Chapter 18 ACID-BASE REACTIONS
advertisement
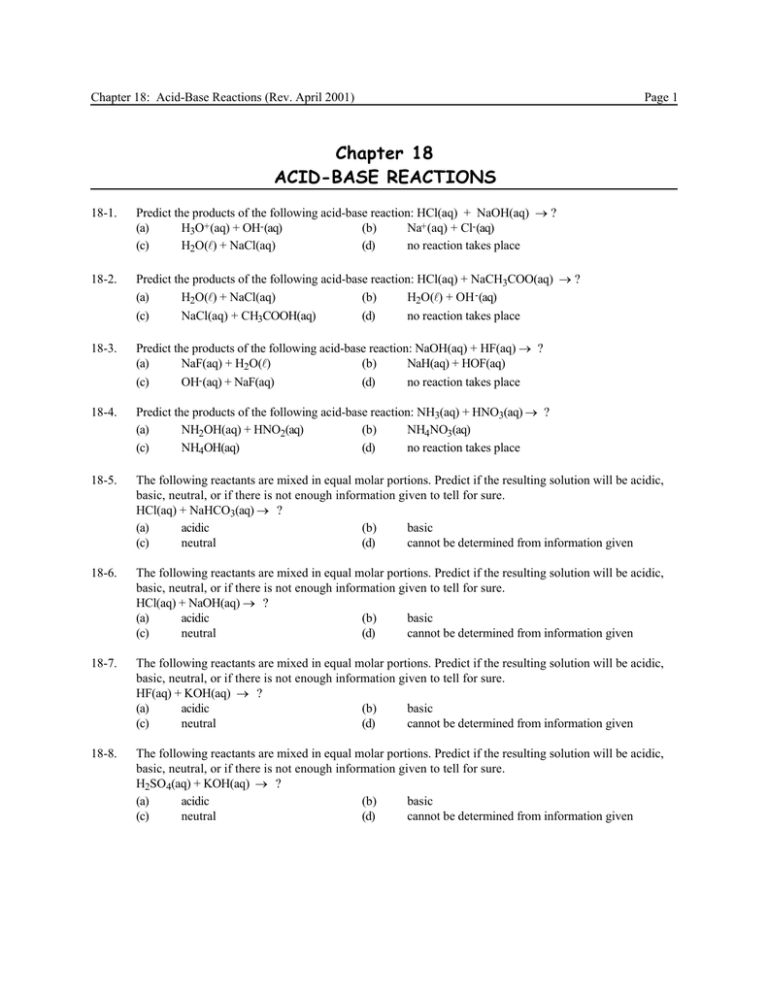
Chapter 18: Acid-Base Reactions (Rev. April 2001) Page 1 Chapter 18 ACID-BASE REACTIONS 18-1. Predict the products of the following acid-base reaction: HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → ? (a) H3O+ (aq) + OH- (aq) (b) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) (c) H2O(l) + NaCl(aq) (d) no reaction takes place 18-2. Predict the products of the following acid-base reaction: HCl(aq) + NaCH3COO(aq) → ? (a) H2O(l) + NaCl(aq) (b) H2O(l) + OH - (aq) (c) NaCl(aq) + CH3COOH(aq) (d) no reaction takes place 18-3. Predict the products of the following acid-base reaction: NaOH(aq) + HF(aq) → ? (a) NaF(aq) + H2O(l) (b) NaH(aq) + HOF(aq) (c) OH (aq) + NaF(aq) (d) no reaction takes place 18-4. Predict the products of the following acid-base reaction: NH3(aq) + HNO3(aq) → ? (a) NH2OH(aq) + HNO2(aq) (b) NH4NO3(aq) (c) NH4OH(aq) (d) no reaction takes place 18-5. The following reactants are mixed in equal molar portions. Predict if the resulting solution will be acidic, basic, neutral, or if there is not enough information given to tell for sure. HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) → ? (a) acidic (b) basic (c) neutral (d) cannot be determined from information given 18-6. The following reactants are mixed in equal molar portions. Predict if the resulting solution will be acidic, basic, neutral, or if there is not enough information given to tell for sure. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → ? (a) acidic (b) basic (c) neutral (d) cannot be determined from information given 18-7. The following reactants are mixed in equal molar portions. Predict if the resulting solution will be acidic, basic, neutral, or if there is not enough information given to tell for sure. HF(aq) + KOH(aq) → ? (a) acidic (b) basic (c) neutral (d) cannot be determined from information given 18-8. The following reactants are mixed in equal molar portions. Predict if the resulting solution will be acidic, basic, neutral, or if there is not enough information given to tell for sure. H2SO4(aq) + KOH(aq) → ? (a) acidic (b) basic (c) neutral (d) cannot be determined from information given Chapter 18: Acid-Base Reactions (Rev. April 2001) Page 2 18-9. The following reactants are mixed in equal molar portions. Predict if the resulting solution will be acidic, basic, neutral, or if there is not enough information given to tell for sure. CH3COOH(aq) + NH3(aq) → ? (a) acidic (b) basic (c) neutral (d) cannot be determined from information given 18-10. The following reactants are mixed in equal molar portions. Predict if the resulting solution will be acidic, basic, neutral, or if there is not enough information given to tell for sure. HCl(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → ? (a) acidic (b) basic (c) neutral (d) cannot be determined from information given 18-11. We mix 100. mL of 0.10 M HCl and 100. mL of 0.10 M NaCN. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (HCN) = 4.0 x 10-10 (a) 8.65 (b) 5.20 (c) 8.80 (d) 5.35 18-12. We mix 100. mL of 0.20 M HBr and 50.0 mL of 0.40 M NaClO. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (HClO) = 3.5 x 10-8 (a) 9.83 (b) 4.07 (c) 4.17 (d) 3.92 We mix 50.0 mL of 0.050 M HNO3 and 25.0 mL of 0.10 M NaCH3COO. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (CH3COOH) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 3.11 (b) 3.02 (c) 2.87 (d) 10.89 18-13. 18-14. We mix 55.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl and 110. mL of 0.050 M NH3. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (NH4+ ) = 5.6 x 10-10 (a) 5.13 (b) 5.36 (c) 8.64 (d) 5.98 18-15. We add 1.00 mL of 10.0 M HNO 3 to 100. mL of 0.10 M NaHCOO. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (HCOOH) = 1.8 x 10 -4 (a) 11.6 (b) 3.45 (c) 1.16 (d) 2.38 18-16. We add 100. mL of 0.10 M NaOH to 100. mL of 0.10 M HClO. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(ClO- ) = 2.9 x 10-7 (a) 10.3 (b) 3.76 (c) 10.1 (d) 3.91 18-17. We add 200. mL of 0.10 M KOH to 50.0 mL of 0.40 M HF. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(F- ) = 1.4 x 10-11 (a) 8.02 (b) 5.97 (c) 9.32 (d) 8.37 Chapter 18: Acid-Base Reactions (Rev. April 2001) Page 3 18-18. We add 100. mL of 0.50 M NaOH to 50.0 mL of 1.00 M NH4Cl. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(NH3) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 11.6 (b) 11.4 (c) 2.61 (d) 9.34 18-19. We add 1.00 mL of 10.0 M NaOH to 50.0 mL of 0.20 M HNO2. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(NO2- ) = 2.2 x 10-11 (a) 8.32 (b) 5.68 (c) 9.17 (d) 10.3 18-20. We add 24.0 mL of 0.45 M NaOH to 20.0 mL of 0.54 M HCN. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(CN- ) = 2.5 x 10-5 (a) 6.83 (b) 11.6 (c) 10.8 (d) 11.4 18-21. We have a solution of NH 3. What effect will addition of HCl have on the pH of the solution? (a) increase pH (b) decrease pH (c) no effect (d) cannot tell from information given 18-22. We have a solution of NH 4Cl. What effect will addition of NH3 have on the pH of the solution? (a) increase pH (b) decrease pH (c) no effect (d) cannot tell from information given 18-23. We have a solution of acetic acid. What effect will addition of sodium acetate have on the pH of the solution? (a) increase pH (b) decrease pH (c) no effect (d) cannot tell from information given 18-24. We have a solution of NH 4Cl. What effect will addition of NaCl have on the pH of the solution? (a) increase pH (b) decrease pH (c) no effect (d) cannot tell from information given 18-25. We have 100. mL of a 0.10 M solution of CH3COOH. It has a pH = 2.9. If we add 0.820 g of NaCH3COO what will the pH be? (Ka (CH3COOH) = 1.8 x 10-5 ) (a) 2.9 (b) 1.8 (c) 3.7 (d) 4.7 18-26. We have 250. mL of a 0.20 M solution of NH4Cl. It has a pH = 4.97. If we add 10.0 mL of a 1.00 M NH3 solution, what will the pH be? Ka (NH4+ ) = 5.6 x 10-10 (a) 10.0 (b) 4.3 (c) 8.6 (d) 5.7 18-27. We have 500. mL of a 0.35 M solution of HCN. It has a pH of 4.92. If we add 0.50 g of NaCN(s), what will the pH of the solution be? Ka (HCN) = 4.0 x 10-10 (a) 8.2 (b) 9.4 (c) 10.6 (d) 3.7 Chapter 18: Acid-Base Reactions (Rev. April 2001) Page 4 18-28. We have 200. mL of a 0.53 M solution of NaF. We add to this solution 100. mL of a 0.20 M solution of HF. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (HF) = 7.2 x 10-4 (a) 3.1 (b) 3.9 (c) 2.4 (d) 7.9 18-29. We have 100. mL of water. We add to this 0.50 g of NaCH3COO and 1.00 mL of 1.00 M CH3COOH. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (CH3COOH) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 8.8 (b) 4.7 (c) 4.0 (d) 5.6 18-30. We have 50.0 mL of water and add to it 2.0 g of NH 4Cl and 3.00 mL of 0.50 M NH3. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(NH3) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 9.26 (b) 4.74 (c) 7.86 (d) 5.53 18-31. We have 500. mL of a 0.10 M NH3 solution. We add 1.0 mL of 10.0 M HCl. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(NH3) =1.8 x 10-5 (a) 5.35 (b) 4.15 (c) 8.64 (d) 9.85 18-32. We have 100. mL of a 0.20 M NaF solution and add to it 10.0 mL of 0.50 M HCl. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(F- ) =1.4 x 10-11 (a) 11.4 (b) 3.6 (c) 3.1 (d) 2.7 18-33. We have 250. mL of 0.33 M NaClO. We add to this solution 50.0 mL of 0.10 M HNO3. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(ClO- ) = 2.9 x 10-7 (a) 9.1 (b) 8.6 (c) 6.3 (d) 5.4 18-34. We have 50.0 mL of 0.58 M NaCN. We add to this solution 10.0 mL of 1.0 M HClO4. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Kb(CN- ) = 2.5 x 10-5 (a) 4.9 (b) 5.3 (c) 9.1 (d) 9.7 18-35. We have 100. mL of a 0.10 M HCN solution. We add to this solution 50.0 mL of 0.10 M NaOH. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (HCN) = 4.0 x 10-10 (a) 9.4 (b) 10.2 (c) 4.6 (d) 7.0 18-36. We have 250. mL of a 0.20 M HF solution. We add to this solution 20. mL of 0.50 M KOH. What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (HF) = 7.2 x 10-4 (a) 10.1 (b) 12.1 (c) 2.5 (d) 3.7 Chapter 18: Acid-Base Reactions (Rev. April 2001) Page 5 18-37. We have 555 mL of a 0.37 M NH4Cl solution. We add to this solution 1.00 g of pure NaOH(s). What is the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (NH4+ ) = 5.6 x 10-10 (a) 6.2 (b) 8.4 (c) 10.1 (d) 9.3 18-38. We have 100. mL of a 0.10 M solution of CH3COOH. How many grams of NaCH3COO must be added to make a buffer solution of pH = 5.00? Ka (CH3COOH) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 0.88 (b) 24.7 (c) 0.56 (d) 1.48 18-39. We have 300. mL of a 0.20 M solution of HF. How many grams of solid KF should be added to make a buffer of pH = 3.00? K a (HF) = 7.2 x 10-4 (a) 2.51 (b) 10.8 (c) 0.45 (d) 8.45 18-40. We have 500. mL of a 0.50 M solution of HNO2. How many grams of NaNO 2 should be added to make a buffer of pH = 4.00? K a (HNO2) = 4.5 x 10-4 (a) 10.2 (b) 0.67 (c) 77.6 (d) 104.3 18-41. We have 100. mL of a 0.20 M solution of NaClO. How many milliliters of 0.10 M HClO should be added to make a buffer of pH = 7.2? Ka (HClO) = 3.5 x 10-8 (a) 45.7 (b) 360 (c) 126 (d) 339 18-42. We have 250. mL of a 0.56 M solution of NaCH3COO. How many milliliters of a 0.50 M CH3COOH solution should be added to make a buffer of pH = 4.40? Ka (CH3COOH) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 198 (b) 231 (c) 754 (d) 622 18-43. We have 375 mL of a 0.68 M solution of NH3. How many grams of solid NH4Cl should be added to make a buffer of pH = 9.50? K a (NH4+ ) = 5.6 x 10-10 (a) 7.70 (b) 4.50 (c) 2.97 (d) 0.34 18-44. We have 100. mL of a buffer solution containing 0.10 M CH3COOH and 0.10 M NaCH3COO. If we add 5.00 mL of 0.50 M HCl to this solution, what will the resulting pH be? Ka (CH3COOH) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 4.97 (b) 4.52 (c) 7.00 (d) 8.48 18-45. We have 200. mL of a buffer solution containing 0.10 M CH3COOH and 0.10 M NaCH3COO. If we add 10.00 mL of 0.20 M NaOH to this solution, what will the resulting pH be? Ka (CH3COOH) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 4.83 (b) 4.66 (c) 8.44 (d) 6.43 Chapter 18: Acid-Base Reactions (Rev. April 2001) Page 6 18-46. We have 300. mL of a buffer solution containing 0.10 M CH3COOH and 0.40 M NaCH3COO. If we add 20.00 mL of 0.10 M NaOH to this solution, what will the resulting pH be? Ka (CH3COOH) = 1.8 x 10-5 (a) 4.11 (b) 8.88 (c) 5.38 (d) 3.26 18-47. We have 100. mL of a buffer solution containing 0.25 M HF and 0.45 M NaF. If we add 5.00 mL of 0.80 M HCl to this solution, what will the resulting pH be? Ka (HF) = 7.2 x 10-4 (a) 2.99 (b) 3.51 (c) 6.43 (d) 3.29 18-48. We have 550 mL of a buffer solution containing 0.50 M HNO2 and 0.15 M NaNO2. If we add 22.0 mL of 1.00 M HNO 3, what will the resulting pH be? Ka (HNO2) = 4.5 x 10-4 (a) 4.04 (b) 2.96 (c) 3.56 (d) 2.66 18-49. We add some ammonium cyanide, NH4CN to some water. What can be said about the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (NH4+ ) = 5.6 x 10-10 ; K b(CN- ) = 2.5 x 10-5 (a) it is acidic (b) it is basic (c) it is neutral (d) nothing can be said 18-50. We add some ammonium sulfate, (NH4)2SO4, to some water. What can be said about the pH of the resulting solution? Ka (NH4+ ) = 5.6 x 10-10 ; K b(SO42- ) = 8.3 x 10-13 (a) it is acidic (b) it is basic (c) it is neutral (d) nothing can be said 18-51. In order to buffer a solution at a pH of 4.57, how many grams of sodium acetate, NaCH3COO, should you add to 500. mL of a 0.150 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH)? (a) 8.20 g (b) 4.50 g (c) 4.11 g (d) 2.05 g 18-52. You add 25.0 mL of 0.015 M HNO3 to 50.0 mL of 0.012 M NH3. What is the final pH of the solution? (a) 4.97 (b) 9.03 (c) 1.82 (d) 7.00 18-53. What is the pH of the buffer solution that consists of 12.6 g of sodium acetate (NaCH3COO) dissolved in 150 mL of 1.8 M acetic acid (CH 3COOH)? (a) 1.50 (b) 3.68 (c) 4.50 (d) 9.50 18-54. What is the pH of a solution created by mixing 30 mL of 0.10 M acetic acid with 15 mL of 0.150.0 M NaOH? (a) 4.74 (b) 9.25 (c) 7.00 (d) 2.87 Chapter 18: Acid-Base Reactions (Rev. April 2001) 18-55. Page 7 What is the concentration of each of the species listed below when you have reached the equivalence point in a titration of 35.00 mL of 0.015 M HCl with 0.012 M NH3? What is the pH of the final solution? [H3O+ ] [NH3] [NH4+ ] pH -6 -6 -3 (a) 6.67 x 10 6.67 x 10 1.93 x 10 5.18 (b) 1.93 x 10-6 1.93 x 10-6 6.67 x 10-3 5.71 (c) 1.50 x 10-2 1.93 x 10-6 1.93 x 10-3 1.82 (d) 1.93 x 10-6 1.93 x 10-6 5.25 x 10-4 5.71 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. c c a b a c b a d b 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. d b b d a c b d a c ANSWERS — CHAPTER 18 11. d 12. c 13. a 14. b 15. d 16. c 17. a 18. b 19. a 20. d 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. b d a b a c d d b a 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. b a a c d c a b d c 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. c b c a b