S 3: R ECTION
advertisement

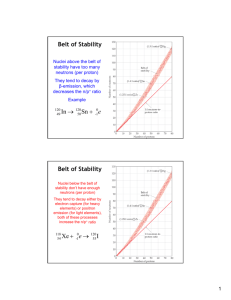
SECTION 3: RADIOACTIVITY Chapter 17: Properties of Atoms WARM-UP: What do you think it means to be radioactive? What is one element or thing that you know of that is radioactive? LEARNING GOALS Explain what radioactivity is. Describe element. the half-life of a radioactive PROTONS AND NEUTRONS Protons and neutrons are packed tightly into the nucleus of an atom. Protons and neutrons are attracted to each other because of the strong force. PROTONS AND NEUTRONS Some atoms, such as uranium (U), have many protons and neutrons in their nuclei. These nuclei are held together less tightly than smaller atoms. If the strong force can keep all of the protons and neutrons together, then the atom is stable. RADIOACTIVITY When the strong force is not strong enough to hold the nucleus together, the nucleus can decay and give off matter and energy. This process is called radioactivity. All nuclei that contain more than 83 protons are radioactive. NUCLEAR DECAY When an unstable nucleus decays, particles and energy called nuclear radiation are emitted. The three types of radiation are: Alpha Beta Gamma NUCLEAR DECAY When alpha radiation occurs, an alpha particle is emitted. An alpha particle is made of two protons and two neutrons NUCLEAR DECAY When an element gives off an alpha particle, it has two fewer protons… so it is a different element. Transmutation: the process of changing one element into another The new element will have two protons and two neutrons less than the original element. NUCLEAR DECAY Sometimes an unstable nucleus decays into a proton and emits an electron. The electron emitted is called a beta particle. The atom now has one more proton than the original atom and becomes a new element. NUCLEAR DECAY Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies and the shortest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. They have no mass, no charge, and travel at the speed of light RADIOACTIVE HALF-LIFE Half-Life: the amount of time it takes for half of the nuclei in a sample of radioactive isotopes to decay. RADIOACTIVE HALF-LIFE Half-lives vary widely among different radioactive elements. Polonium-214 = less than 0.001 sec Uranium-238 = 4.5 billion years Carbon-14 = 5,730 years RADIOACTIVE HALF-LIFE Carbon-14 is often used to estimate the ages of plant and animal remains. Carbon-14 is found in molecules such as carbon dioxide Which is used by plants to make sugar When animals eat plants, the carbon-14 is added to their bodies RADIOACTIVE HALF-LIFE The ratio of carbon-12 and carbon-14 in a plant or animal is nearly constant when the organism is alive. When it dies, the carbon-14 atoms decay and the ratio changes By measuring this ratio, the age of the organism’s remain can be estimated. CHECK-IN: Why are large nuclei unstable?