Document 17788779
advertisement

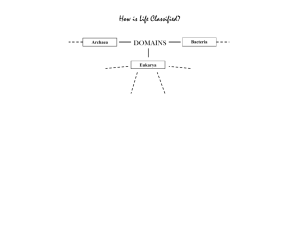
Evolution • Darwin Studied finches in the Galapagos Islands – He noticed how different each bird beak was due to adaptive radiation • Evidence of evolution – The best evidence is matching AA sequences or DNA – We can also look at anatomy. What was the difference between homologous and analogous structures? What is Classification? • Classification/taxonomy is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities • Taxonomists are scientists that identify & name organisms 3 Benefits of Classifying • Accurately & uniformly names organisms • Prevents misnomers such as starfish & jellyfish that aren't really fish • Uses same language (Latin or some Greek) for all names Sea”horse”?? 4 Standardized Naming Turdus migratorius •Binomial nomenclature •Genus species •Latin or Greek American Robin 5 Binomial Nomenclature What is different in the scientific name of the polar bear and the grizzly bear? 6 Hierarchy-Taxonomic Groups BROADEST TAXON • Domain • Kingdom • Phylum • Class • Order • Family • Genus • Species Know in order, how the taxa are arranged from broadest to most specific 7 Domains • Broadest, most inclusive taxon • Three domains: • Archaea and Eubacteria • unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) • Eukarya • more complex and have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles 8 Kingdoms • • • • • • Eubacteria Archaea Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Know which are prokaryotes and which are eukaryotes Know the difference between and prokaryote and eukaryote Kingdom Eubacteria Cell Type Prokaryotic Cell Wall Flagella Capsule Cell Wall Number of Cells Mode of Nutrition Examples Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Capsid Nucleic Acid Envelope Flagella Cilia Spores Pseudopods -Cell walls made of chitin -Filamentous forms with specialized, complex cells Chloroplasts Central vacuole Cell wall of cellulose Specialized, complex cells All Multi-cellular except for yeast (unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular OR Multicellular Autotroph/ Heterotroph Autotroph/ Heterotroph Autotroph/ Heterotroph Absorptive heterotroph saprobe Autotrophic Heterotroph Salmonella E. Coli Anthrax HIV Hepatitis Tobacco Mosaic Virus Protozoans Algae Water Mold Slime Mold Molds Yeasts Mushrooms Mosses Ferns Non-woody & woody flowering plants Invertebrates Fishes Reptiles Amphibians Birds Mammals Fungus • Are not plants-they do NOT carry out photosynthesis! The only thing they have in common are cell walls. • Cell walls of chitin • Absorb food through cell walls – What do they do? Why is this important? What would we do without them? – An ex of a fungus? Yeast-how does it make bread rise? Protists • Not plants, not fungi – Algae, slime molds etc – These guys are important for creating most of the O2 for us through photosynthesis! – Form red tides (caused from Dinoflagellates) that kill fish and other animals in the ocean • Caused by farm runoff • Are a junk drawer – Uni/multicellular – Eukaryotes – Auto/heterotrophs Dichotomous Keying • Used to identify organisms • Characteristics given in pairs • Read both characteristics and either go to another set of characteristics OR identify the organism Be able to identify characteristics that set organisms apart from the rest! 13 Prokaryotic – do not have nucleus Single-celled – unicellular Cell wall – made of peptidoglycan What are two key differences between a prokaryote and eukaryote? Virus • Has DNA/RNA • Would we treat with antibiotics or vaccine? Both? • Lytic vs Lysogenic cycle Treating Pathogenic Bacteria • Gram Stain – stained bacteria reveals whether to prescribe antibiotics • Antibiotics – medicine used to block growth and reproduction of BACTERIA only • Ex: Pencillium • Vaccines – weakened pathogen PREVENTS disease in both viruses and bacteria Beneficial Bacteria • Bacteria are beneficial to our environment by acting as: 1. Decomposers - recycle of nutrients to atmosphere 2. Nitrogen fixators - convert nitrogen into a form plants can use Beneficial Bacteria Cont… 3. Symbiotic Relationship – Two organisms benefit from one another Ex. Humans and E. coli E.coli lives in our intestines, breaks down food for digestion Preventing Bacterial Growth 1. Heat – inc in temp 2. Disinfection – using chemicals 3. Refrigeration – slows down bacterial growth 4. Light – slows down bacterial growth How are Bacterial Infections Transmitted? • Exchange of bodily fluids • Skin to skin contact, dirty hands • Contamination • Airbourne • We use Penecillum as an antibiotic