Which arrangement of two coils has the larger mutual inductance
advertisement
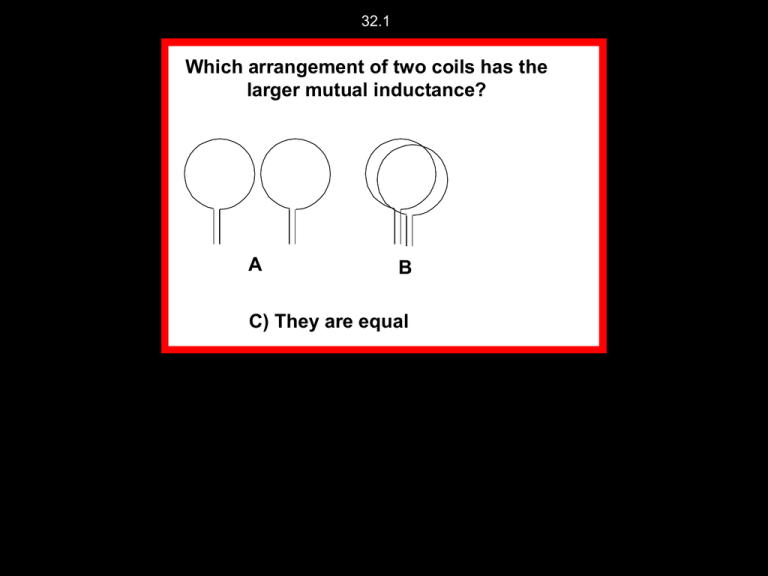
32.1 Which arrangement of two coils has the larger mutual inductance? Pink A B Yellow C) They are equal 32.2 A large-diameter two-turn coil (coil 2) is wrapped around a long smaller-diameter solenoid (coil 1) as shown. Which is larger M12 or M21 ? M 12 1 I2 coil 2 coil 1 M 21 2 I1 A) M12 B) M21 C) M12 = M21 32.2b Now the number of turns in coil 2 is doubled. What happens to M = 2/I1? A: M is half B: M remains constant. coil 2 C: M doubles D: M quadruples coil 1 E: None of these Electric toothbrush CT 33.21 Inductor 1 consists of a single loop of wire. Inductor 2 is identical to 1 except it has two loops on top of each other. What is the B field at the center of coil 2, B2, compared to the field in the center of coil 1? A: B2 = B1 B: B2 = 2 B1 C: B2 = 4 B1 D: B2 = B1/2 I Coil 1 Coil 2 I CT 33.22 Inductor 1 consists of a single loop of wire. Inductor 2 is identical to 1 except it has two loops on top of each other. How do the self-inductances of the two loops compare? (Recall, L = /I = N B A/ I) A: L2 = 2 L1 B:L2 > 2L1 C:L2 < 2L I Coil 1 Coil 2 I HL IN 1 What is the inductance of a solenoid with length d, area A, and turns/length n? A: m0 n2 A B: m0 n2 A d C: m0 n2 d D: m0 n A d E: m0 n A uestion CT 32.4 Two long solenoids, each of inductance L, are connected together to form a single very long solenoid of inductance Ltotal. What is Ltotal? + A) 2L B) 4L C) 8L D) none of these L = L Ltotal = ? CT 33.28 The switch is closed at t=0. What is the current through the resistor, at t=0+ ? R = 20 A) 0 A V = 10V B) 0.5 A C) 1 A D) 10 A E) other L = 10H CT 33.27 The switch is closed at t=0. What is the initial rate of change of current di/dt in the inductor, at t=0+ ? (Hint: what is the V(init) across the inductor?) R = 20 A) 0 A V = 10V B) 0.5 A/s C) 1 A/s D) 10 A/s E) other L = 10H CT 33.29 The switch is closed at t=0. What is the current through the resistor after a very long time? R = 20 A) 0 A V = 10V B) 0.5 A C) 1 A D) 10 A E) other L = 10H HL IN 2 What are the units of L/R? A: V B: A C:A/s D: S E: 1/S HL IN 2 What is the voltage across an inductor as a function of time for a “charging” LR circuit? t V A) E L e R B) C) E L Ve t t D) E L VL1 e t E) E L V 1 e E L VLe t CT 33.30 At time t=0, the switch is closed. What is the current thru the inductor L just after the switch is closed (t= 0+)? R1 = 10 V = 10V A: 0 A B) 0.5 A L = 10H C) 1.0 A R2 = 10 D) other CT 33.31 At time t=0, the switch is closed. What is the current thru the inductor L after a long time? R1 = 10 V = 10V A: 0 A B) 0.5 A L = 10H C) 1.0 A R2 = 10 D) other CT 33.32 Now suppose the switch has been closed for a long time and is then opened. Immediately after the switch is opened, the current thru R2 is R1 = 10 V = 10V A: 0 A L = 10H B) Not 0 amps. R2 = 10 CT 32.7 The same current i flows through solenoid 1 and solenoid 2. Solenoid 2 is twice as long and has twice as many turns as solenoid 1, and has twice the diameter. (Hint) for a solenoid B = mo n i ) What is the ratio of the magnetic energy contained in solenoid 2 to that in solenoid 1, that is, what is E 2 E1 A) 2 B) 4 C) 8 D) 16 E) None of these. I 1 2 I HL AC 1 What is the average power dissipated by the resistor? A) zero B) positive C) negative D) Not enough information CT 33.34 A light bulb is attached to a wall plug. (120 VAC, 60 Hz) How many times a second is the instantaneous power output to the bulb equal to zero? A: Never, there is always power B: 30 times/sec C: 60 times/sec D: 120 times/sec E: Other 19 CT 33.35 A 100 W light bulb is attached to a wall plug. (120 VAC, 60 Hz) What is the peak power output to the bulb? A) 100 W B) Sqrt[2]*100 W = 141 W C) 200 W D) Other 20 CT 33.15 A transformer is attached to a battery and a resistor as shown. The voltage difference across the resistor R is ... V N2 N1 R iron core A: V D: 0 B: V N1/N2 E: Other C: V N2/N1 CT 33.17 A step-down transformer is attached to an AC voltage source and a resistor. How does IR compare to the current that is drawn from the AC source I(in) Iin I(input) A) IR > I(input) B) IR < I(input) IIRR C) IR = I(input)