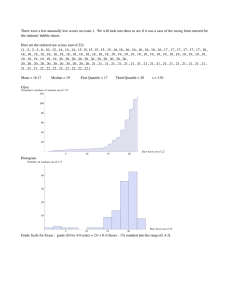
Document 17959125
advertisement

Algebra Unit 6 –Measures of Central Tendencies
Data analysis- Box and Whisker – HistogramsCumulative Histograms
Key Vocabulary
Topics Covered
1. Measures of Central Tendencies 1-6
2. Analyzing Data and Identifying Data
NY-2
3. Frequency and Cumulative Frequency
Tables NY-2
4. Quartiles
5. Box-Whisker Graphs
6. Frequency and Cumulative frequency
Tables
7. Frequency Histograms
8. Cumulative Frequency Histograms
9. Assessment 6 (Data
And Terms
Bias
Causal
Correlation
Quantitative Data
Qualitative Data
Bivariate
Univariate
Mean
Median
Mode
Range
Quartiles
Box and Whisker
Tally
Frequency
Histogram
Cumulative Frequency Histogram
Name:____________________________________________
1
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
NY 2 Analyzing Data and Identifying Bias
1. Which situation describes a correlation that is not a causal relationship?
(1) The rooster crows and the sun rises.
(2) More miles driven, the more gas is used.
(3) The more powerful the microwave, the faster the food cooks
(4) The faster the pace of a runner, the quicker the runner finishes.
2. Which variables do not have a causal relationship?
(1) Age versus color of eyes
(2) Distance walked versus time elapsed
(3) Number of pages versus weight of book
(4) Hours of studying versus grade on test.
3. Which situation does not describe a causal relationship?
(1) The higher the volume on a radio, the louder the sound will be.
(2) The faster a student types a research paper, the more pages the paper will have.
(3) The shorter the distance driven, the less gasoline that will be used.
(4) The slower the pace of a runner the longer it will take the runner to finish the race.
4 Which set of data can be classified as qualitative?
(1) Scores of students in an algebra class
(2) Number of students in history class
(3) Ages of students in a biology class
(4) Eye color of student in math class.
5. A survey is being conducted to determine which school board candidate
would best serve the Yonkers community. Which group,
when randomly surveyed, would likely produce the most bias?
(1) 15 members of the Yonkers school district
(2) 25 people driving past Yonkers High school
(3) 75 people who enter a Yonkers grocery store
(4) 100 people who visit the local Yonkers shopping mall.
6. Which could be described as qualitative data?
(1) The ages of the students in Ms. Marshall’s Spanish class.
(2) The test scores of the students in Ms. Fitzgerald’s class.
(3) The favorite ice cream flavor of each of Mr. Hayden’s students.
(4) The heights of the players on the basketball team.
2
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
NY 2 Analyzing Data and Identifying Bias
7. Which situation should be analyzed using bivariate data?
(1) A list of the amount of time Jena spends on her homework.
(2) Mr. Benjamin tires to see if his students’ shoe size are directly related to their
heights.
(3) Mr. Destefan records his customers’ best video game scores.
(4) Mr. Chan keeps track of his daughter’s algebra grades for the quarter.
8. Which relationship can be described as causal?
(1) Height and intelligence
(2) Shoe size and running speed
(3) Number of correct answers on a test and test score.
(4) Number of students in a class and number of students with brown hair.
9. Which data set describes a situation that could be classified as quantitative??
(1) The phone numbers in a telephone book
(2) The addresses of students at Hopkins High school
(3) The zip codes of residents in the city of Buffalo, NY
(4) The time it takes each of Mr. Harper’s students to complete a test.
10. Which set of data could be classified as qualitative?
(1) Scores of students in an algebra class
(2) Ages of student in a biology class
(3) Number of students in a history class
(4) Eye color of students in an economic class.
11. Erica is conducting a survey about the proposed increase in sports budget in
the Hometown school district. Which survey method would likely contain the most
bias?
(1) Erica asks every third person entering the Hometown Grocery Store.
(2) Erica asks every third person leaving the hometown shopping Mall.
(3) Erica asks every fifth person entering Hometown High school on Monday
morning.
(4) Erica asks every fifth person leaving Saturday’s Hometown High School.
Football game
3
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
NY 2 Analyzing Data and Identifying Bias
12. Which set of data is considered bivariate?
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Number of hours studied for a test.
Number of hours worked each day.
Number of days studied and number of days worked.
Number of days worked each week.
13. Which is considered as univariate data?
(1) Number of CD’s you own
(2) A person’s age and height
(3) Circumference and radius
(4) Amount of fuel used and miles driven
14. Which situation describes a correlation that is not a causal relationship?
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
The length of the edge of a cube and the volume of the cube.
The distance traveled and the time spent driving.
The age of a child and the number siblings the child has.
The number of classes taught in a school and the number of teachers employed.
15. Four hundred licensed drivers participated in the math club’s survey on driving habits. The
accompanying table shows the number of drivers surveyed in each age group.
Which statement best describes the conclusion based on the data in the table?
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
It may be biased because no one younger than 16 was surveyed.
It would be fair because no one younger than 16 was surveyed.
It would be fair because the survey was conducted by the math club students.
It may be biased because the majority of drivers were in the younger age intervals.
Age Group
Number of Drivers
16-25
150
26-35
129
36-45
33
46-55
57
4
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Measures of Central Tendencies
1. What is the mean score for the test results of 60. 60, 70, 75 and 80?
2. Jamar’s test grades were 75, 83, 87, 90 and 90. What is the median of these grades?
3. The high temperatures during 5 days were 82, 86, 91, 79 and 91. Find the mode for
these temperatures. Find the range.
4. If a student’s heights are 176cm, 172 cm, and 160 cm, what is the mean height of these
students? Find the range.
5. What is the median score for the test results of 50, 60, 80, and 90?
6. Find the mode for the following data: 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 3, 5.
7. Express the mean of x + 1 and 3x – 3 as a binomial.
8. Express the mean of 3x – 1, 2x and x + 7 as a binomial.
9. Which set of data as more than one mode?
(1) 2, 2, 4, 6, 7, 9
(2) 2, 2, 4, 6, 9, 9
(3) 2, 2, 2, 6, 7, 9
(4) 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 9
10. If a group of data consists of the numbers 2, 2, 5, 6, and 15, which is true?
(1) median > mean
(2) mean = median
(3) mode < median
(4) median = mode
11. If a group of data consists of the numbers 5, 5.5, 7, and 7.5 which is true?
(1) The median and mean are each 6.5
(2) The median and mode are 6.5
(3) The median and mean are each 6.25
(4) The median and mode are each 6.25
5
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Measures of Central Tendencies
12. If a group of data consists of the numbers 6, 6, 6.5, 8 and 8.5 which is true?
(1) median < mean
(2) median < mode
(3) median = mean
(4) median = mode
13. A student received test scores of 82, 94, and 96. What must she receive as a fourth score
so that the mean of 4 scores will be exactly 90?
14. A student received test scores of 72, 84, and 86. What must the score be on the fourth test
so that the mean of these score will be 85?
15. Given the following quiz scores: 5, 12, 7, 15, 20, 14, 7. If the teacher decides to add three
points to each of these scores, explain the effect, if any, it will have on the mean, median and
mode.
16. Ms. Mosher recorded the math scores of six students in the accompanying table.
Student
Student Score
Andrew
72
John
60
George
85
Amber
93
Betty
78
Roberto
80
Determine the mean of the student scores to the nearest tenth.
Determine the median of the students’ scores. Describe the effect on the mean and median if
Ms. Mosher adds 5 bonus points to each of the six students’ scores.
6
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Box and Whisker
1.
A box-and-whisker plot shown below represents the data for the number of tickets sold, in hundreds.
Which conclusion can be made using this plot?
1) The second quartile is 600.
3) The range of the attendance is 300 to
600.
2) The mean of the attendance is 400.
4) Twenty-five percent of the attendance is
between 300 and 400.
2.The box-and-whisker plot below represents the math test scores of 20 students.
What percentage of the test scores are less than 72?
1) 25
2) 50
3) 75
4) 100
7
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Box and Whisker
3. What is the range of the data represented in the box-and-whisker plot shown below?
4.The box-and-whisker plot below represents students' scores on a recent English test.
5.What is the value of the upper quartile?
1) 68
3) 84
2) 76
4) 94
6.Which number represents the second quartile of the number of cans of food collected?
1) 29.5
3) 40
2) 30.5
4) 60
8
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Box and Whisker
1.What is the value of the third quartile shown on the box-and-whisker plot below?
1) 6
3) 10
2) 8.5
4) 12
2.The test scores from Mrs. Gray’s math class are shown below.
72, 73, 66, 71, 82, 85, 95, 85, 86, 89, 91, 92
3.Construct a box-and-whisker plot to display these data.
4. The number of songs fifteen students have on their MP3 players is:
120,124, 132, 145,200,255,260,292,
308,314,342,407,421,435,452
5. State the values of the minimum, 1st quartile, median, 3rd quartile, and maximum. Using these
values, construct a box-and-whisker plot using an appropriate scale on the line below.
9
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Box and Whisker
1. Based on the box-and-whisker plot below, which statement is false?
1) The median is 7.
2) The range is 12.
3) The first quartile is 4.
4) The third quartile is 11.
2. The data set 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 9, 9, 10, 12, 14, 17, 17, 18, 19, 19 represents the number of hours spent on the
Internet in a week by students in a mathematics class. Which box-and-whisker plot represents the data?
1)
3)
2)
4)
10
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Frequency Tables
1. The data represents the distribution of test grades of students on a
mathematics test: 60, 65, 70, 75, 75, 80, 80, 80, 85, 85, 85, 85, 90, 90, 95.
a.) Complete the tally and total frequency column.
b.) Find the mode
c.) Find the median
d.) Find the mean
Grade
Tally
Frequency
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
11
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Frequency Tables
2. The points scored by Rosa in twenty basketball games are 35, 33, 27, 35, 29,
37, 32, 35, 35, 32, 23, 37, 32, 29, 26, 30, 28, 31, 29, and 35.
Interval
Tally
Frequency
23-25
26-28
29-31
32-34
35-37
a.) Complete the table
b.) Find the mode
c.) Find the median
3. The graph below shows the distribution of scores on a math test. How many
students took the test?
12
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Cumulative Frequency Tables
3. On a test 15 students received the following grades: 17, 14, 16, 18, 17, 19, 15,
15, 16, 13, 17, 12, 18, 16, 17.
Grade
Frequency
Cumulative Frequency
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
a.) Complete the table
b.) Find the mode
c.) Find the 75 th. Percentile
13
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Cumulative Frequency Tables
The following table shows the cumulative frequency distribution of scores of 30
students on a test.
Scores
Cumulative Frequency
41-50
1
41-60
2
41-70
8
41-80
16
41-90
27
41-100
30
a.) How many students scored from 61 – 70?
b.) How many students scored form 81 – 90?
c.) How many students scored from 91 -100?
d.) How many students scored from 51 – 60?
14
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Frequency Tables
1.The test scores for 18 students in Ms. Mosher’s class are listed below:
86, 81, 79, 71, 58, 87, 52, 71, 87,
87, 93, 64, 94, 81, 76, 98, 94, 68
Complete the frequency table below.
Draw and label a frequency histogram on the grid below.
15
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Frequency Tables
1. The Fahrenheit temperature readings on 30 April mornings in Stormville, New York, are shown below.
41°, 58°, 61°, 54°, 49°, 46°, 52°, 58°, 67°, 43°, 47°, 60°, 52°, 58°, 48°,
44°, 59°, 66°, 62°, 55°, 44°, 49°, 62°, 61°, 59°, 54°, 57°, 58°, 63°, 60°
Using the data, complete the frequency table below.
2. On the grid below, construct and label a frequency histogram based on the table.
16
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Frequency Tables
1. Ms. Hopkins recorded her students' final exam scores in the frequency table below.
On the grid below, construct a frequency histogram based on the table.
17
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Cumulative frequency Histograms
The diagram below shows a cumulative frequency histogram of the students' test scores in Ms. Wedow's
algebra class.
Determine the total number of students in the class. Determine how many students scored higher than
State which ten-point interval contains the median. State which two ten-point intervals contain the
same frequency.
18
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet
Cumulative Frequency Histograms
1. Twenty students were surveyed about the number of days they played outside in one week. The results of
this survey are shown below.
{6,5,4,5,0,7,1,5,4,4,3,2,2,3,2,4,3,4,0,7}
Complete the frequency table below for these data.
Complete the cumulative frequency table below using these data.
On the grid below, create a cumulative frequency histogram based on the table you made.
19
Algebra- Unit 6 Packet