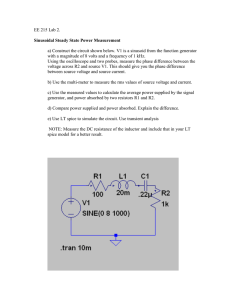
9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER
advertisement

11/18/2012 9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER The instantaneous power is the power at any instant of time. It is the rate at which an element absorbs energy. Let the voltage and current at the terminals of the circuit be; 1 11/18/2012 9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER are the amplitudes (or peak) values, are the phase angles of the voltage and current. and The instantantaneous power absorbed by the circuit is; 9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER This shows us that the instantaneous power has two parts. The first part is constant or time independent. İts value depends on the phase on difference between the voltage and the current. The second part is a sinusoidal function whose frequency is 2ω, which is twice the angular frequency of the voltage or current. 2 11/18/2012 9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER In figure; 2 / p(t) is periodic. is the period of voltage or current. and has a period of We also observe that p(t) is positive for some part of each cycle and negative for the rest of cycle When p(t) is positive, power is absorbed by the circuit. When p(t) is negative power is absorbed by the source; thar is power is transferred from the circuit to the source. This is possible because of the storage elements in the circuit. 9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER 3 11/18/2012 9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER 0 9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER 4 11/18/2012 9.1. INSTANTANEOUS AND AVERAGE POWER Example 9.1: For given voltage and current, find the intantaneous power and the average power absorbed by the passive linear network. Solution: 5 11/18/2012 Example 9.1: Example 9.2: Solution: 6 11/18/2012 Example 9.3: For the circuit in Figure find the average power supplied by the source and the average power absorbed by the resistor. Solution: Example 9.3: 7 11/18/2012 Example 9.4: Determine the power generated by each source and the average power absorbed by each passive element in the circuit of figure. Solution: Example 9.4: 8 11/18/2012 This average power absorbed by the source, in view of the direction and the polarity of the voltage source. That is the circuit delivering average power to the voltage source. Example 9.4: 9 11/18/2012 Example 9.4: 9.2. Maximum Average Power Transfer 10 11/18/2012 9.2. Maximum Average Power Transfer Our objective is to adjust the load parameters that P is maximum. For maximum average power transfer, so that and and so must be selected 9.2. Maximum Average Power Transfer In a situation in whcih the load is purely real, the condition for the maximum power transfer is obtained by setting, 0. 11 11/18/2012 Example 9.5: Determine the load impedance that maximizes the average power drawn from the circuit of Figure. What is the maximum average power? Solution: Example 9.5: 12 11/18/2012 Example 9.6: Solution: Example 9.6: 13