Objective
advertisement

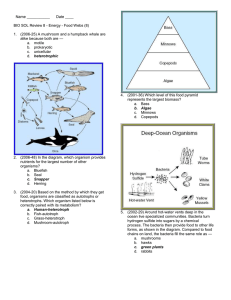
Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. Name _________________________________________________________ Diversity of Living Things Worksheet, Part I 1.1 – Single-celled organisms have all of the characteristics of living things (pgs. 9-14). 1. An individual fungus, in Oregon, covers more than ______________________ football fields. (Enter a number) 2. Most of the fungus is found where? a. Above the ground. b. Below the ground. c. Both above and below the ground. 3. The prefix “micro-“ means… a. very large. b. between small and large. c. very small. 4. A microorganism is a(n)… a. very small organism. b. organism very far away. c. organism very close. d. very large organism. 5. Compare and contrast the words microorganism and organism. (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. An organism is any living thing. b. Only microorganisms are living. c. Only organisms are living. d. Microorganisms are living things too small to see. 6. Most microorganisms are made of… a. many cells. b. one cell. 7. The _________ is the basic unit of life. a. microorganism b. cell c. virus d. heart ~1~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. Use the graph to answer questions #8-#10. Growth of Bacteria Over Time Number of Bacteria 140 128 120 100 80 64 60 40 32 20 0 1 1 2 2 4 8 16 3 4 5 6 7 8 Hours 8. After three hours, there are ______________ bacteria. (Enter a number) 9. After seven hours, there are ______________ bacteria. (Enter a number) 10. Suppose the colony continues growing. After nine hours, there will be ______________ bacteria. (Enter a number) 1.2 – Bacteria are single-celled organisms without a nucleus (pgs. 16-21). 11. ______________ are the simplest form of life. a. Archae b. Bacteria c. Fungi d. Protozoan 12. These are the smallest living things. (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. Archae b. Bacteria c. Fungi d. Protozoan ~2~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. Identify the parts of a bacterium. A C B _____13. Cell Membrane A. A _____14. Cell Wall B. B _____15. Cytoplasm C. C _____16. DNA D. D D Use the picture to answer questions #17-#19. A B C 17. Spiral-shaped (spirilli) bacteria. a. A b. B c. C ~3~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. 18. Rod-shaped (bacilli) bacteria. a. A b. B c. C 19. Round-shaped (cocci) bacteria. a. A b. B c. C Match the organism with its description. _____20. Archae A. Live in very salty lakes and ponds. _____21. Halophiles B. Single-celled organisms that can survive in the largest range of environment. _____22. Methanogens C. These that their name from the natural gas they produce. They die if exposed to oxygen. _____23. Thermophiles D. Thrive in extreme heat or cold. 24. Bacteria that transform energy from sunlight into energy that can be used by cells are called… a. consumers. b. parasites. c. producers. d. decomposers. 25. _________ get energy by breaking down materials in dead or decaying organisms. a. consumers. b. parasites. c. producers. d. decomposers. 26. Some bacteria live in a very close relationship either inside or on the surface of other organisms. a. consumers. b. parasites. c. producers. d. decomposers. ~4~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. 27. One shovelful of dirt contains _____________ of bacteria. a. thousands b. millions c. billions d. trillions 28. What do cities use to break down sewage? a. Archae b. Bacteria c. Fungi d. Protozoan 29. Which is a way bacteria can cause symptoms of disease? a. They can invade parts of the body, multiplying in body tissues. b. They can poison the body with chemicals the produce and release. c. They can poison the body with chemicals that are part of the bacteria themselves. d. All of the above. ~5~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. Diversity of Living Things Text Worksheet – Key 1.1 – Single-celled organisms have all of the characteristics of living things (pgs. 9-14). 1. An individual fungus, in Oregon, covers more than ______________________ football fields. (Enter a number) 2. Most of the fungus is found where? a. Above the ground. b. Below the ground. c. Both above and below the ground. b. Below the ground (3 choices) 3. The prefix “micro-“ means… a. very large. b. between small and large. c. very small. c. very small (3 choices) 4. A microorganism is a(n)… a. very small organism. b. organism very far away. c. organism very close. d. very large organism. a. very small organism. ~6~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. 5. Compare and contrast the words microorganism and organism. (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. An organism is any living thing. b. Only microorganisms are living. c. Only organisms are living. d. Microorganisms are living things too small to see. a. An organism is any living thing; d. Microorganisms are living things too small to see. 6. Most microorganisms are made of… a. many cells. b. one cell. b. one cell. (2 choices) 7. The _________ is the basic unit of life. a. microorganism b. cell c. virus d. heart b. cell ~7~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. Use the graph to answer questions #8-#10. Growth of Bacteria Over Time Number of Bacteria 140 128 120 100 80 64 60 40 32 20 0 1 1 2 2 4 8 16 3 4 5 6 7 8 Hours 8. After three hours, there are ______________ bacteria. (Enter a number) 4 9. After seven hours, there are ______________ bacteria. (Enter a number) 32 10. Suppose the colony continues growing. After nine hours, there will be ______________ bacteria. (Enter a number) 256 ~8~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. 1.2 – Bacteria are single-celled organisms without a nucleus (pgs. 16-21). 11. ______________ are the simplest form of life. a. Archae b. Bacteria c. Fungi d. Protozoan a. Bacteria 12. These are the smallest living things. (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. Archae b. Bacteria c. Fungi d. Protozoan a. Archae; b. Bacteria Identify the parts of a bacterium. A C B D ~9~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. _____13. Cell Membrane A. A _____14. Cell Wall B. B _____15. Cytoplasm C. C _____16. DNA D. D A 14. Cell Membrane C 14. Cell Wall B 15. Cytoplasm D 16. DNA A 14. Cell Membrane C 14. Cell Wall B 15. Cytoplasm D 16. DNA ~10~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. Use the picture to answer questions #17-#19. A B C 17. Spiral-shaped (spirilli) bacteria. a. A b. B c. C c. C (3 choices) 18. Rod-shaped (bacilli) bacteria. a. A b. B c. C a. A (3 choices) 19. Round-shaped (cocci) bacteria. a. A b. B c. C b. B (3 choices) ~11~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. Match the organism with its description. _____20. Archae A. Live in very salty lakes and ponds. _____21. Halophiles B. Single-celled organisms that can survive in the largest range of environment. _____22. Methanogens _____23. Thermophiles B 10. Archae C. These that their name from the natural gas they produce. They die if exposed to oxygen. D. Thrive in extreme heat or cold. A 11. Halophiles C 12. Methanogens D 13. Thermophiles 24. Bacteria that transform energy from sunlight into energy that can be used by cells are called… a. consumers. b. parasites. c. producers. d. decomposers. c. producers. 25. _________ get energy by breaking down materials in dead or decaying organisms. a. consumers. b. parasites. c. producers. d. decomposers. d. decomposers. ~12~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. 26. Some bacteria live in a very close relationship either inside or on the surface of other organisms. a. consumers. b. parasites. c. producers. d. decomposers. b. parasites. 27. One shovelful of dirt contains _____________ of bacteria. a. thousands b. millions c. billions d. trillions d. trillions 28. What do cities use to break down sewage? a. Archae b. Bacteria c. Fungi d. Protozoan d. Bacteria 29. Which is a way bacteria can cause symptoms of disease? a. They can invade parts of the body, multiplying in body tissues. b. They can poison the body with chemicals the produce and release. c. They can poison the body with chemicals that are part of the bacteria themselves. d. All of the above. d. All of the above. ~13~ Objective – Understand that microorganisms range from simple to complex, are found almost everywhere, and are both helpful and harmful. Diversity of Living Things Text Worksheet Scoring Guide 28-29 – 4 26-27 – 3.5 25 – 3 22-24 – 2.5 19-21 – 2 16-18 – 1.5 13-15 – 1 1-12 – .5 0–0 ~14~