Crusades 1095-1292 1095-1292.
advertisement

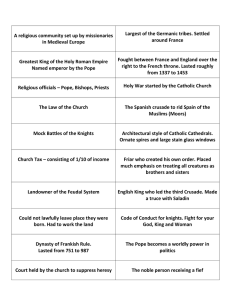
Crusades 1095-1292 Crusade = Western Christian military effort to regain Holy Land from the Muslim Turks ≈ 1095-1292. “Deus Vult” – God wills it! War cry of First Crusade. 1. Causes Turkish attacks on Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire Turkish violence toward Christian pilgrims Christian desire to regain Holy Land http://www.sacredsites.com/middle_east/saudi_arabia/mecca.html 2. Motives of Crusaders Deus Vult Glory Adventure Personal gain 3. Events of significance ≈ 6-8 Formal Crusades intended for Holy Land (only first succeeds) 1st Crusade sets up feudal kingdoms/principalities in Holy Land o Gradually Crusaders lose grip on the lands gained in first Crusade o Each new Crusade was in response to land lost again after the first one rd 3 Crusade attempted to retake Jerusalem after its conquest by Saladin 4th Crusade captured Constantinople from the Byzantines and was held for 50 years in early 1200s 4. Crusades as reflection of Medieval World Power of Church and Pope Religious devotion of people of W. Europe Nobles = fighters Warlike nature of society and people Sibling (love-hate-need) relation of East and West 5. Major effects of Crusades in West Improved technology – ships, maps, weapons, use of compass, etc. Increased use of currency leads to trade, cities, wealth, leisure Increased trade leads to rise of Italian city-states, global exploration, New World Feudalism declines, kings grow stronger o Nobles die, kings often get land o Currency allows for paid armies = kings don’t need nobles Broadened worldview through exposure to Byzantine and Arab world Crusades 1095-1292 Crusade = Western Christian military effort to regain Holy Land from the Muslim Turks ≈ 1095-1292. “Deus Vult” – God wills it! War cry of First Crusade. 1. Causes 2. Motives of Crusaders 3. Events of significance ≈ 6-8 Formal Crusades intended for Holy Land 1st Crusade sets up feudal kingdoms/principalities in Holy Land o o 4th Crusade captured Constantinople from the Byzantines and was held for 50 years in early 1200s 5. Crusades as reflection of Medieval World Power of Church and Pope Religious devotion of people of W. Europe Nobles = fighters Warlike nature of society and people Sibling (love-hate-need) relation of East and West 5. Major effects of Crusades in West Improved technology – ships, maps, weapons, use of compass, etc. Increased trade leads to rise of Italian Feudalism declines, kings grow stronger o o Currency allows for paid armies = Broadened worldview through exposure to