Unexpected Pregnancy Outcomes Abortion
advertisement

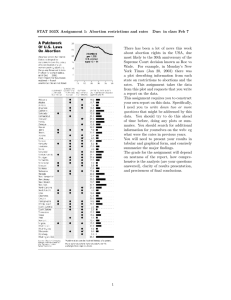
Unexpected Pregnancy Outcomes Abortion I. For unplanned pregnancies, the first decision to be made is whether or not to continue A. Sometimes it is allowed to continue, something goes wrong & fetus stops developing; such natural cessations of pregnancy are spontaneous abortions (miscarriages) B. Abortions requiring intervention to end pregnancy are technically called induced abortions II. Abortion procedures A. Vacuum aspiration – almost all abortions performed in US are performed during first trimester using surgical procedure called vacuum aspiration B. Manual vacuum aspiration (MVA) – variation of vacuum aspiration that can be used from detection of pregnancy to up to 12 weeks since the last menstrual period (LMP) C. Medical abortions – relatively new procedures that use drugs to induce abortions, including mifepristone or methotrexate in combination with misoprostol 1. Mifepristone – discovered by French pharmaceutical company in 1978; was known as RU486 (RU refers to Roussel Uclaf, the French pharmaceutical company 2. Methotrexate – blocks folic acid & prevents cell division 3. Women who choose a medical abortion should understand that there is a 4 – 8% chance they will need to return for a surgical abortion D. Dilation & evacuation – during second trimester of pregnancy, dilation & evacuation (D&E) is abortion procedure used 1. It involves dilating the cervix, scraping the walls of the uterus & removing the endometrial lining with suction Abortion: The Law and the Debate I. For more than 3 decades, abortion has been vehemently debated in the political sector A. Neither IVF, contraception nor sterilization generates the political, religious & emotional heat that abortion does B. Prolife political groups actively support candidates who are totally opposed to abortion C. Groups labeled prochoice believe that women should have the right to decide for themselves what they will do with their bodies 1. Thus, they oppose legislative restrictions on the availability of abortion to women who choose that option 2. They wish to uphold the Supreme Court decision of 1973, which established the current status of abortion in the US (Roe v. Wade) 3. The Court ruled that abortion should be available to women during the 1st trimester; the decision is made by the pregnant woman & her physician 4. In 1983, Supreme Court reaffirmed its 1973 decision 5. 1989 – a more conservative Court due to new appointments decided in Webster v. Reproductive Health Services that 6. Later, 2 other cases were taken before Court & decided in 1990 a. Hodgson v. MN – Court rejected a law requiring a physician to notify both parents of a minor before abortion could be performed b. Ohio v. Akron Ctr for Reproductive Health – Court held that similar law that required notification of one parent & included judicial bypass was constitutional 7. 1992 – Court reaffirmed constitutionality of states attaching regulations to abortions, although they also reaffirmed right of woman to have abortion if she chooses a. Planned Parenthood of SE PA v. Casey – Court ruled PA could require woman seeking abortion to receive counseling & to wait 24 hrs before getting abortion b. Court refused to overturn Roe v. Wade as many opponents of abortion had hoped such a Court would do 8. 2000 – Steinberg v. Carhart – Court ruled bans on intact D&E (partial birth abortions) unconstitutional since did not take into account pregnant woman's health 9. 1980 – Court decision profoundly affected availability of legal abortions II. Current Laws on Abortion Services A. People who oppose legalized abortion have unsuccessfully tried to outlaw abortion services completely, but they have limited availability under many circumstances B. October 1998 – Congress passed a $500 billion appropriations bill which contained many restrictions on abortion; it prohibited: C. Many states have also passed laws limiting abortion services – limits on public & private funding for abortion, parental consent laws, waiting periods, bans on some procedures III. Who has abortions? A. Alan Guttmacher Institute monitors abortion laws & the characteristics of those having abortions B. Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC) also monitors abortion in the US; most current CDC reported data at time book was written was 2001 1. 51% of abortions were done for women younger than 25 years; 1/3 of abortions were done for women aged 20 – 24 years; teenagers have 18% of abortions C. Religion plays a role as well – women who report no religious affiliation are >4 times as likely to get one as other women (Guttmacher Inst.) D. Marital status is another variable – 79% of abortions are obtained by women who are not married E. 3 primary reasons women give for seeking an abortion – Guttmacher Inst. 1. ¾ say that having a baby would interfere with their work, education or other responsibilities 2. ~2/3 say they cannot afford a child 3. Half say they do not want to be single parent or are having problems with husband/partner F. Other reasons The Safety of Abortions I. Abortion is an extremely safe procedure A. <1% of abortion patients experience a major complication; of these the primary risks are: B. For abortions performed during the 1st 8 weeks of pregnancy, 1 death occurs per million abortions C. There is no effect on subsequent pregnancies or births in women who have had the most common abortion procedure (vacuum aspiration) within the first 12 weeks II. Some concern has been raised about the psychological health of women as a result of experiencing an abortion, but there is little evidence that women are negatively affected A. Study of >5000 American women – those who had had abortion actually had higher selfesteem & greater feelings of self-worth & capability than women who had not had one Attitudes About Abortion: Changing & Unchanging I. Since Roe v. Wade, attitudes about abortion have been evolving; many studies have been done to identify Americans' attitudes A. Most of the studies asked only a few questions, leaving the interpretation of the results unclear II. 2003 – 23% of Americans believed abortion should be legal under any circumstance, 15% believed it should be legal under most circumstances, 42% in only a few circumstances III. Percentage saying abortion should be legal in all circumstances rose from 21% in 1975 to 34% in 1992 & slipped back to 25% in 1996 where it has remained since IV. Abortion is considered more acceptable during early stages of pregnancy than during later stages A. When woman's life is endangered or pregnancy is result of rape or incest, a majority of Americans believe abortion ought to be an option even during the third trimester B. When prochoice & prolife supporters are surveyed about their attitudes toward abortion, not only whether they support abortion or not, they differ significantly C. Latest data indicate Americans are less supportive of abortion than in the recent past 1. 2005 – when asked if they oppose or favor Supreme Court decision making abortion legal up to 3 months of pregnancy, 52% favored & 47% opposed Roe v. Wade Availability of Legal Abortion I. It is becoming increasingly difficult for a woman to have an abortion in the US A. Number of abortion providers in US fallen by 37% since 1982 & 11% between 1996 & 2000 1. Proportion of women who live in a county with no abortion provider increased from 28% in 1992 to 34% in 2001 B. Many abortion clinics are picketed on regular basis C. Violence has also plagued many abortion clinics 1. From 1996 to 1997, number of arsons doubled & bombings tripled against abortion clinics 2. Abortion providers have been murdered at the clinics where they work in Florida & Massachusetts D. 33 states have passed laws requiring that adolescents have parental consent or notification for abortion II. Public & private funding for abortion A. Patchwork of state laws concerning public funding for abortion is complex B. Each state establishes its own abortion funding policy related to state revenues Emotions & Abortion I. Emotional reactions to abortion are varied – some women feel guilty, depressed, angry & ashamed; others feel none, or just a limited extent, of these feelings II. Religious & moral beliefs, reactions of medical staff, relatives & friends & strength of relationship between partners all affect emotional responses A. The earlier the abortion is performed, the lower the emotional cost B. Realizing this, a film was developed by abortion opponents & shown widely in US 1. Entitled The Silent Scream, the film is a 28-minute depiction of an abortion using ultrasound visualization 2. Many physicians & others have taken issue with it 3. Others argue the following points C. Other extreme emotions associated with the issue of abortion (besides The Silent Scream) 1. Abortion facilities have been bombed, and staff & patients have been targets of harassment 2. Some professionals choose not to subject themselves to this type of treatment & therefore refuse to work at abortion facilities Adoption I. Another response to an unwanted pregnancy is delivery of the baby followed by adoption placement A. Women who are unwed & choose not to raise baby or who do not have financial resources necessary to raise baby often choose adoption II. Types of adoptions – 2 basic types A. Closed adoptions – confidential; there is no contact between the birth parents & the adoptive parents; identities of the birth parents & adoptive parents are kept secret B. Open adoptions – allow contact between the birth parents & the adoptive parents III. Adoptions are legally binding & irreversible after a limited period, although there have been some highly publicized cases of birth parents' seeking to reverse them A. Birth parents sign relinquishment papers after the baby is born IV. Adoptions are arranged in 3 ways: agency adoption, independent adoption, & adoption by relatives A. Agency adoption – the parents relinquish their baby to an adoption agency 1. These agencies are licensed by the government & may offer a number of services B. Independent adoptions – birth parents select the adoptive parents & relinquish the baby into their care 1. Often arranged through a physician or a lawyer &, in some cases, by independent adoption centers 2. Independent adoptions are usually open adoptions &, although not legal in all states, are supervised by a lawyer, who usually represents both sides C. Adoption by relatives – used when the birth parents want the child to stay in the family Contemplating Adoption I. Adopting a child is a decision that requires a great deal of consideration; so does the decision of giving a child up for adoption II. Planned Parenthood of America suggests that anyone considering giving a child up for adoption should ask the following questions III. Someone planning to put their baby up for adoption should discuss the above questions with her partner, clergy, professional counselor or a trusted relative or friend Foster Care and Adoption I. For parents not ready to decide between adoption & parenting, many cities & counties provide temporary residences for their children; this arrangement is called foster care A. To arrange for this option, birth parents must sign a legal foster care agreement that allows another family to care for the child B. Often foster care agreements specify: II. Although foster care arrangements & regulations vary from state to state, if the foster care agreement is violated, the birth parents can lose the child permanently III. Foster care also provided for children taken from birth parents for abuse, neglect or other behavior that precludes them from being able to raise their children & places the children at risk IV. US foster care system includes >500,000 children, of which 131,000 are eligible for adoption; fortunately, more & more of these children are being adopted A. 1995 – 20,000 children in the foster care system were adopted; increased to 28,000 in1996 & to 31,000 in 1997 B. 1997 – Congress passed the Adoption & Safe Families Act, designed to speed up adoption of children in the foster care system 1. Legislation provided bonuses of $4000 to states for every child in the child protective system for whom they arranged adoption C. 2003 – 49,000 children in foster care system were adopted Finding the Birth Parent I. Since they seek to determine their complete history or because they are curious or for some other reason, many adults who were adopted seek to identify their birth parents A. There is lots of disagreement as to whether & how this process should be facilitated B. Before WWII, it was common for adoption records to be open C. Oregon residents decided this issue for themselves in November 1998 1. Approved a ballot initiative requiring the state to unseal confidential birth records 2. On request, adoptees would be given all the information about their past – in spite of the wishes of their birth parents