Unit 6 Quiz 5 5/6/08
advertisement
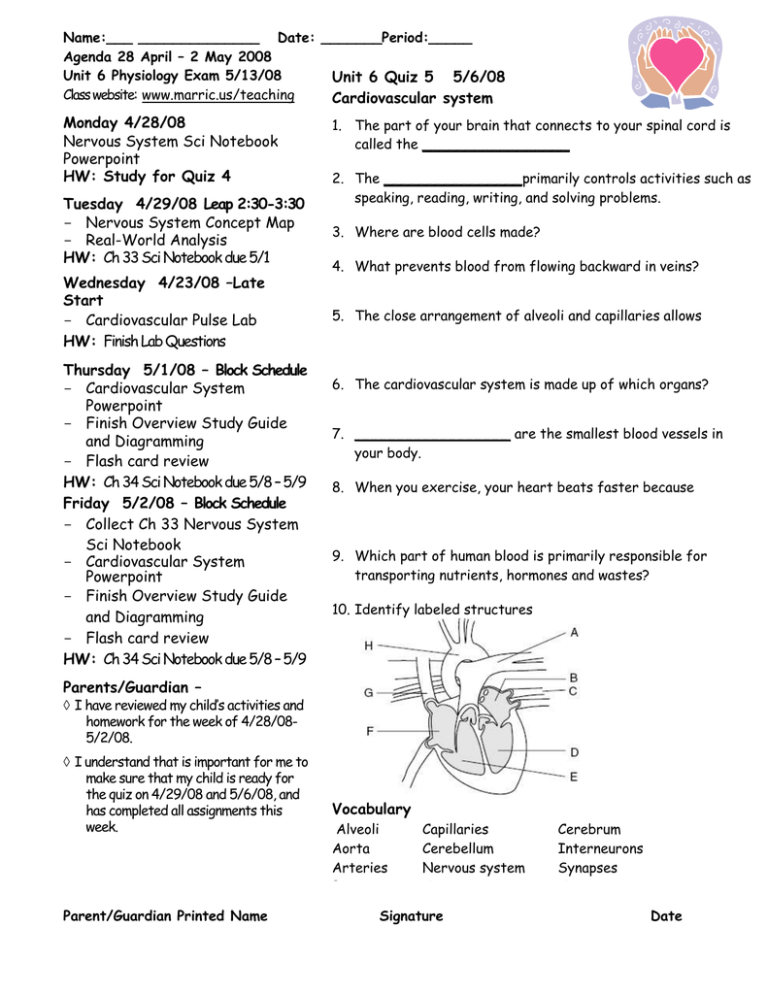
Name:___ ______________ Date: _______Period:_____ Agenda 28 April – 2 May 2008 Unit 6 Physiology Exam 5/13/08 Unit 6 Quiz 5 5/6/08 Class website: www.marric.us/teaching Cardiovascular system Monday 4/28/08 Nervous System Sci Notebook Powerpoint HW: Study for Quiz 4 Tuesday 4/29/08 Leap 2:30-3:30 - Nervous System Concept Map - Real-World Analysis HW: Ch 33 Sci Notebook due 5/1 Wednesday 4/23/08 –Late Start - Cardiovascular Pulse Lab HW: Finish Lab Questions Thursday 5/1/08 – Block Schedule - Cardiovascular System Powerpoint - Finish Overview Study Guide and Diagramming - Flash card review HW: Ch 34 Sci Notebook due 5/8 – 5/9 Friday 5/2/08 – Block Schedule - Collect Ch 33 Nervous System Sci Notebook - Cardiovascular System Powerpoint - Finish Overview Study Guide and Diagramming - Flash card review HW: Ch 34 Sci Notebook due 5/8 – 5/9 1. The part of your brain that connects to your spinal cord is called the _________________ 2. The ________________primarily controls activities such as speaking, reading, writing, and solving problems. 3. Where are blood cells made? 4. What prevents blood from flowing backward in veins? 5. The close arrangement of alveoli and capillaries allows 6. The cardiovascular system is made up of which organs? 7. __________________ are the smallest blood vessels in your body. 8. When you exercise, your heart beats faster because 9. Which part of human blood is primarily responsible for transporting nutrients, hormones and wastes? 10. Identify labeled structures Parents/Guardian – I have reviewed my child’s activities and homework for the week of 4/28/085/2/08. I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is ready for the quiz on 4/29/08 and 5/6/08, and has completed all assignments this week. Parent/Guardian Printed Name Vocabulary Alveoli Aorta Arteries Bone marrow Capillaries Cerebellum Nervous system Vena cava Signature Cerebrum Interneurons Synapses Veins Date Bell Ringers: Week of 28 April – 2 May 2008 Monday – Nicotine in cigarettes makes blood vessels become narrower. As a result, the heart _____ a. does not have to work as hard to pump blood. b. has to work harder to pump blood. c. becomes weaker. d. becomes stronger. Explain The specific type of blood cells that engulf large numbers of bacteria is______________ a. macrophage. b. antibody c. platelet. d. red blood cell. Tuesday – Lymph nodes create ____________________. a. macrophages b. antibodies c. nodes d. bacteria The skin can destroy bacteria because it is ______. a. sticky b. poisonous c. basic d. acidic Antibodies bind to _________ on invading bacteria. a. antigens b. cell walls c. cilia d. DNA Explain the difference between antibodies against bacteria and against pollen. Wednesday – Which of the following is a false statement about antibodies? a. Antibodies are specific in their recognition of antigens. b. Antibodies are produced by lymphocytes. c. Antibodies are formed in response to antigens. d. Antibodies are made of DNA. Explain why the statement is false Thursday/Friday – Each B-cell produces ____________________________________________ a. antibodies for many antigens. c. only one type of antibody. b. many types of antibodies. d. antibodies for all antigens. The production of antibodies following the first injection of a vaccine is a __________________ a. lymph node reaction. c. primary immune response. b. suppressor T-cell reaction. d. secondary immune response. Explain how the production of antibodies is different when a pathogen is presented after vaccination against the pathogen has occurred. Name:_______________________________ Date:____________________ Period:______ Unit 6 Quiz 5 5/6/08 Cardiovascular system 1. Where are blood cells made? 2. The part of your brain that connects to your spinal cord is called the _________________ 3. The ________________primarily controls activities such as speaking, reading, writing, and solving problems. 4. What prevents blood from flowing backward in veins? 5. The close arrangement of alveoli and capillaries allows what? 6. The cardiovascular system is made up of which organs? 7. __________________ are the smallest blood vessels in your body. 8. When you exercise, your heart beats faster because 9. Which part of human blood is primarily responsible for transporting nutrients, hormones and wastes? 10. Identify labeled structures A. _______________________________ B. _______________________________ C. _______________________________ D. _______________________________ E. _______________________________ F. _______________________________ G. _______________________________ H. _______________________________ Extra Credit – Human Brain A. _______________________________ B. _______________________________ C. _______________________________ Vocabulary Matching ____ Alveoli ____ Capillaries A. All the nerve cells of an animal; B. The major artery in blood-circulating systems; sends blood to the other body tissues from the heart; contains oxygenated blood. _____ Cerebrum C. Part of the vertebrate hindbrain (rhombencephalon) located dorsally; functions in unconscious coordination of movement and balance. _____ Interneurons D. A large vein that brings blood from the tissues to the right atrium of the four-chambered mammalian heart. _____ Aorta E. right and left hemispheres, of the vertebrate forebrain; the integrating center for memory, learning, emotions, and other highly complex functions of the central nervous system. _____ Arteries F. A vessel that returns blood to the heart. _____ Cerebellum G. A microscopic blood vessel that penetrates the tissues, consists of a single layer of endothelial cells that allows exchange between the blood and interstitial fluid. _____ Nervous system H. One of the deadend, multilobed air sacs that constitute the gas exchange surface of the lungs. _____ Vena cava I. A vessel that carries blood away from the heart to organs throughout the body _____ Synapses J. is the soft tissue found in the hollow interior of bones. In adults, in large bones produces new blood cells. ____ Bone marrow K. An association neuron – a go-between; a nerve cell within the central nervous system that forms synapses with sensory and motor neurons and integrates sensory input and motor output. ____ Veins L. The location where one neuron communicates with another neuron in a neural pathway; a narrow gap between a an axon and a dendrite of another neuron or effector cell


