Unit Ten: Acids and Bases, Reactions and Equilibrium
advertisement

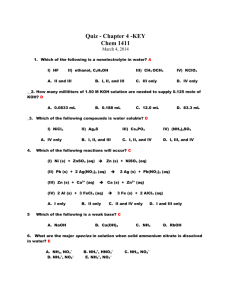
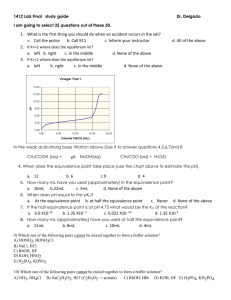
Unit Ten: Acids and Bases, Reactions and Equilibrium Review Problems 1. Classify each of the following species as a Bronsted acid or base and then write an equation to justify your classification: a. OH - b. H3O+ c. NH3 + d. NH4 2- e. CO3 2. Identify the acid-base conjugate pairs in each of the following reactions: a. CH3COO - (aq)+ - HCN(aq) CH3COOH(aq) + CN (aq) + (aq) b. HF(aq) + NH3 (aq) NH4 - c. H2PO4 (aq)+ - + F (aq) 2(aq) NH3 (aq) HPO4 + (aq) + NH4 + (aq) d. HOCl(aq) + CH3NH2 (aq) CH3NH3 2 - e. CO3 - (aq) + H2O (l) HCO3 - (aq) - + ClO (aq) + OH (aq) 3. What are the [H3O+] and the [OH-] concentration of a solution at 25 C that is 0.0125 M barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2? 4. Soda at 25 C has a hydroxide-ion concentration of 2.3 x 10 solution acidic, basic, or neutral? -10 M. Is the -4 5. A sample of vinegar has a hydronium-ion concentration of 9.2 x 10 M. What is the pH of vinegar? 6. What does the ionization constant (Ka) tell us about the strength of an acid? -5 7. The Ka for benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10 . Calculate the concentration of all the + species (C6H5COOH, C6H5COO , H3O , OH ) in a 0.10 M benzoic acid solution. 8. The pH of a 0.30 M solution of a weak base is 10.66. What is the Kb of the base? + 9. In a 0.080 M NH3 solution, what percent of the NH3 is present as NH4 ? 10. A 12.5 mL volume of 0.500 M HCl neutralizes 50.0 mL of NaOH. What is the concentration of the NaOH solution? 11. A 0.2688 g sample of a monoprotic acid is neutralized by 16.4 mL of 0.08133 M KOH solution. Calculate the molar mass of the acid. 12. When the following solutions are mixed, would the final solution have a pH equal to, less than or greater than 7? a. 100 mL of 1.0 M HCl mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH. b. 50 mL of 2.0 M HCl mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH. c. 50 mL of 2.0 M HCl mixed with 50 mL of 1.0 M NaOH. d. 50 mL of 1.0 M HCl mixed with 50 mL of 2.0 M NaOH. 13. 35.0 mL of a 0.20 M acetic acid solution (Ka = 1.8 x 10-5) is titration with 0.20 M NaOH. What is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point. 14. A 0.10 M solution of ammonia (Kb = 1.8 x 10-5) is used to titrate a 25.0 mL sample of 0.10 M HCl. What is the pH at the end point. 15. A 25.00 ml sample of propionic acid (Ka = 1.34 x 10-5) of unknown concentration was titrated with 0.104 M NaOH. The equivalence point was reached when 35.31 mL of the base had been added. What is the molarity of the original propionic acid? What is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point.