4416DW1T1 M6 2.0 (3) Max Table 35. Surface Mount General–Purpose JFETs The following table is a listing of surface mount small–signal general purpose FETs. These devices are intended for small–signal amplification for DC, audio, and lower RF frequencies. They also have applications as oscillators and general–purpose, low–voltage switches. Pinout: 1–Drain, 2–Source, 3–Gate Yfs @ VDS D i Device M ki Marking V(BR)GSS mmhos Min IDSS mmhos Max Volts mA Min mA Max S l Style 5.0 6.0 15 15 1.0 4.0 5.0 16 10 10 1.0 4.0 15 1.0 5.0 10 1.0 5.0 15 1.0 5.0 7 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — N–Channel MMBF5457LT1 MMBF5459LT1 6D 6L 25 25 1.0 2.0 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — P–Channel MMBF5460LT1 M6E 40 Case 419B–01 — SOT–363 — Dual N–Channel MBF5457DW1T1 6D 25 (3) Max Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–23 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Surface Mount FETs (continued) Table 36. Surface Mount Choppers/Switches JFETs The following is a listing of small–signal surface mount JFET devices intended for switching and chopper applications. Pinout: 1–Drain, 2–Source, 3–Gate D i Device M ki Marking RDS(on) Ohms Max toff ns Max VGS(off) IDSS V(BR)GSS Volts Min Volts Max mA Min mA Max S l Style 40 30 30 30 30 –4.0 –4.0 –2.0 –2.0 –0.5 –10 –10 –6.0 –5.0 –3.0 50 50 20 25 5.0 — 150 100 75 30 10 10 10 10 10 30 30 3.0 0.8 6.0 2.5 7.0 1.5 60 20 10 10 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — N–Channel MMBF4856LT1 MMBF4391LT1 MMBF4860LT1 MMBF4392LT1 MMBF4393LT1 AAA 6J 6F 6K 6G 25 30 40 60 100 25 20 50 35 50 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — P–Channel MMBFJ175LT1 MMBFJ177LT1 6W 6Y 125 300 — — Table 37. TMOS FETs The following is a listing of small–signal surface mount TMOS FETs which exhibit low RDS(on) characteristics. Pinout: 1–Gate, 2–Source, 3–Drain RDS(on) @ ID D i Device M ki Marking VGS(th) Switching Time VDSS Volts Min Volts Max ton ns toff ns S l Style 60 100 50 60 20 20 30 0.8 0.8 0.5 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 3.0 2.8 1.5 2.5 2.4 2.4 2.4 10 20 20 20 2.5 2.5 2.5 10 40 20 20 15 16 16 21 21 21 21 21 21 21 50 20 20 20 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.7 2.4 2.0 2.4 1.0 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 16 16 16 16 21 21 21 21 mA VDSS Volts Min Volts Max ton ns toff ns S l Style 1000 1000 200 200 60 90 240 200 1.0 0.8 0.8 1.0 3.5 2.0 2.0 3.0 15 5.0 — 15 15 5.0 — 15 3 3 3 3 20 1.0 2.4 2.5 15 8 20 1.0 2.4 2.5 16 8 Ohm mA Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — N–Channel MMBF170LT1 BSS123LT1 BSS138LT1 2N7002LT1 MMBF0201NLT1 MGSF1N02LT1 MGSF1N03LT1 6Z SA J1 702 N1 N2 N3 5.0 6.0 3.5 7.5 1.0 0.085 0.09 200 100 200 500 300 1200 1200 Case 318–08 — TO–236 (SOT–23) — P–Channel BSS84LT1 MMBF0202PLT1 MGSF1P02LT1 MGSF1P02ELT1 PD P3 PC PE 6.0 1.4 0.35 0.16 100 200 1500 1500 Pinout: 1–Gate, 2–Drain, 3–Source, 4–Drain RDS(on) D i Device M ki Marking Ohm VGS(th) Switching Time Case 318E–04— SOT–223 — N–Channel MMFT960T1 MMFT6661T1 MMFT2406T1 MMFT107T1 FT960 T6661 T2406 FT107 1.7 4.0 10 14 Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 — N–Channel MMBF2201NT1 N1 1.0 300 Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 — P–Channel MMBF2202PT1 P3 2.2 200 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–24 Motorola Master Selection Guide Tuning and Switching Diodes CASE 29–04 TO–226AA (TO–92) Tuning Diodes — Abrupt Junction 1 Motorola supplies voltage–variable capacitance diodes serving the entire range of frequencies from HF through UHF. Used in RF receivers and transmitters, they have a variety of applications, including: • Phase–locked loop tuning systems • Local oscillator tuning • Tuned RF preselectors • RF filters • RF phase shifters • RF amplifiers • Automatic frequency control • Video filters and delay lines • Harmonic generators • FM modulators Two families of devices are available: Abrupt Junction and Hyper Abrupt Junction. The Abrupt Junction family includes devices suitable for virtually all tuned–circuit and narrow–range tuning applications throughout the spectrum. 1 3 2 STYLE 15 2 23 CASE 51–02 DO–204AA (DO–7) 1 CASE 182–02 TO–226AC (TO–92) 1 2 STYLE 1 2 Cathode 1 Anode STYLE 1 1 2 3 Cathode 3 CASE 318–08 TO–236AB SOT–23 1 Anode STYLE 8 1 2 1 3 2 3 1 STYLE 9 2 CASE 463–01 SOT–416/SC–90 Typical Characteristics Diode Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage 100 1000 50 C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) 70 1N5148,A 30 20 1N5144,A 10 1N5140,A 7 5 TA = 25°C f = 1 MHz 1N5450A MV1638 1N5456A MV1650 100 (See Tables 38 Thru 40) 10 1N5441A MV1620 3 1 2 0.6 1 2 4 6 10 20 40 60 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 1N5452A MV1642 0.1 1N5445A MV1628 1 10 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 100 MV2109 MMBV2109LT1 100 C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) 1000 MV2115 100 10 MV2101 MMBV2101LT1 1 0.1 MV2105 MMBV2105LT1 1 10 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 100 70 40 MV104G MMBV432LT1 MV104 20 TA = 25°C f = 1 MHz EACH DIODE 10 0.3 0.5 (See Tables 41 and 42) Motorola Master Selection Guide 1 2 3 5 10 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 20 30 (See Table 43) 5.1–25 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Tuning Diodes — Abrupt Junction (continued) Table 38. General–Purpose Glass Abrupt Tuning Diodes High Q Capacitance Ratio @ 4.0 Volts/60 Volts The following is a listing of axial leaded, general–purpose, abrupt tuning diodes. These devices exhibit high Q characteristics. CT @ VR = 4.0 V, 1.0 MHz D i (19) Device pF Min pF Nominal pF Max V(BR)R Volts Cap Ratio C4/C60 Min Q 4.0 V, 50 MHz Min 6.1 9.0 16.2 19.8 24.3 42.3 6.8 10 18 22 27 47 7.5 11 19.8 24.2 29.7 51.7 60 60 60 60 60 60 2.7 2.8 2.8 3.2 3.2 3.2 350 300 250 200 200 200 Case 51–02 — DO–204AA (DO–7) 1N5139 1N5140 1N5143 1N5144 1N5145 1N5148 Table 39. General–Purpose Glass Abrupt Tuning Diodes High Q Capacitance Ratio @ 2.0 Volts/30 Volts The following is a listing of axial leaded, general–purpose, abrupt tuning diodes. These devices exhibit very high Q characteristics. CT @ VR = 4.0 V, 1.0 MHz Device D i (20) pF Min pF Nominal pF Max VR(BR)R Volts Cap Ratio C2/C30 Min Q 4.0 V, 50 MHz Min 6.1 10.8 16.2 19.8 24.3 29.7 35.1 42.3 50.4 73.8 90 6.8 12 18 22 27 33 39 47 56 82 100 7.5 13.2 19.8 24.2 29.7 36.3 42.9 51.7 61.6 90.2 110 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 2.5 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.7 2.7 450 400 350 350 350 350 300 250 200 175 175 Case 51–02 — DO–204AA (DO–7) 1N5441A 1N5444A 1N5446A 1N5448A 1N5449A 1N5450A 1N5451A 1N5452A 1N5453A 1N5455A 1N5456A (19)Suffix A = 10.0% (20)Suffix B = 5.0% Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–26 Motorola Master Selection Guide Tuning Diodes — Abrupt Junction (continued) Table 40. General–Purpose Glass Abrupt Tuning Diodes Capacitance Ratio @ 2.0 Volts/20 Volts The following is a listing of axial leaded, general–purpose, abrupt tuning diodes. These devices exhibit high Q characteristics. CT @ VR = 4.0 V, 1.0 MHz D i Device pF Min pF Nominal pF Max V(BR)R Volts Cap Ratio C2/C20 Min Q 4.0 V, 50 MHz Typ 6.1 9.0 10.8 13.5 16.2 19.8 24.3 29.7 35.1 42.3 50.4 73.8 90 6.8 10 12 15 18 22 27 33 39 47 56 82 100 7.5 11 13.2 16.5 19.8 24.2 29.7 36.3 42.9 51.7 61.6 90.2 110 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 300 300 300 250 250 250 200 200 200 200 150 150 150 Case 51–02 — DO–204AA (DO–7) MV1620 MV1624 MV1626 MV1628 MV1630 MV1634 MV1636 MV1638 MV1640 MV1642 MV1644 MV1648 MV1650 Table 41. General–Purpose Plastic Abrupt Tuning Diodes Capacitance Ratio @ 2.0 Volts/30 Volts The following is a listing of plastic package, general–purpose, abrupt tuning diodes. These devices exhibit high Q characteristics. CT @ VR = 4.0 V, 1.0 MHz D i Device pF Min pF Nominal pF Max VR(BR)R Volts Cap Ratio C4/C30 Min Q 4.0 V, 50 MHz Typ 6.8 10 12 15 22 27 33 47 68 82 100 7.5 11 13.2 16.5 24.2 29.7 36.3 51.7 74.8 90.2 110 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.6 400 350 350 350 300 250 200 150 150 100 100 Case 182–02 — TO–226AC (TO–92) — 2–Lead MV2101 MV2103 MV2104 MV2105 MV2107 MV2108 MV2109 MV2111 MV2113 MV2114 MV2115 6.1 9.0 10.8 13.5 19.8 24.3 29.7 42.3 61.2 73.8 90 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–27 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Tuning Diodes — Abrupt Junction (continued) Table 42. Surface Mount Abrupt Tuning Diodes Capacitance Ratio @ 2.0 Volts/30 Volts The following is a listing of surface mount abrupt junction tuning diodes intended for general–purpose variable capacitance circuit applications. CT @ VR = 4.0 V, 1.0 MHz Device D i pF pF pF Min Nominal Max VR(BR)R Volts 6.1 9.0 10.8 13.5 19.8 24.3 29.7 6.8 10 12 15 22 27 33 7.5 11 13.2 16.5 24.2 29.7 36.3 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 Q Cap Ratio C2/C30 4.0 V, 50 MHz Min Typ 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 400 350 350 350 300 250 200 Case 318–08 — DO–236AB (SOT–23) MMBV2101LT1 MMBV2103LT1 MMBV2104LT1 MMBV2105LT1 MMBV2107LT1 MMBV2108LT1 MMBV2109LT1 Table 43. Abrupt Tuning Diodes for FM Radio — Dual The following is a listing of abrupt tuning diodes that are available as dual units in a single package. CT @ VR(22) D i Device pF Min pF Max 42 Volts Cap Ratio C3/C30 Min Q 3.0 V, 50 MHz Min V(BR)R Volts D i Device Marking S l Style 3.0 2.5 100 32 — 15 2.0 1.5(21) 100 14 M4B 9 Case 29–04 — TO–226AA (TO–92) MV104 37 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) MMBV432LT1 43 48.1 (21)C2/C8 (22)Each Diode Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–28 Motorola Master Selection Guide Tuning Diodes — Hyper–Abrupt Junction 2 The Hyper–Abrupt family exhibits higher capacitance, and a much larger capacitance ratio. It is particularly well suited for wider–range applications such as AM/FM radio and TV tuning. CASE 51–02 DO–204AA (DO–7) 1 Cathode CASE 182–02 TO–226AC (TO–92) 2 Anode CASE 318–08 TO–236AB SOT–23 3 Cathode 2 Anode STYLE 1 1 1 1 Cathode STYLE 1 2 3 1 1 Anode STYLE 8 2 4 CASE 318E–04 SOT–223 1 2 1 2, 4 3 STYLE 2 Typical Characteristics Diode Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage 40 36 16 14 C T , CAPACITANCE (pF) C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) 20 18 MMBV105GLT1 12 10 8 TA = 25°C f = 1 MHz 6 4 2 0 32 28 MMBV109LT1 MV209 24 20 16 12 8 4 0.3 0.5 1 2 3 5 10 20 0 30 1 3 10 30 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) Figure 1. Diode Capacitance Figure 2. Diode Capacitance Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–29 100 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Tuning Diodes — Hyper–Abrupt Junction (continued) 10 9 C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) 40 32 MMBV409LT1 MV409 24 16 8 0 1 3 10 20 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 8 7 6 MMBV809LT1 5 4 3 2 1 0 0.5 1 2 Figure 3. Diode Capacitance Figure 4. Diode Capacitance 50 36 32 28 C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) 40 MMBV3102LT1 24 20 16 12 TA = 25°C f = 1 MHz 8 4 0 0.3 0.5 1 2 3 5 10 20 40 f = 1 MHz 20 10 0 30 MMBV609LT1 30 1 2 7 10 20 Figure 5. Diode Capacitance Figure 6. Diode Capacitance Each Die 500 C T , CAPACITANCE (pF) 500 100 50 4 30 40 MVAM109/MV7005T1 1000 C T , CAPACITANCE (pF) 5 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) MVAM108 1 3 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 1000 10 3 4 5 8 10 15 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 100 50 10 8 1 3 5 7 9 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) Figure 7. Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage Figure 8. Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–30 Motorola Master Selection Guide Tuning Diodes — Hyper–Abrupt Junction (continued) MVAM115 MVAM125 500 500 C T , CAPACITANCE (pF) 1000 C T , CAPACITANCE (pF) 1000 100 50 10 2 6 10 14 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 100 50 10 18 Figure 9. Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage 2 6 10 14 18 22 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 26 Figure 10. Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) 500 TA = 25°C f = 1 MHz 300 200 100 MV1405 50 30 20 MV1403 10 MV1404 1 MV7404T1 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 9 10 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) Figure 11. Diode Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage Table 44. Hyper–Abrupt Tuning Diodes for Telecommunications — Single The following is a listing of hyper–abrupt tuning diodes intended for high frequency, FM radio, and TV tuner applications. CT @ VR (f = 1.0 MHz) D i Device pF Min pF Max Cap Ratio @ VR Q 50 MHz Max V(BR)R Volts Device D i Marking Case C Style CV Curve Fig Volts Min Max Volts 3.0 V Min 3.0 3.0 5.0 1.5 6.5 2.0 3/25 3/8 200 200 — — 30 20 — — 1 1 2 3 25 3.0 3.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 1.5 1.8 4.5 6.5 6.5 1.9 2.6 — 3/25 3/25 3/8 2/8 3/25 200 200 200 300 200 — — — — — 30 30 20 20 30 M4E M4A X5 5K M4C 8 8 8 8 8 1 2 3 4 5 3.0 5.0 6.5 3/25 200 — 30 M4A 8 — Case 182–02 — TO–226AC (TO–92) MV209 MV409 26 26 32 32 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) MMBV105GLT1 MMBV109LT1 MMBV409LT1 MMBV809LT1 MMBV3102LT1 1.5 26 26 4.5 20 2.8 32 32 6.1 25 Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 MBV109T1 26 32 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–31 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Tuning Diodes — Hyper–Abrupt Junction (continued) Table 45. Hyper–Abrupt Tuning Diodes for Communications — Dual CT @ VR (f = 1.0 MHz) D i Device pF Min pF Max Cap Ratio @ VR Q Volts Min Max Volts 3.0 V Min 3.0 1.8 2.4 3/8 250 50 MHz Max V(BR)R Volts Device D i Marking Case C Style CV Curve Fig — 20 5L 9 6 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) MMBV609LT1 26 32 Table 46. Hyper–Abrupt Tuning Diodes for Low Frequency Applications — Single The following is a listing of AM, hyper–abrupt tuning diodes that have a large capacity range and are designed for low frequency circuit applications. CT @ 1.0 MHz D i Device pF Min Cap Ratio @ VR pF Max Volts Min 560 520 560 560 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 15 12 15 15 Volts V(BR)R Volts S l Style CV Curve Figure 1.0/8.0 1.0/9.0 1.0/15 1.0/25 12 15 18 28 1 1 1 1 7 8 9 10 Case 182–02— TO–226AC (TO–92) MVAM108 MVAM109 MVAM115 MVAM125 440 400 440 440 Table 47. Hyper–Abrupt High Capacitance Voltage Variable Diode — Surface Mount The following are high capacitance voltage variable diodes intended for low frequency applications and circuits requiring large tuning capacitance. CT @ f = 1.0 MHz D i Device V(BR)R Volts IR nA Min pF Max pF Cap Ratio C R i Min Q Min S l Style CV Curve Figure 400 96 520 144 12(26) 10(27) 150(28) 200(29) 2 2 8 11 Case 318E–04— SOT–223 Pinout: 1–Anode, 2, 4–Cathode, 3–NC MV7005T1 MV7404T1 15 12 100 100 Table 48. Hyper–Abrupt High Capacitance Tuning Diodes — Axial Lead Glass Package CT @ VR D i Device pF Min pF Max 144 210 300 Volts Cap Ratio C2/C10 Min Q 2.0 V, 1.0 MHz Min V(BR)R Volts Style CV Curve Figure 2.0 2.0 2.0 10 10 10 200 200 200 12 12 12 1 1 1 11 11 11 Case 51–02 — DO–204AA (DO–7) MV1404 MV1403 MV1405 96 140 200 (26) V = 1.0 V/V = 9.0 V R R (27) V = 2.0 V/V = 10 V R R (28) V = 1.0 V, f = 1.0 MHz R (29) V = 2.0 V, f = 1.0 MHz R Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–32 Motorola Master Selection Guide Schottky Diodes CASE 182–02 TO–226AC (TO–92) Schottky diodes are ideal for VHF and UHF mixer and detector applications as well as many higher frequency applications. They provide stable electrical characteristics by eliminating the point–contact diode presently used in many applications. 1 CASE 425–04 SOD–123 STYLE 1 STYLE 1 2 2 Cathode 1 Cathode 1 Anode 6 CASE 419–02 SC–70/SOT–323 1 1 3 2 Single 3 1 2 Anode 5 4 CASE 419B–01, STYLE 6 SOT–363 3 CASE 318–08 TO–236AB SOT–23 2 STYLE 8 STYLE 9 1 STYLE 11 3 1 21 2 Single Series 3 Common Cathode 3 STYLE 12 STYLE 19 Cathode 1 Anode 3 2 1 Series 3 2 Cathode Typical Characteristics Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage 2.8 TA = 25°C MBD101 MMBD101LT1 MMBD352LT1* MMBD353LT1* MMBD354LT1* 0.9 TA = 25°C 2.4 C T , CAPACITANCE (pF) C T , CAPACITANCE (pF) 1 0.8 0.7 2 MBD301, MMBD301LT1 1.6 1.2 0.8 0.4 0.6 MBD701, MMBD701LT1 0 0 1 2 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) 3 4 0 * EACH DIODE 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) (See Table 49) Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–33 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Schottky Diodes (continued) Table 49. Schottky Diodes The following is a listing of Schottky diodes that exhibit low forward voltage drop for improved circuit efficiency. CT @ VR pF Max VF @ 10 mA Volts Max IR @ VR nA Max Minority Lifetime pS (TYP) Device Marking S l Style 1.0 @ 20 V 1.5 @ 15 V 1.0 @ 0 V 1.0 0.6 0.6 200 @ 35 V 200 @ 25 V 250 @ 3.0 V 15 15 — — — — 1 1 1 70 30 7.0 7.0 7.0 7.0 7.0 30 1.0 @ 20 V 1.5 @ 15 V 1.0 @ 0 V 1.0 @ 0 V 1.0 @ 0 V 1.0 @ 0 V 1.0 @ 0 V 1.5 @ 1.5 V 1.0 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 200 @ 35 V 200 @ 25 V 250 @ 3.0 V 250 @ 3.0 V 250 @ 3.0 V 250 @ 3.0 V 250 @ 3.0 V 200 @ 25 V 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 5H 4T 4M M5G M4F M6H MJ1 5N 8 8 8 11 19 9 12 11 70 30 4 1.0 @ 20 V 1.5 @ 15 V 1.0 @ 0 V 1.2 0.6 0.6 0.2 @ 35 V 0.2 @ 25 V 0.25 @ 3 V 15 15 15 5H 4T 4M 1 1 1 1.5 @ 15 V 1.0 @ 20 V 0.6 1.0 0.2 @ 25 V 0.2 @ 35 V — — 4T 5H 2 2 V(BR)R Volts D i Device Case 182–02 — TO–226AC (TO–92) MBD701 MBD301 MBD101 70 30 7.0 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) MMBD701LT1 MMBD301LT1 MMBD101LT1 MMBD352LT1 (23) MMBD353LT1 (23) MMBD354LT1 (23) MMBD355LT1 (23) MMBD452LT1 (23) Case 425–04 — (SOD–123) MMSD701T1 MMSD301T1 MMSD101T1 Case 419–02 — (SC–70/SOT–323) MMBD330T1 MMBD770T1 30 70 (23) Dual Diodes Case 419B–01 — SOT–363 – Duals V(BR)R D i Device IR VF M ki Marking Min Volts @ IBR (µA) Max (µA) @ VR Volts Min Volts Max Volts @ IF (mA) CT(30) Max (pF) trr Max (ns) Case C Style M4 T4 H5 7 30 70 10 10 10 200 200 200 25 25 25 — — — 0.6 0.4 0.5 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.5 1.0 — — — 6 6 6 MBD110DWT1 MBD330DWT1 MBD770DWT1 (30) V = 0 V, f = 1.0 MHz R Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–34 Motorola Master Selection Guide Switching Diodes Small–signal switching diodes are intended for low current switching and steering applications. Hot–Carrier, PIN and general–purpose diodes allow a wide selection for specific application requirements. 1 CASE 29–04 TO–226AA (TO–92) 2 CASE 182–02 TO–226AC (TO–92) 1 2 3 STYLE 3 1 2 STYLE 1 3 Typical Characteristics 1 10 C T , DIODE CAPACITANCE (pF) 2 Cathode STYLE 4 Capacitance versus Reverse Voltage 1 Anode 2 TA = 25°C f = 1 MHz 3 2 3 MPN3404 CASE 318–08 TO–236AB SOT–23 1 2 1 0.5 0.3 0.2 MMBV3401LT1 20 V MAX VR STYLE 8 MPN3700 MMBV3700LT1 1 STYLE 12 3 1 2 SINGLE 0 0 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 3 COMMON ANODE 54 VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) (See Table 50) STYLE 9 STYLE 18 1 2 2 STYLE 1 SINGLE 1 Cathode 2 Anode 3 COMMON CATHODE CASE 425–04 SOD–123 STYLE 11 STYLE 19 1 ANODE 3 3 1 3 2 CATHODE 3 1 2 3 SERIES 3 SERIES 2 3 CASE 463–01 SOT–416/SC–90 CASE 318D–04 SC–59 1 2 1 CATHODE STYLE 4 1 2 ANODE STYLE 5 STYLE 2 2 1 CASE 419–02 SC–70/SOT–323 3 2 2 3 SINGLE STYLE 5 1 2 1 2 STYLE 4 STYLE 5 1 3 STYLE 3 1 SINGLE STYLE 4 SINGLE 3 STYLE 2 2 2 3 COMMON CATHODE Motorola Master Selection Guide 1 3 COMMON CATHODE 2 3 COMMON ANODE 3 COMMON ANODE 5.1–35 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Switching Diodes (continued) Table 50. PIN Switching Diodes The following PIN diodes are designed for VHF band switching and general–purpose low current switching applications. CT @ VR @ 1.0 MHz V(BR)R Volts Min D i Device Series Resistance Ohm Max D i Device Marking S l Style pF Max Volts IR @ VR µA Max 1.0 2.0 20 15 0.1 @ 150 0.1 @ 25 V 1.0 @ 10 mA 0.85 @ 10 mA — — 1 1 1.0 1.0 20 20 0.1 @ 150 0.1 @ 25 V 1.0 @ 10 mA 0.7 @ 10 mA 4R 4D 8 8 Case 182–02 — TO–226AC (TO–92) MPN3700 MPN3404 200 20 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) MMBV3700LT1 MMBV3401LT1 200 35 Table 51. General–Purpose Signal and Switching Diodes — Single The following is a listing of small–signal switching diodes in surface mount packages. These diodes are intended for low current switching and signal steering applications. V(BR)R D i Device M ki Marking Min Volts @ IBR (µA) IR VF CT(30) trr Max (µA) @ VR Volts Min Volts Max Volts @ IF (mA) Max (pF) Max (ns) Case Style Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) BAS21LT1 MMBD914LT1 BAS16LT1 MMBD6050LT1 BAL99LT1 JS 5D A6 5A JF 250 100 75 70 70 100 100 100 100 100 0.1 5.0 1.0 0.1 2.5 200 75 75 50 70 — — — 0.85 — 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.1 1.0 100 10 50 100 50 5.0 4.0 2.0 2.5 1.5 50 4.0 6.0 4.0 6.0 8 8 8 8 18 40 40 100 100 0.1 0.1 35 35 — — 1.2 1.2 100 100 2.0 2.0 3.0 3.0 4 2 75 40 80 100 1.0 100 100 100 0.02 0.1 0.1 5.0 20 35 75 75 — — — — 1.25 1.2 1.2 1.0 150 100 100 10 2.0 2.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 3.0 3.0 4.0 2 2 2 2 100 100 — 100 100 — 5.0 5.0 0.5 75 75 80 — — — 1.0 1.0 1.2 10 10 100 4.0 4.0 2.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 1 1 1 Case 318D–04 — SC–59 M1MA151AT1 M1MA151KT1 MA MH Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 BAS16WT1 M1MA141KT1 M1MA142KT1 M1MA174T1 A6 MH MI J6 Case 425–04— SOD–123 MMSD914T1 MMSD4148T1 MMSD71RKT1 5D 5I 6S (30) V = 0 V, f = 1.0 MHz R Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–36 Motorola Master Selection Guide Switching Diodes (continued) Table 52. General–Purpose Signal and Switching Diodes — Dual The following is a listing of small–signal switching diodes in surface mount packages. These diodes are intended for low current switching and signal steering applications. V(BR)R D i Device M ki Marking Min Volts @ IBR (µA) IR VF CT(30) trr Max (µA) @ VR Volts Min Volts Max Volts @ IF (mA) Max (pF) Max (ns) Case Style Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) MMBD7000LT1 MMBD2836LT1 MMBD2838LT1 BAV70LT1 BAV99LT1 BAW56LT1 MMBD6100LT1 BAV74LT1 MMBD2835LT1 MMBD2837LT1 M5C A2 A6 A4 A7 A1 5BM JA A3 A5 100 75 75 70 70 70 70 50 35 35 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 5.0 100 100 1.0 0.1 0.1 5.0 2.5 2.5 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 50 50 50 70 70 70 50 50 30 30 0.75 — — — — — 0.85 — — — 1.1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.1 1.0 1.0 1.0 100 10 10 50 50 50 100 100 10 10 1.5 4.0 4.0 1.5 1.5 2.0 2.5 2.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 6.0 4.0 6.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 11 12 9 9 11 12 9 9 12 9 40 40 100 100 0.1 0.1 35 35 — — 1.2 1.2 100 100 15 2.0 10 3.0 5 3 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 0.1 0.1 2.5 5.0 2.5 2.5 0.1 0.1 75 75 70 70 70 70 35 35 — — — — — — — — 1.2 1.2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.2 1.2 100 100 50 50 50 50 100 100 2.0 15 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.5 2.0 15 3.0 10 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 3.0 10 5 4 4 5 9 10 5 4 70 — 1.2 100 3.5 4.0 4 70 — 1.2 100 3.5 4.0 5 CT(30) trr Case 318D–04 — SC–59 M1MA151WAT1 M1MA151WKT1 MN MT Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 M1MA142WKT1 M1MA142WAT1 BAW56WT1 BAV70WT1 BAV99WT1 BAV99RWT1 M1MA141WKT1 M1MA141WAT1 MU MO A1 A4 A7 F7 MT MN 80 80 70 70 70 70 40 40 Case 463–01 — SOT–416/SC–90 (Common Anode) DAP222 P9 80 100 100 Case 463–01 — SOT–416/SC–90 (Common Cathode) DAN222 N9 80 100 100 Table 53. Low–Leakage Medium Speed Switching Diodes — Single V(BR)R D i Device M ki Marking Min Volts @ IBR (µA) IR VF Max (nA) @ VR Volts Min Volts Max Volts @ IF (mA) Max (pF) Max (ns) Case Style 100 100 5.0 0.5 75 30 — — 1.0 0.95 10 10 2.0 2.0 3000 3000 8 6 30 100 0.5 30 — 0.95 10 2.0 3000 2 30 100 0.5 30 — 0.95 10 2.0 3000 2 30 100 0.5 30 — 0.95 10 2.0 3000 1 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) BAS116LT1 MMBD1000LT1 JV AY 75 30 Case 419–02 — (SOT–323)/(SC–70) MMBD2000T1 DH Case 318D–04 — (SC–59) MMBD3000T1 XP Case 425–04 — (SOD–123) MMSD1000T1 4K Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–37 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Switching Diodes (continued) Table 54. Low–Leakage Medium Speed Switching Diodes — Dual V(BR)R D i Device M ki Marking Min Volts @ IBR (µA) IR VF CT(30) trr Max (nA) @ VR Volts Min Volts Max Volts @ IF (mA) Max (pF) Max (ns) Case Style 5.0 5.0 5.0 0.5 0.5 70 70 70 30 30 — — — — — 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.95 0.95 10 10 10 10 10 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 3000 3000 3000 3000 3000 9 11 12 12 9 100 100 0.5 0.5 30 30 — — 0.95 0.95 10 10 2.0 2.0 3000 3000 4 5 100 100 0.5 0.5 30 30 — — 0.95 0.95 10 10 2.0 2.0 3000 3000 5 3 Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) BAV170LT1 BAV199LT1 BAW156LT1 MMBD1005LT1 MMBD1010LT1 JX JY JZ A3 A5 70 70 70 30 30 100 100 100 100 100 Case 419–02 — (SOT–323)/(SC–70) — DUAL MMBD2005T1 MMBD2010T1 DI DP 30 30 Case 318D–04 — (SC–59) — DUAL MMBD3005T1 MMBD3010T1 XQ XS 30 30 (30) V = 0 V, f = 1.0 MHz R Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–38 Motorola Master Selection Guide Multiple Switching Diodes Multiple diode configurations utilize monolithic structures fabricated by the planar process. They are designed to satisfy fast switching requirements as in core driver and encoding/decoding applications where their monolithic configurations offer lower cost, higher reliability and space savings. 14 14 16 16 1 1 1 1 CASE 646–06 PIN DIP PLASTIC CASE 648–08 PIN DIP PLASTIC CASE 751A–03 SO–14 PLASTIC CASE 751B–05 SO–16 PLASTIC Diode Array Diagrams Dual 10 Diode Array 7 1 3 4 12 13 14 5 8 9 10 11 2 6 8 Diode Array (Common Cathode) 14 8 Diode Array (Common Anode) 14 1 2 3 5 9 10 13 14 1 4 5 6 12 7 2 2 9 11 12 3 5 7 8 9 11 12 3 5 7 4 5 6 7 8 16 15 14 13 12 11 12 9 Isolated 7 Diode Array 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 6 1 2 3 8 NC Pin 1, 4, 6, 10, 13 3 1 16 Diode Array 8 2 5 3 8 7 Isolated 8 Diode Array NC Pin 1, 4, 6, 10, 13 2 11 Dual 10 Diode Array 7 4 1 1 8 9 14 11 12 Dual 8 Diode Array 8 2 3 4 5 14 9 10 7 NC Pin 6, 13 NC Pin 4,6,10,13 Motorola Master Selection Guide 11 12 5.1–39 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Multiple Switching Diodes (continued) Table 55. Diode Arrays Case 646 — TO–116 D i Device MAD130P MAD1103P MAD1107P MAD1109P F Function i Pin Connections Diagram Number Dual 10 Diode Array 16 Diode Array Dual 8 Diode Array 7 Isolated Diode Array 1 3 6 8 8 Isolated Diode Array 7 Dual 10 Diode Array 16 Diode Array 8 Diode Common Cathode Array 8 Diode Common Anode Array Dual 8 Diode Array 7 Isolated Diode Array 2 3 4 5 6 8 8 Isolated Diode Array 7 Case 648–08 MAD1108P Case 751A–03— SO–14 MMAD130 MMAD1103 MMAD1105 MMAD1106 MMAD1107 MMAD1109 Case 751B–05 — SO–16 MMAD1108 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–40 Motorola Master Selection Guide 3 3 1 1 2 2 CASE 318–08 TO–236AB SOT–23 CASE 318D–04 SC–59 3 Plastic–Encapsulated Surface Mount Devices 1 2 CASE 425–04 SOD–123 Energy. It’s something Motorola is putting a lot of energy into helping save. That’s why we’re introducing our GreenLine portfolio of devices, featuring energy–conserving traits superior to those of our existing line of standard parts for the same usage. GreenLine devices can actually help reduce the power demands of your products. CASE 419–02 SC–70/SOT–323 • Low–Leakage Switching Diodes: With reverse leakage specifications guaranteed to 500 pA, they help extend battery life, making them ideal for small battery–operated systems in which standby power is essential. Applications include ESD protection, reverse voltage protection, and steering logic. • Small Signal HDTMOS: These devices provide our lowest ever drain–source resistance versus package size. Lower rDS(on) means less wasted energy through dissipation loss, making them especially effective for low–current applications where energy conservation is crucial, such as low current switchmode power supplies, uninterruptable power supplies (UPS), power management systems, and bias switching. This makes them ideal for portable computer–type products or any system where the combination of power management and energy conservation is key. • Bipolar Output Driver Transistors: Offering ultra–low collector saturation voltage, they deliver more energy to the intended load with less power wasted through dissipation loss. They are especially effective in today’s lower voltage battery–powered applications, and prolong battery life in portable and hand–held communications and personal digital equipment. Save Energy — Save Money In an increasingly power–hungry world, Motorola’s GreenLine portfolio makes powerful sense. So much sense that we plan to continue adding devices to the portfolio. Chances are, there are Motorola GreenLine devices applicable to one or more of your products — ones that can help save energy, dollars — and the environment. Wide Range of Applications Currently, our portfolio consists of three families. Table 56. Bipolar Driver Transistor — PNP These offer ultra–low collector saturation voltage. Pinout: 1–Base, 2–Emitter, 3–Collector hFE@ IC D i T Device Type MMBT1010LT1 MSD1010T1 M ki Marking C Case V(BR)CEO VCE(sat) VBE(sat) Min Max mA GLP GLP SOT–23 SC–59 15 15 0.1 0.1 1.1 1.1 300 300 600 600 100 100 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–41 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes GreenLine (continued) Table 57. Low Leakage Switching Diodes These offer reverse leakage specifications guaranteed to 500 pA. Versions available in single and dual. IR V(BR)R M ki Marking C Case Style Min Volts @ IBR (µA) Max (nA) @ VR Volts MMBD1000LT1 MMBD1005LT1 MMBD1010LT1 AY A3 A5 SOT–23 SOT–23 SOT–23 Single Dual Anode Dual Cathode 30 30 30 100 100 100 0.5 0.5 0.5 30 30 30 MMBD2000T1 MMBD2005T1 MMBD2010T1 DH DI DP SC–70 SC–70 SC–70 Single Dual Anode Dual Cathode 30 30 30 100 100 100 0.5 0.5 0.5 30 30 30 MMBD3000T1 MMBD3005T1 MMBD3010T1 XP XQ XS SC–59 SC–59 SC–59 Single Dual Anode Dual Cathode 30 30 30 100 100 100 0.5 0.5 0.5 30 30 30 MMSD1000T1 4K SOD–123 Single 30 100 0.5 30 D i T Device Type Table 58. Small Signal HDTMOS These provide the lowest drain–source resistance versus package size. VGS(th) RDS(on) D i T Device Type M ki Marking Ch Channel l Ohm mA VDSS Switching Time Volts Min Volts Max t(on) ns t(off) ns S l Style Case 318–08 — TO–236AB (SOT–23) — P–Channel and N–Channel MMBF0201NLT1 MMBF0202PLT1 MGSF1N02LT1 MGSF1N03LT1 MGSF1P02LT1 MGSF1P02ELT1 N1 P3 — — — — N P N N P P 1.0 1.4 0.08 0.09 0.20 0.16 300 200 2000 2000 1500 1500 20 20 20 30 20 20 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.7 2.4 2.4 2.4 2.4 2.4 1.0 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 15 16 16 16 16 16 21 21 21 21 21 21 P N 1.5 0.7 200 300 20 20 1.0 1.0 2.4 2.4 2.5 2.5 16 15 7 7 Case 419–02 — SC–70/SOT–323 MMBF2202PT1 MMBF2201NT1 P3 N1 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes 5.1–42 Motorola Master Selection Guide Small Signal Multi–integrated Devices CASE 318–08 SOT–23 CASE 318A–05 SOT–143 VCC (3) Vout R1 (3) Vin 1.0 k Q1 6.8 V (1) R2 33 k GND 6 Vref (4) R3 Q2 Iout (2) 1 R4 (2) 5 4 2 3 CASE 419B–01 SOT–363 GND (1) INTERNAL CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS Table 59. Low Voltage Bias Stabilizer A silicon SMALLBLOCK integrated circuit which maintains stable bias current in various discrete bipolar junction and field effect transistors. VCC (Volts) D i Type Device T M ki Marking Min Max ICC µA Vref Volts ∆Vref Volts Case 318A–05 — SOT–143 MDC5000T1 E5 1.8 10 200 2.1 ± 50 E6 1.8 10 200 2.1 ± 50 Case 419B–01 — SOT–363 MDC5001T1 Table 60. Integrated Relay/Solenoid Driver Monolithic circuit block to switch 3.0 V to 5.0 V relays. It is intended to replace an array of three to six discrete components. VCC (Volts) D i Type Device T Vin (Volts) Min Max Min Max Vsat (Volts) Iin (mA) IC(on) (mA) 2.0 5.5 2.0 5.5 0.4 2.5 250 Case 318–08 — SOT–23 MDC3105LT1 Devices listed in bold, italic are Motorola preferred devices. Motorola Master Selection Guide 5.1–43 Small Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes