Quick Introduction to Phase Margin
advertisement

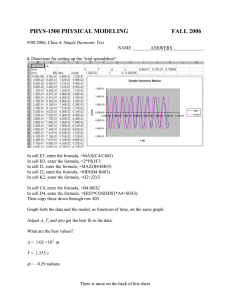
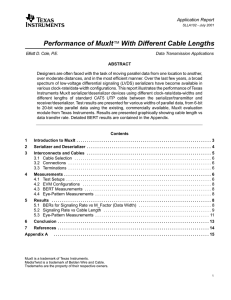
Quick Introduction to Phase Margin Excess phase shift in an operational amplifier can cause oscillation in the user’s application Defining Phase Margin • Applies to feedback around an amplifier with negative gain at low frequency • If |Gain| > 1 and phase shift > 180 degrees, the circuit oscillates • If phase is too close to 180 degrees gives overshoot to step input • Phase margin for the amplifier is how many degrees of phase shift could be added too the loop gain by the feedback block K(s) before oscillation would start Open loop gain is defined as: GOL A s K s Usually phase is a monotonic function so the phase margin is 180 – Phase(A(s)) at frequency for which |A(s)| = 1X (0 dB) 180 140 LF353 Open Loop Gain 120 160 Gain in dB Unity Gain Point (2.8 MHz) 100 140 Phase shift in degrees 80 Gain (dB) 60 100 40 80 20 60 0 Phase margin for the LF353 – 64 deg. ‐20 40 20 ‐40 ‐60 10 100 1,000 10,000 100,000 Frequency (Hertz) 1,000,000 10,000,000 0 100,000,000 Phase Shift (degrees) 120 Schematic of Phase Shift Oscillator Open Loop Gain and Phase of Oscillator Circuit 100 140 80 100 Phase margin is minus 40 degrees 60 Gain (dB) 180 60 20 40 Open Loop Gain in dB Zero Phase Frequency (450 KHz) 20 ‐20 Phase Shift in Degrees ‐60 0 ‐20 ‐100 ‐40 ‐140 ‐60 ‐180 10,000,000 10 100 1,000 10,000 Frequency (Hertz) 100,000 1,000,000 Phase (degrees) 120 V(vout) 20 18 16 Output Signal (volts) 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0.00E+00 1.00E‐05 2.00E‐05 3.00E‐05 Time (seconds) 4.00E‐05 5.00E‐05 Common Source Stage with Miller Compensation • Complete Circuit • Small Signal Model – Omits CGS and CGD Transfer Function with RM = 0 Zero – Bad for phase!!! H (s) g m rO 1 sCM / g m s CO roCM ri s 1 g m rO CM ri CO rO CM rO 1 2 Second pole Miller effect Dominant pole Transfer Function with RM in Place Zero term bad for phase H (s) g m rO 1 sCM / g m sCM RM Zero – New term good for phase Make RM > 1/gm s CO roCM ri RM s 1 g m rO CM ri CO rO CM rO CM RM 1 2