Algebra II - CCSD Course Goals

Algebra II - CCSD Course Goals
First Quarter: Units 1 – 3 (8 weeks)
Unit 1 Review of Functions: 2 weeks
Transformations
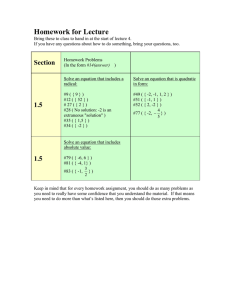
1.1 To apply transformations to parent functions (Absolute Value, Linear, Quadratic, and
Exponential). [ F.IF.B.5-1, F.IF.C.7b-1, F.BF.B.3-1 ]
Inverse Functions
1.2 To find and graph the inverse of a linear function. [ F.BF.B.4a-1 ]
1.3 To perform compositions of linear functions. [ F.BF.A.1c ]
1.4 To verify the linear inverse by composition. [ F.BF.B.4b ]
Piecewise Functions
1.5 To write and graph linear piecewise functions. [ F.IF.B.5-1, F.IF.C.7b-1 ]
Unit 2 Curve Fitting with Linear: 1 week
2.1 To draw a line of best fit given a scatter plot. [ S.ID.B.6a ]
2.2 To fit a linear regression to a data set. [ S.ID.B.6a, S.ID.B.6c ]
2.3 To use a residual plot to select the best linear model. [ S.ID.B.6b ]
2.4 To interpret the correlation coefficient for a linear model in context. [ S.ID.C.8 ]
Unit 3 Quadratic Functions: 5 weeks
Graphing Quadratic Functions
3.1 To use transformations to graph quadratic functions. [ F.IF.C.7a, F.BF.B.3-1 ]
3.2 To use standard form to graph quadratic functions. [ F.IF.C.7a ]
Complex Numbers
3.3 To define and use imaginary and complex numbers. [ N.CN.A.1 ]
3.4 To perform arithmetic operations with complex numbers. [ N.CN.A.2 ]
Solving Quadratic Equations and Inequalities
3.5 To solve quadratic equations by graphing. [ F.IF.C.7a ]
3.6 To solve quadratic equations by finding the square root of both sides of the equation.
[ N.CN.C.7, A.REI.B.4b ]
3.7 To solve quadratic equations by factoring. [ A.SSE.B.3a, A.REI.B.4, F.IF.C.8a ]
3.8 To solve quadratic equations by completing the square. [ A.REI.B.4b, F.IF.C.8a ]
3.9 To solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. [ N.CN.C.7, A.REI.B.4b ]
3.10 To solve quadratic inequalities. [ A.CED.A.1-2, A.CED.A.3-2 ]
Applying Quadratic Functions
3.11 To find the inverse of a quadratic function and verify it by composition. [ F.BF.B.4,
F.BF.B.4a-1, F.BF.B.4b, F.BF.B.4d, A.CED.A.4-2, F.IF.B.5-2 ]
3.12 To graph a piecewise function that includes a quadratic portion. [ F.IF.C.7b-1,
F.IF.B.5-2 ]
3.13 To use quadratic functions to model data. [ A.CED.A.2-2, A.CED.A.3-2 ]
3.14 To use quadratic models to analyze and make predictions. [ S.ID.B.6a, S.ID.B.6b ]
Second Quarter: Units 4 – 5 (8 weeks)
Unit 4 Polynomial Functions: 6 weeks
Introduction to Polynomials
4.1 To identify, classify, evaluate, add and subtract polynomials. [ A.SSE.A.1a, A.APR.A.1-2 ]
4.2 To multiply polynomials and use binomial expansions to expand a binomial expression raised to positive integer powers. [ A.APR.C.4, A.APR.C.5, A.APR.A.1-2 ]
4.3 To factor polynomials. [ A.APR.B.2, A.APR.B.3, A.APR.C.4, A.SSE.A.2-2 ]
4.4 To divide polynomials. [ A.APR.B.2, A.APR.D.6 ]
4.5 To apply the Factor Theorem and Remainder Theorem. [ A.APR.B.2 ]
Graphing Polynomial Functions
4.6 To use properties of end behavior to describe, analyze and graph polynomial functions.
[ F.IF.C.7c, F.IF.B.4-2 ]
4.7 To identify and use maxima and minima of polynomial functions to solve problems.
[ F.IF.B.4-2 ]
Solving Polynomial Functions
4.8 To apply the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to predict the number of real and imaginary solutions. [ N.CN.C.9 ]
4.9 To solve polynomial equations by factoring. [ A.APR.B.3, A.REI.D.11-2 ]
Applying Polynomial Functions
4.10 To use the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to write polynomial equations of least degree with given roots. [ N.CN.C.9 ]
4.11 To transform polynomial functions. [ F.BF.B.3-2 ]
4.12 To use polynomial functions to model data. [ A.CED.A.2-2, A.CED.A.3-2 ]
4.13 To use finite differences to determine the degree of a polynomial function that will fit a set of data. [ A.CED.A.3-2 ]
Unit 5 Radical Functions: 2 weeks
Create, Graph and Solve Radical Functions
5.1 To use properties of rational exponents to re-write radicals. [ N.RN.A.2, A.SSE.A.2-2 ]
5.2 To evaluate expressions with rational exponents. [ N.RN.A.2 ]
5.3 To graph radical functions and inequalities. [ F.IF.B.5-2, F.IF.C.7b-2 ]
5.4 To transform radical functions. [ F.BF.B.5, F.BF.B.3-2 ]
5.5 To solve radical equations and inequalities. [ A.REI.A.2, F.IF.B.5-2 ]
Applying Radical Functions
5.6 To find the inverse of a radical function and verify it by composition. [ F.BF.B.4b,
A.CED.A.4-2, F.IF.B.5-2, F.BF.B.4a-2 ]
5.7 To graph piecewise functions including radical portions. [ F.IF.B.5-2, F.IF.C.7b-2 ]
5.8 To create and solve radical equation and inequalities [ A.CED.A.1-2 ]
Third Quarter: Units 6 – 8 (8 weeks)
Unit 6 Rational Functions: 2 weeks
6.1 To transform the graph of y = 1/x. [ F.IF.B.5-2, F.BF.B.3-2 ]
6.2 To simplify rational expressions. [ A.SSE.A.2-2 ]
6.3 To add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions. [ A.APR.D.6, A.APR.D.7 ]
6.4 To solve rational equations and inequalities. [ A.REI.A.2, A.CED.A.1-2, F.IF.B.5-2 ]
6.5 To compose a rational function with other functions. [ F.BF.A.1c ]
6.6 To create and apply a rational function to a real life situation. (e.g. concentrations from chemistry) [ A.CED.A.2-2, A.CED.A.3-2 ]
Unit 7 Exponential and Log Functions: 4 weeks
Discrete to Continuous
7.1 To apply and graph arithmetic sequences, deriving the sum of arithmetic series.
[ F.BF.A.2 ]
7.2 To apply and graph geometric sequences; deriving the sum of geometric series.
[ A.SSE.B.4, F.BF.A.2, F.LE.A.2 ]
Exponential Functions and Logarithms
7.3 To graph exponential functions modeling growth and decay. [ F.IF.C.8b, A.CED.A.2-2,
A.CED.A.3-2, F.IF.B.5-2, F.IF.C.7e-2 ]
7.4 To find and graph the inverse of an exponential function. [ F.BF.B.4c, F.IF.B.5-2 ]
7.5 To evaluate and graph logarithmic functions. [ F.BF.B.5, A.CED.A.2-2, A.CED.A.3-2,
F.IF.B.5-2, F.IF.C.7e-2 ]
7.6 To use properties to simplify logarithmic expressions. [ A.SSE.B.3c ]
Applying Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
7.7 To solve exponential equations and inequalities. [ F.LE.A.4, A.CED.A.1-2, A.REI.D.11-2,
F.IF.B.5-2 ]
7.8 To use base e to solve and graph exponential and logarithmic functions. [ F.LE.A.4,
A.CED.A.2-2, A.CED.A.3-2, A.REI.D.11-2, F.IF.B.5-2, F.IF.C.7e-2 ]
7.9 To graph and transform exponential and logarithmic functions. [ A.CED.A.2-2, A.CED.A.3-2,
F.IF.B.5-2, F.IF.C.9-2, F.BF.B.3-2, F.IF.C.7e-2 ]
7.10 To use exponential and logarithmic functions to model data. [ S.ID.B.6a, S.ID.B.6b,
A.CED.A.2-2, A.CED.A.3-2 ]
Unit 8 Trigonometry and Angles Part I: 2 weeks
Trigonometry and Angles
8.1 To solve right triangles using trigonometric functions. [ F.TF.A.3 ]
8.2 To measure angles in standard position using degree and radian measure. [ F.TF.A.2 ]
8.3 To find values of trigonometric functions on the unit circle. [ F.TF.A.1, F.TF.A.2, F.TF.A.4 ]
8.4 To evaluate inverse trigonometric functions and use them to solve problems.
[ F.TF.B.6, F.TF.B.7 ]
Fourth Quarter: Units 8 – 9 (8 weeks)
Unit 8 Trigonometry and Angles Part II: 3 weeks
Trigonometry and Angles
8.5 To use the Law of Sines to solve a triangle. [ G.SRT.D.10, G.SRT.D.11 ]
8.6 To use the Law of Cosines to solve a triangle. [ G.SRT.D.10, G.SRT.D.11 ]
8.7 To find the area of a triangle given side-angle-side information or by using Heron’s Formula.
[ G.SRT.D.9 ]
Graphing Trigonometric Functions
8.8 To recognize and graph sine, cosine and tangent functions. [ A.CED.A.2-2, A.CED.A.3-2,
F.IF.B.5-2, F.IF.C.7e-2 ]
8.9 To recognize and graph transformations of sine, cosine and tangent functions.
[ F.BF.B.5, A.CED.A.3-2, F.BF.B.3-2 ]
8.10 To use trigonometric functions to model periodic phenomena. [ F.TF.B.5 ]
Unit 9 Statistical Inference: 5 weeks
Gathering Data
9.1 To identify and perform an appropriate method of gathering data (experiment, simulations, observational studies including sample surveys). [ S.IC.B.3 ]
9.2 To understand the importance of randomization, and the difference between random sampling and random assignment. [ S.IC.B.3 ]
9.3 To organize data. [ S.ID.A.1, S.ID.A.2, S.ID.A.3 ]
Normal Distribution
9.4 To know and apply the empirical rule. [ S.ID.A.4 ]
9.5 To use and apply normal distributions when appropriate (z-score, %-tile). [ S.ID.A.4 ]
Informal Inference
9.6 To know the difference between a parameter and a statistic. [ S.IC.A.1 ]
9.7 To understand that inference is drawing a conclusion about a population parameter based on a random sample from that population. [ S.IC.B.4 ]
9.8 To determine whether empirical results are consistent with the theoretical model.
[ S.IC.A.2 ]
9.9 To develop the concept of margin of error through the use of simulation models for random sampling. [ S.IC.B.4 ]
9.10 To use data from a randomized experiment to compare two treatments. [ S.IC.B.5 ]
9.11 To use simulations to decide if the difference between two statistics is significant.
[ S.IC.B.5 ]
9.12 To evaluate reports based on data. [ S.IC.B.6 ]