The Legacy of the Western World Chapter 1
advertisement

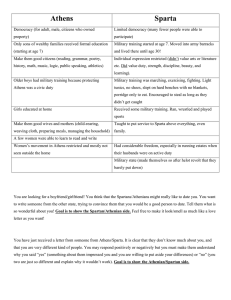
The Legacy of the Western World Chapter 1 The Legacy of the Western World Chapter 1 Section 1: The First Civilizations What is civilization? The word "civilization" comes from the Latin word for townsman or citizen, civis, and its adjectival form, civilis. To be "civilized" essentially meant being a townsman, governed by the constitution and legal statutes of that community The rise of civilization Civilization is defined as: highly organized society marked by advanced knowledge of trade, government, arts, science and often time written language The Parthenon in Athens is an example of classical Greek Civilization. The ruins of Machu Picchu, "the Lost City of the Incas," has become the most recognizable symbol of the Inca civilization. What is culture? Culture - has been called "the way of life for an entire society." As such, it includes codes of manners, dress, language, religion, rituals, norms of behaviors and systems of belief. What is the first know society The earliest known civilizations (as defined in the traditional sense) arose in Mesopotamia between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in modern-day Iraq, Persia in modern-day Iran, the Nile valley of Egypt. The inhabitants of these areas built cities, created writing systems, learned to make pottery and use metals, domesticated animals, and created complex social structures with class systems. Asia Minor • This is the area were most civilization began in prehistory and history. • With many water ways and food source the fertile crescent became the center of the universe to its people. • It is believed that this area was an abundant food source to the hunters and gathers. • With farming a big population of people emerged out of the land ANCIENT MESOPOTAMIA • Oldest known civilization • Cradle of Human Civilization • Hammurabipowerful ruler Political:Mesopotamian Law • Code of Hammurabi = 282 laws • Retaliation “eye for an eye tooth for a tooth” fundamental to the code • Punishment different between classes of society Patriarchal Society • Dominated by men • Woman’s duties were in the home • Children must be obedient Egyptian civilization • Egyptian civilization arose a bit after Mesopotamia. • Geography: It was centered around the Nile River. Egyptian Social Hierarchy Political:Egyptian Pharaohs • Egyptians were led by Pharaohs. • They were priestkings • King Tut is the most famous • Using computers, this image was reconstructed using his remains Solomon’s Kingdom Split into two kingdoms after Solomon’s death: Israel and Judah Judaism a monotheistic (one god) religion arose from the region. They believed they had a covenant with God and prophets spoke for God. Indus Valley Civilization 3000 B.C. Indus Economy • Just like the other river valley civilizations, the Indus river valley people were mostly farmers. • Traditional economy • They did trade with Chinese and with Sumerians (Mesopotamians). Indus River Valley • First people were displaced by the Aryans. • Developed a caste system based on occupation and extended family networks. The Caste System Two major religions of Hinduism and Buddhism emerged from the Indus civilization Siddhartha Gautama (563-483 BCE) Born in NE India (Nepal). Raised in great luxury to be a king. At 29 he rejected his luxurious life to seek enlightenment and the source of suffering. Lived a strict, ascetic life for 6 yrs. Rejecting this extreme, sat in meditation, and found nirvana. Became “The Enlightened One,” at 35. ANCIENT CHINA Began 2000 B.C. As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained an almost infinite number of ethnic groups and languages. This history, in which a vast area populated by diverse ethnic groups became, over time, a more or less single culture, began in the Yellow River Valley. China Confucius: sixth century teacher and philosopher • Confucianism: humanity, learning, family, peace and justice - Confucious • People were naturally good • Obedience to leaders was important The Legacy of the Western World Chapter 1 Section 2: The Civilization of the Greeks Polis = City-State Greece was divided into city-states, each known as a polis. The two main city-states were Sparta and Athens. The greatest of these was Athens which was a center of intellectual and cultural development - “the nursery of western civilization.” Geography In History The ancient Greek city-states never united because the land was very mountainous and hilly making travel difficult. This is one case where geography influenced history. Structure of the Polis Each polis was built around an acropolis, a fortified hill with the temple of the local god at the top. Structure of the Polis At the foot of the acropolis was the agora, an open area used as a marketplace. By 700 B.C. this inner part of the polis had become a city. With the villages and farmland around it, it made up a city-state. TYRANT Rulers who seized power by force and were not subject to the law. A PERSON WHO RULES A NATION WITH ABSOLUTE POWER Political: Athens was the first democracy. • Democracy: type of government where people vote. • Athens was a direct democracy where people vote on everything. • The U.S. today is a representative democracy, where we vote for people to make decisions for us. Political terms • All of Greece wasn’t a democracy. • Most of Greece was a monarchy type of government ruled by a king or queen. Sparta • Sparta was an isolated city-state that was culturally and politically different from Athens. • Sparta was an oligarchy, government ruled by a few. They had 2 kings. • During the Peloponnesian Sparta sacked Athens. Political: Sparta was an oligarchy. • oligarchy : rule by a few. • Sparta had two kings who led the army. • Five citizens were elected yearly as ephors to supervise education and conduct of the polis . • Council of Elders: Two kings and 28 citizens over age 60 who decided what issues the assembly of all citizens could vote on with no debate allowed. Spartan Goal Sparta tried to become the strongest state in Greece. They also disliked change. This would later prove to be a weakness for them. Spartans preferred actions to words. A “Spartan lifestyle” both then and today is one that is simple and highly disciplined with few luxuries. Now that’s tough! There is a story about a Spartan boy who, in order to conceal a fox which he had stolen, hid it beneath his cloak and allowed the fox to gnaw him rather than let the theft be revealed. He died of the wounds. If he had been discovered, the disgrace would not have been in the stealing, but in allowing it to be detected. The boy's action illustrates the main purpose of the Spartan educational system, which was to produce men capable of showing such bravery as soldiers. Military strength was felt to be necessary to Sparta for their very survival. Sparta Sparta was known for its great army and was a rival of Athens. Their army was known for holding off the Persian army of 250,000 at Thermopylae for three days with only 7000 soldiers. This gave the people of Athens time to escape before the Persians invaded there. Sparta • Spartan society was obsessed with war. • Boys were sent to military school at a young age. • Boys who are born deformed are left to die on mountainsides Direct participation was the key to Athenian democracy. In the Assembly, every male citizen was not only entitled to attend as often as he pleased but also had the right to debate, offer amendments, and vote on proposals. Every man had a say in whether to declare war or stay in peace. Basically any thing that required a government decision, all male citizens were allowed to participate in. Athens Government & Education Athenian democracy was for free, male Athenians only. Education for men was highly valued. Only boys of wealthy families attended schools. The term academy comes from Athens. Direct Democracy All male citizens debate and vote on issues in an open assembly Pericles • Reformed Athenian democracy by introducing pay for elected officials. • Helped to make Athens the “school of Greece.” Classical Greek Philosophy Socrates 470-399 BC • Simple man – Stonemason “The unexamined life is not worth living.” • Believed in a single, all powerful God • Used dialectics (Socratic Method) to find ultimate truth Socrates • Socratic Method – Posed questions and then questioned the answers – Searched for the ultimate nature of qualities • What is Duty? • What is Truth? • What is Evil? Socrates • Accused and convicted of “corrupting the youth” by encouraging critical thinking. • He did not put on a defense • Sentenced to death • Drank hemlock (Poison) Plato 427-347 BC • Student of Socrates • Born an aristocrat • Founded the Academy – First university – Purpose-thinking about deeper meanings • Wrote dialogues of Socrates, his own political theory and works of ethics Plato • The Republic – Ideal society of three groups 1. Rule by the philosopherkings 2. Warriors to protect society 3. Masses – Believed women should be educated and have access to all positions in society. Aristotle 384-322 BC • Son of a physician • Born in Macedonia • Attended the Academy • Became Plato’s foremost student • Left the Academy when Plato died • Founded the Lyceum in Athens – More focused in natural science Aristotle • Aristotelian Scientific Method – Used for 2000 years – Basic assumptions based on reasoning • Deductive method – Observations used to confirm the assumptions • Example: Elements of earth (4) and heavens • Example: Qualities of things – Did not employ experimentation • Disturbs nature Aristotle • Wrote on politics – Assembled 158 constitutions to compare – Three type of governments existed • Rule by one man—monarchy/tyranny • Rule by a few men—aristocracy/oligarchy • Rule by many—polity/democracy – Individual considered greater than the state Classical Greek Philosophy Alexander Xenophon Eschines Socrates Alcibiades Plato Aristotle Zeno Epicurus Averroes Parmenides Hypatia Anaxagoras Anaximander Pythagoras Raphael Zoroaster Diogenes Ptolemy Heraclitus Euclid Greek Decline The Greeks began to lose their sense of community and fought with one another. In 338 B.C. Philip II of Macedonia north of Greece (Alexander the Great’s father) conquered Greece. The Legacy of the Western World Chapter 1 Section 3: Rome and the Rise of Christianity Two Groups Patricians: wealthy landowners became a ruling class Plebeians: less wealthy farmers, merchants and craftsman Roman Republic A republic is a government were the leader is not a monarch and certain citizens have a right to vote. In Rome both patricians and plebeians could vote but only patricians could hold office. Republican Government 2 Consuls (Rulers of Rome) Senate (Representative body for patricians about 300 members) Tribal Assemblies (Representative body for plebeians) Republican Government • Ruled by a senate and the people – SPQR= Senate and the People of Rome – Senate (patricians) appointed consuls (1 year) • Foreign affairs and the military • Direct access by the people to the consul – People (plebs) organized by tribes and they elected 10 tribunes • Governed local affairs • Had veto power (individually) Constitution (balanced power) • Senate – Never made laws but advice was accepted – Had power to appoint a person to solve a specific problem (He was a "speaker" or "dictator") – Appointed censors (moral guardian/rank judge) – Appointed governors • Concilium plebis – Made all the laws (called plebecites) – Elected magistrates (administrators) and judges • Comitia Curiata/Centuriata – plebs and patricians – Committed the emporium (military power) • All met in the forum (looked over each other) • Pontifex Maximus – Religious leader The Twelve Tables, 450 BCE Providing political and social rights for the plebeians. Applied only to Roman citizens. Law of Nations Succeeded the 12 Tables to include non-Romans as the republic became an empire. It is the basis of modern legal systems today. Rule of Law • It means nobody is above the law, not the king, not the senate, not the people, not the police. • Laws are written down and must be respected Roman Expansion (outside Italy) • Conquest of the East and West – Master of the Mediterranean Sea – Toleration – Extended citizenship to conquered people – Latin language spread – Romans influenced laws, architecture and engineering Building an Empire • Structure of the "empire" – Still a republican form of government – Checks and balances – Two parties emerged • Optimares (conservatives, Cato and Cicero) • Populares (power to people) • Family considered important • Values (according to the Romans) – – – – – – Piety Discipline Frugality Not greedy Righteous wars Never quit The Roman Empire Caesar Augustus • 63 BC-14 AD • Octavian was winner of 18 years civil war • Designated heir of Julius Caesar • Was of the family of Caesar (adopted) so he took the name Caesar • Given the name Augustus by the Senate Caesar Augustus • Beginning the Empire – Augustinian Code • Roman Law was rewritten and solidified • Basis of western laws today • Equity – Honest government – Added to the road system • 53,000 miles of paved roads – Postal system and other city infrastructure – Standard currency system – Improved harbors Roman Christianity The origins and early spread of Christianity took place in the Roman Empire. It was based on the teachings of Jesus Christ. Spread during the Pax Romana. Despite persecution of the early Christians, Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire. The Greatest Extent of the Roman Empire – 14 CE The Rise of Christianity The Spread of Christianity Constantine • 306-337 AD • Succeeded his father as Caesar after fighting 7 other claimants • Made Christianity official religion of the empire Catholic Church • Became the official Christian church of Rome • Served as an intermediary between people and God The Legacy of the Western World Chapter 1 Section 4: New Patterns of Civilization (500-1600) The World of Islam • RELIGIOUS CAPITAL IS MECCA • ISLAM: ”SURRENDER”, RELATED TO ‘SALAAM’, OR PEACE. • ISLAM IS ALSO A CODE FOR SOCIAL CONDUCT • SPREAD FROM ARABIAN PENNISULA WEST TO SPAIN AND EAST TO INDIA THE RELIGION OF ISLAM IS LEAD BY M U H A M M A D BUT ALL ARE EQUAL SO NO PRIESTS ARE IN CHARGE Islam, 610-632 • 571 Muhammad born in Mecca. • 610 First revelation in the Harraa cave (27 Ramadan). • 622 “Hijra”or Escape. Muhammad and followers escape prosecution and go to Almadinah (Yathrib). Year 1 in the Islamic calendar ‘Missionaries’ sent all over Arabia – building peaceful coalition • 629 Muhammad conquers Mecca peacefully (NO REVENGE) destroys idols in Alqaaba. single-handedly, brings peace to war-torn Arabia • 632 Muhammad dies in Almadinah. Unmarked grave (his will) The Quran: • Islam’s holy book, an inspired scripture. God’s word inspired to his messenger, • 114 Chapters (chapter = Surah), 4 to >200 verses/chapter (verse = Aiyah) • Confirms most narratives and prophets of the Jewish and Christian faiths • Allah is the word for God used by Christian and Muslim Arabs God = Allah (Arabic) = Eluhim (Hebrew) = El (Aramaic) • One and only one God, no trinity • Arabic as the language of the Quran Charlemagne: 742 to 814 King of the Franks based in modern Germany, France and Northern Italy. Made Holy Roman Emperor by the Pope. Charlemagne’s Empire The late Middle Ages Land = power Now Money = power Feudalism (political system) • The kings had lots of land; he gave land to lords in exchange for protection and $. • Lords gave their land to knights in exchange for protection, $. • Knights let serfs work the land and he would protect them. • Serfs got food and shelter. • Thus, each person had rights and responsibilities Feudalism A political, economic, and social system based on loyalty and military service. William I helped make England what it is today and codified feudalism (gave it the force of law). Magna Carta • Signed in 1215 • Example of Rule of Law • English King John was a bad king so his nobles forced him to sign it. • Limited powers of the English kings. • Great Charter” • monarchs were not above the law. • Kings had to consult a council of advisors. • Kings could not tax arbitrarily. The Beginnings of the British Parliament Great Council: middle class merchants, townspeople [burgesses in Eng., bourgeoisie in Fr., burghers in Ger.] were added at the end of the 13c. eventually called Parliament. by 1400, two chambers evolved: o House of Lords nobles & clergy. o House of Commons knights and burgesses. RENAISSANCE AND REFORMATION • REBIRTH OF CULTURE & LEARNING • STARTED IN ITALY BUT SPREAD THROUGH EUROPE • EARLY 1300’S – 1600 • ART, POETRY, PAINTING, INVENTIONS • GROWTH OF CITIES, TRADE AND LEARNING THE RENAISSANCE MAN Mona Lisa painting • Leonardo da Vinci a painter, sculptor, architect, inventor, and mathematician. • Idealized as the example of what a man of the period should be. Drawing of a helicopter Leonardo da Vinci Role of Church in Middle Ages • Never was there a time when the Church was so powerful in Western Civilization. • The Church was led by popes. Priests and nuns converted, gave care to people Role of Church • Monks were spiritual leaders (obviously) • They lived in monasteries that acted like trade schools and YMCAs Role of Church • They spent years transcribing the Bible since the printing press wasn’t used in Europe yet. Role of Church • Since there were no strong empires or kingdoms the Church was one organization that had respect and power. • Popes were more powerful than kings! Churches and Cathedrals during the Middle Ages VS MARTIN LUTHER HAS PROBLEMS WITH THE CATHOLIC CHURCH BECAUSE THEY SOLD INDULGENCES TO THE RICH FOR THEIR SINS WRITES “95 THESES” & PINS TO CHURCH DOOR PROTESTANT REFORMATION PEOPLE BEGAN TO SPEAK OUT AGAINST THE POWERFUL CATHOLIC CHURCH AND NEW CHRISTIAN RELIGIONS EMERGED MARTIN LUTHER AND JOHN CALVIN This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com Self-Check Quiz Visit the Glencoe World History: Modern Times Web site at wh.mt.glencoe.com and click on Self-Check Quizzes-Chapter 1 to assess your knowledge of chapter content.